 Professionalism Equals Strength! The China Software Evaluation Center appreciates your attention. We are here to share technology news and interesting facts based on third-party services with you,Welcome to join us.
Professionalism Equals Strength! The China Software Evaluation Center appreciates your attention. We are here to share technology news and interesting facts based on third-party services with you,Welcome to join us.
Keywords: Industrial Robot, Control System, Performance Testing, Pose Accuracy, Path Accuracy
2016 was a year of rapid development for the robotics industry. From the robot dance at the CCTV Spring Festival Gala in the Year of the Monkey to the various robot operating systems and control system companies that have sprung up everywhere, from robotics conferences and forums across the country to the integration of robots with the Internet, big data, and other emerging technologies, robots have long ceased to be mere substitutes for repetitive heavy labor in the traditional sense. They are becoming increasingly intelligent and common. More and more robots are entering ordinary enterprises, and for these companies, the performance of the robot control system is a key focus.
Currently, there is no specific performance testing standard for industrial robot control systems in the industry. When performance specifications are mentioned in the robotics sector, they generally refer to the entire machine. There are many indicators for evaluating the performance of industrial robot systems, and based on different design purposes and uses, the matching of components, structural design, and parameter adjustments vary, with the control system being just one aspect. The performance of the overall robot is greatly influenced by components such as the engine (servo motor), transmission (reducer), and chassis/suspension (structural parts).
The national standard GB/T 12642 – 2001 defines performance indicators for more than a dozen types of robots, among which three are frequently mentioned: repeatability accuracy, pose accuracy, and path accuracy.
Generally speaking, the performance of industrial robot control systems can be indirectly represented by the robot’s pose accuracy and path accuracy.
1. Pose Accuracy:
The pose accuracy of a robot generally refers to the repeatability of the pose.
The pose of the robot refers to its position and orientation relative to a reference coordinate system, and its repeatability pose accuracy is one of the most important technical indicators of the robot. This indicator reflects the electromechanical performance and usage effect of the robot, that is, the degree of consistency of the actual pose after the robot responds n times to the same command pose from the same direction. Generally, a laser tracker is used to measure pose accuracy, as shown in the figure below:
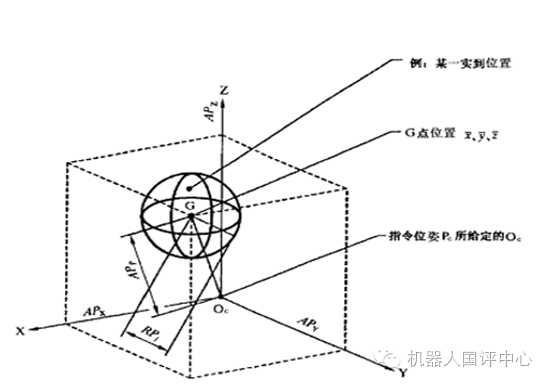
To achieve high pose accuracy, the control system must provide the following functions:
-
Compensate for kinematic parameter errors of mechanical linkages, such as processing errors, assembly errors, and mechanical tolerances;
-
Compensate for joint flexibility and linkage flexibility;
-
Provide high-precision mechanical zero-point calibration functions.
2. Path Accuracy:
The path accuracy of a robot generally refers to the repeatability of the path, indicating the degree of consistency of the actual path when the robot repeats the same path command n times. A laser tracker is generally used for testing, allowing the robot to repeat a certain path n times and then taking the radius of the cross-section of the n paths. As shown in the figure below:
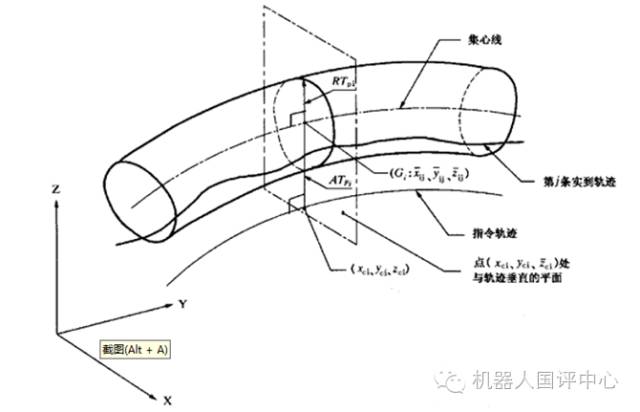
Model-based control is generally used to improve path accuracy. ABB has demonstrated a comparison between its Quick Move and True Move, showing that after using model control, the robot can maintain very high path consistency at any speed allowed by the system.
Additionally, to achieve high path accuracy, it is also essential to compensate for joint friction in the robot.
Source: China Software Evaluation Center, Wan Binbin
