“Internet of Things Communication and Sensing: Theory and Practice”
ISBN: 9787302683834
Authors: Wang Jiliang, Tong Shuai
Price: 69 Yuan
Comprehensively introduces the fundamental principles and implementations of Internet of Things communication and sensing, closely aligned with the forefront of the field;
Combining theory and practice, covering basic knowledge, specific cases, and implementation code, providing a comprehensive overview of the Internet of Things from theory to practice, enabling one-stop learning from basics to practical applications;
Navigating you through the vast ocean of the Internet of Things amidst the sea of signals.
Content Summary
This book starts from the basic knowledge of the Internet of Things, focusing mainly on Internet of Things communication and sensing. It comprehensively introduces the architecture, technical principles, application fields, and development trends of the Internet of Things, covering multiple levels such as the perception layer, network layer, and application layer, providing readers with a complete knowledge system of the Internet of Things. At the same time, it combines numerous practical application cases to demonstrate the application and value of Internet of Things technology in real life.
This book can serve as a teaching reference for senior undergraduate students majoring in Internet of Things at higher education institutions, as well as for beginners interested in wireless communication and the Internet of Things or engineering and technical personnel engaged in related technology research and development.
Book Features
Comprehensive and In-Depth Content:This book starts from the basic knowledge of the Internet of Things, covering the basic concepts, core principles, application fields of Internet of Things communication and sensing, and provides detailed explanations from basic to advanced technologies, offering a complete knowledge system of the Internet of Things.
Strong Practicality:This book not only introduces theoretical knowledge but also combines numerous practical cases to demonstrate the application of Internet of Things technology in real life.
Cutting-Edge Technology:This book focuses on the latest technologies and research achievements in the field of the Internet of Things, such as the integration of the Internet of Things with artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and other technologies, providing readers with the most cutting-edge information on Internet of Things technology.
Experimental Integration:The book includes many experiments on Internet of Things communication and sensing, allowing readers to practice hands-on to deepen their understanding of theoretical knowledge.
Table of Contents
Part One: Basic Theories of the Internet of Things
Chapter 1: Overview of the Internet of Things
Chapter 2: Basics of Wireless Signal Processing in the Internet of Things
2.1 Generation, Transmission, and Reception of Signals
2.2 Introduction to Analog and Digital Signals
2.3 Signal Sampling and the Sampling Theorem
2.4 Signal Quantization
2.5 Case Study: Implementing a Recording and Playback Program
References
Chapter 3: Time-Frequency Domain Signal Analysis in the Internet of Things
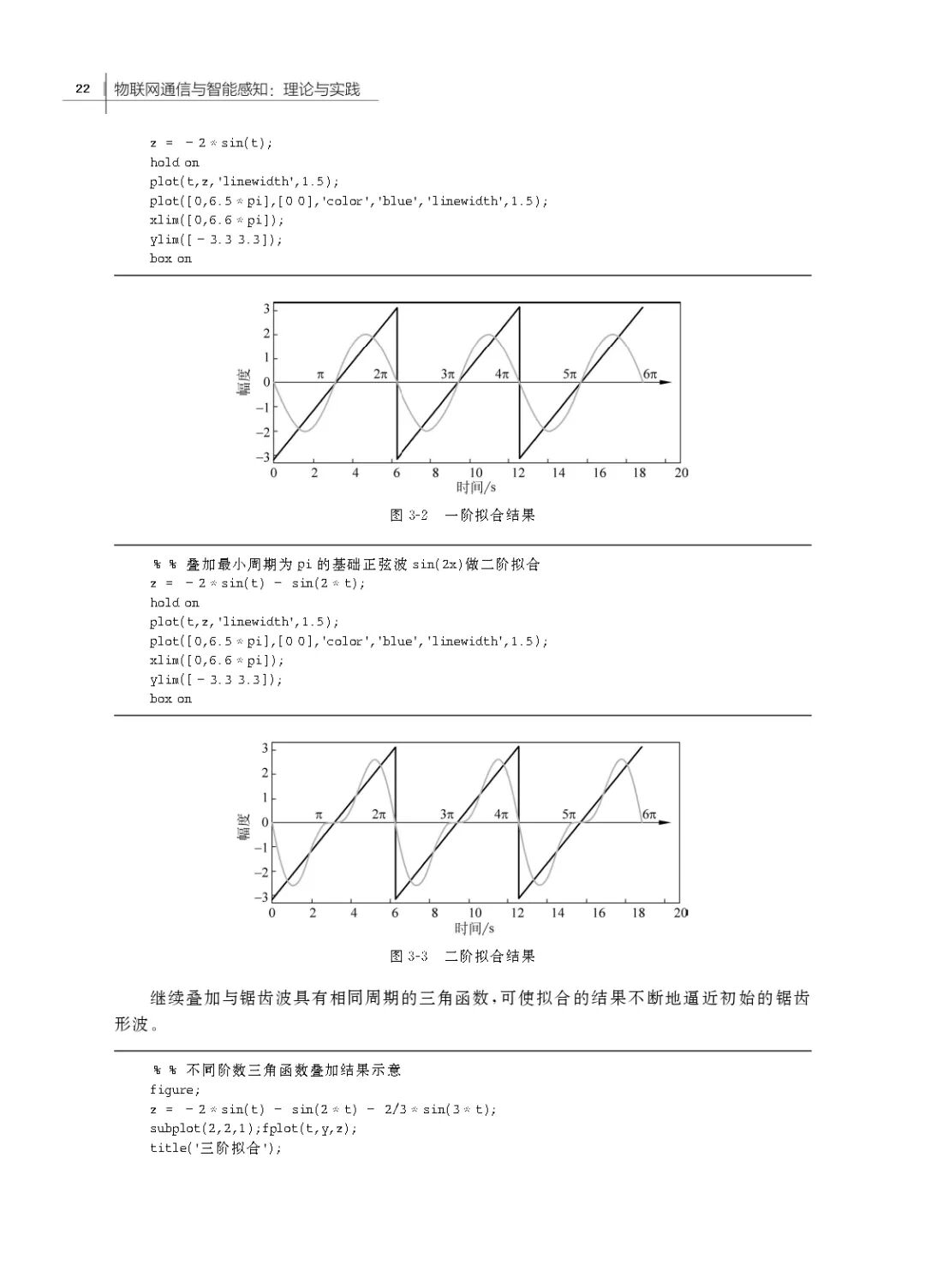
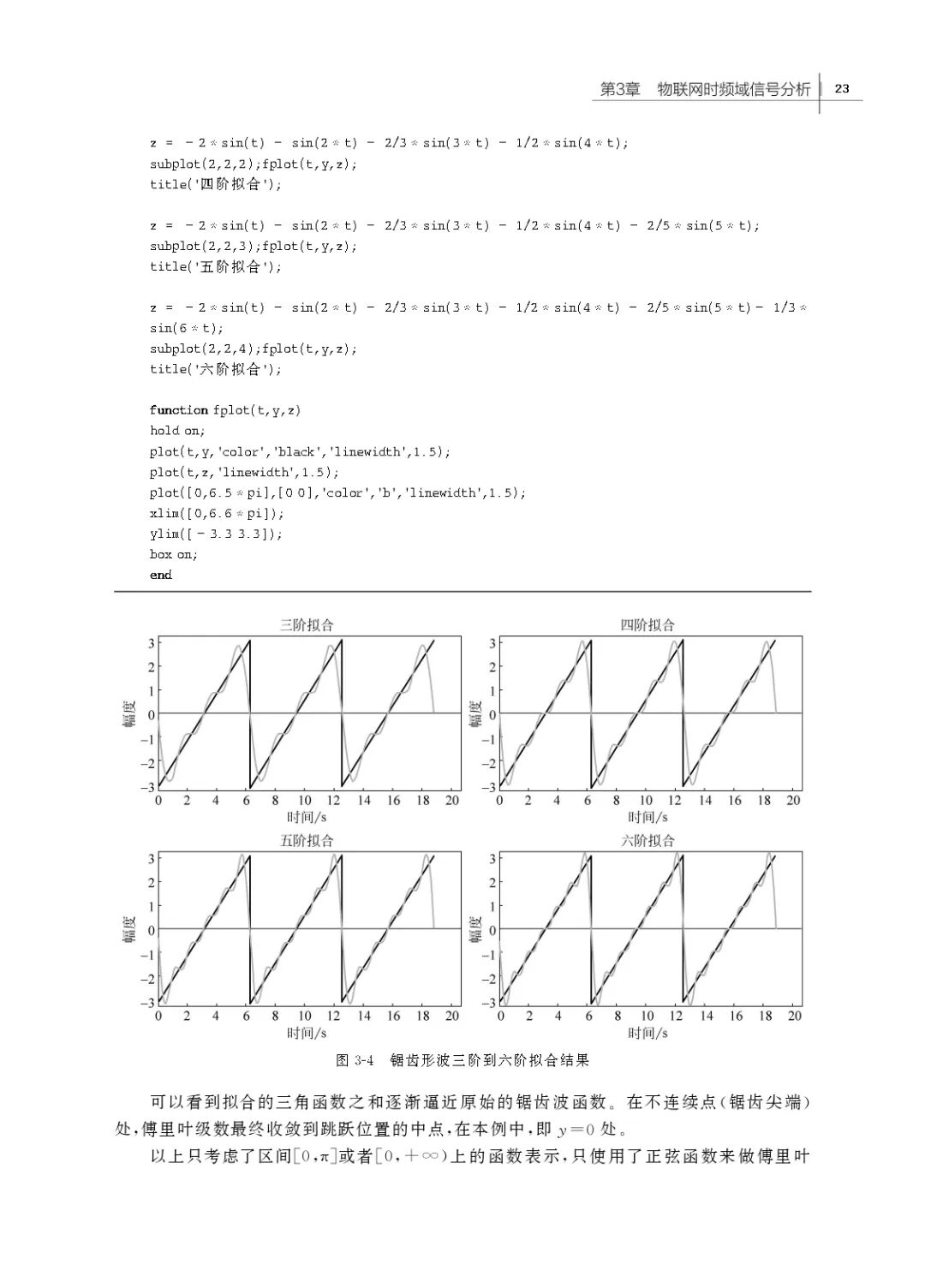
3.1 Principles of Time-Frequency Analysis of Signals
3.2 Discrete Fourier Analysis
3.2.1 Discrete Fourier Series
3.2.2 Discrete Time Fourier Transform
3.2.3 Discrete Fourier Transform
3.2.4 Fast Fourier Transform
3.3 Short-Time Fourier Transform
3.4 Case Study: Applying Fourier Transform to Analyze Internet of Things Signals
References
Chapter 4: Signal Propagation Models in the Internet of Things
4.1 Wireless Channels
4.1.1 Definition of Channels
4.1.2 Channel Impulse Response
4.1.3 Channel Frequency Response
4.1.4 Channel State Information
4.1.5 Channel State Estimation
4.2 Path Loss and Shadow Fading
4.2.1 Path Loss Models
4.2.2 Shadow Fading
4.2.3 Signal-to-Noise Ratio
4.3 Multipath Channel Models
4.3.1 Multipath Effects
4.3.2 Multipath Fading Models
4.3.3 Multipath Measurement
4.4 Case Study: Channel Simulation and Measurement
4.4.1 Channel Fading Simulation
4.4.2 Multipath Simulation
4.4.3 Fading Overlay Synthesis
References
Chapter 5: Signal Noise Processing in the Internet of Things
5.1 Introduction to Digital Filters
5.2 Moving Average Filter
5.2.1 Introduction
5.2.2 Convolution Implementation of Moving Average
5.2.3 Noise Suppression and Window Selection
5.2.4 Frequency Response
5.2.5 Frequency Domain Parameters
5.2.6 Filter Implementation
5.3 FIR Digital Filters
5.3.1 Introduction
5.3.2 FIR Filter Design
5.4 IIR Digital Filters
5.5 Common Filter Designs
5.5.1 Filter Frequency Domain Response
5.5.2 Filter Usage
5.6 Case Study: Sound Filtering
5.6.1 Time Domain Filtering
5.6.2 Bandpass Filtering
Part Two: Internet of Things Communication
Chapter 6: Data Modulation and Demodulation
6.1 Introduction to Modulation and Demodulation
6.2 Amplitude Modulation
6.3 Frequency Modulation
6.4 Phase Modulation
6.4.1 Relationship between I/Q and Phase
6.4.2 BPSK
6.4.3 QPSK
6.4.4 Implementing QPSK with Sound Waves
6.4.5 8PSK
6.5 Upconversion of Carrier Signals
6.6 Advanced Modulation Techniques
6.6.1 OQPSK
6.6.2 QAM
6.6.3 OFDM
6.6.4 Initial Implementation of OFDM
6.7 Case Study: Sound Wave Signal Communication
6.7.1 Pulse Interval Modulation
6.7.2 Encoding
6.7.3 Modulation
6.7.4 Demodulation
6.7.5 Decoding
References
Chapter 7: Wireless Communication Technologies in the Internet of Things
7.1 Traditional Wireless Communication Technologies
7.1.1 WiFi
7.1.2 Bluetooth
7.1.3 IEEE 802.15.4/ZigBee
7.2 Backscatter Communication
7.3 Radio Frequency Identification Tags
7.3.1 RFID Protocol Standards
7.3.2 Computable RFID – WISP
7.3.3 Environment Signal-Based Backscatter Technology
7.4 Low Power Wide Area Networks
7.4.1 LoRa
7.4.2 LoRa Encoding and Decoding
7.4.3 Sound Wave-Based LoRa Communication
7.4.4 LoRa-Based Backscatter Communication
7.4.5 Concurrent Transmission and Collision Decoding
7.4.6 Large-Scale Wireless Network Experiments
7.4.7 Weak Signal Decoding
7.4.8 Weak Signal Decoding Method Design
7.5 Other Communication Methods
References
Part Three: Internet of Things Sensing
Chapter 8: Wireless Ranging
8.1 Ranging Based on Signal Strength
8.1.1 Definition of Received Signal Strength
8.1.2 RSS Ranging Principles
8.2 Ranging Based on Signal Propagation Time
8.2.1 ToF Ranging Principles
8.2.2 Unilateral Bidirectional Ranging
8.2.3 Bilateral Bidirectional Ranging
8.2.4 Measuring Distance Using Reflected Signals
8.3 Case Study: Ranging
8.3.1 Sound Wave FMCW Ranging
8.3.2 Sound Round-Trip Time Ranging
References
Chapter 9: Wireless Positioning
9.1 Trilateration Positioning Algorithm
9.2 TDOA Positioning Algorithm
9.3 AoA Positioning Algorithm
9.3.1 Arrival Angle Calculation Methods
9.3.2 Positioning Based on Arrival Angle
9.3.3 Sound Wave AoA Positioning
9.4 Wireless Fingerprint Positioning Algorithm
9.5 Bluetooth AoA Direction Finding
9.6 UWB Positioning
9.6.1 Bidirectional Ranging Algorithm
9.6.2 TDOA and Concurrent Algorithms
9.6.3 AoA Algorithms
9.6.4 V-TWR Algorithm
9.7 Active Device Location Sensing Based on Visible Light Signals
9.7.1 Color Polarization
9.7.2 Camera Positioning Algorithm Based on Optical Tag Color Results
References
Chapter 10: Wireless Tracking
10.1 Tracking Methods Based on Doppler Effect
10.1.1 Principles of Doppler Tracking
10.1.2 Implementation of Doppler Tracking
10.2 Tracking Methods Based on FMCW
10.3 Tracking Methods Based on Signal Phase
10.3.1 Implementation of Phase Tracking
10.3.2 High-Precision Device Tracking Based on Sound Wave Signal Phase
10.4 Case Study: Two-Dimensional Tracking Based on FMCW
10.4.1 System Design
10.4.2 Experimental Results
10.4.3 Experimental Code
References
Chapter 11: Wireless and Intelligent Sensing
11.1 Sound Wave Gesture Recognition
11.1.1 Main Principles
11.1.2 Sample Code and Data
11.1.3 Result Presentation
11.2 Sound Wave Device Authentication
11.3 Positioning and Tracking
11.3.1 Method for Enhancing Wireless Positioning Accuracy Based on Neural Networks
11.3.2 Method for Enhancing Generalization of Wireless Positioning Based on Neural Networks
11.4 Action Recognition
11.4.1 Fall Detection Method
11.4.2 Method for Enhancing Wireless Sensing Features Based on Neural Networks
11.5 Component Recognition
11.5.1 Fine-Grained Liquid Sensing Based on Neural Networks
11.5.2 Method for Sensing Fruit Ripeness Based on Regression Models
11.6 Wireless Sensing Signal Generation Based on Diffusion Models
References
Exciting Sample Chapters
Swipe up to read