This article is brought to you by Semiconductor Industry Insights (ID: ICVIEWS).
Spot prices have already begun to recover.

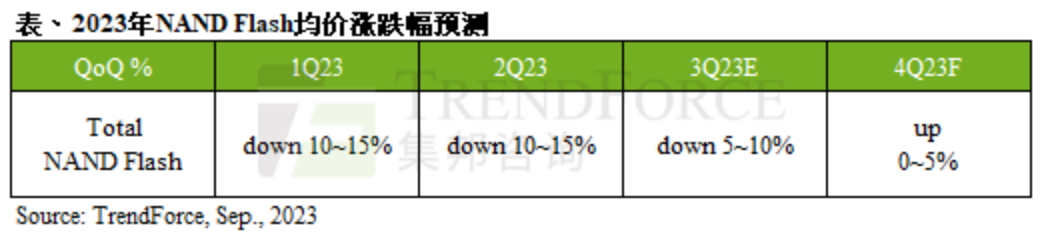
According to TrendForce, NAND Flash suppliers are expected to increase production cuts in Q4 to accelerate inventory reduction. It is estimated that the average price of NAND Flash in Q4 may stabilize or slightly increase, with an expected increase of about 0-5%.In terms of pricing, TrendForce predicts that the rebound in NAND Flash prices will occur earlier than that of DRAM. Due to the continuous expansion of losses among NAND Flash suppliers, sales prices have approached production costs. Suppliers are choosing to increase production cuts to maintain operations and drive prices to stop falling and rebound. Among them, the contract price of NAND Flash wafers rebounded in August, and as the production cuts expand, customer stocking is expected to recover, further supporting the continued rise of NAND Flash wafer contract prices in September. However, for the NAND Flash price increase to continue into 2024, it still relies on sustained production cuts and monitoring whether Enterprise SSD procurement orders will significantly rebound. Supplier losses are expected to narrow, benefiting module manufacturersOn the supplier side, TrendForce states that even though NAND Flash has a more elastic price advantage compared to DRAM, the demand has not improved this year. Additionally, the shipment scale of general-purpose servers continues to be squeezed by AI servers, leading to a poor overall NAND Flash market trend this year, with the average price continuing to decline in Q3 and supplier losses continuing to expand.According to TrendForce’s survey of supplier inventory levels, Samsung has announced that in response to the continued weakening demand, it will increase production cuts to 50% starting in September, focusing on processes below 128 layers. To effectively reduce inventory before the end of the year, it relies on end-user application customers to increase stocking, which is actually a slow remedy. The best way to bring supply and demand back to a reasonable level is to strictly control production capacity. Samsung’s significant production cuts are expected to lead to a rebound in prices for some products primarily supplied by Samsung, which may drive the overall NAND Flash bit shipment volume in Q4 and gradually narrow supplier losses, while also helping module manufacturers improve future profitability.Phison Electronics stated that the SSD module shipment volume began to show signs of recovery in August, with PCIe SSD modules growing nearly 60% (YoY), and the overall NAND storage bit growth rate reaching nearly 50% (YoY), indicating that system customers have started to replenish inventory as their inventory levels return to normal or below normal levels.
Supplier losses are expected to narrow, benefiting module manufacturersOn the supplier side, TrendForce states that even though NAND Flash has a more elastic price advantage compared to DRAM, the demand has not improved this year. Additionally, the shipment scale of general-purpose servers continues to be squeezed by AI servers, leading to a poor overall NAND Flash market trend this year, with the average price continuing to decline in Q3 and supplier losses continuing to expand.According to TrendForce’s survey of supplier inventory levels, Samsung has announced that in response to the continued weakening demand, it will increase production cuts to 50% starting in September, focusing on processes below 128 layers. To effectively reduce inventory before the end of the year, it relies on end-user application customers to increase stocking, which is actually a slow remedy. The best way to bring supply and demand back to a reasonable level is to strictly control production capacity. Samsung’s significant production cuts are expected to lead to a rebound in prices for some products primarily supplied by Samsung, which may drive the overall NAND Flash bit shipment volume in Q4 and gradually narrow supplier losses, while also helping module manufacturers improve future profitability.Phison Electronics stated that the SSD module shipment volume began to show signs of recovery in August, with PCIe SSD modules growing nearly 60% (YoY), and the overall NAND storage bit growth rate reaching nearly 50% (YoY), indicating that system customers have started to replenish inventory as their inventory levels return to normal or below normal levels.
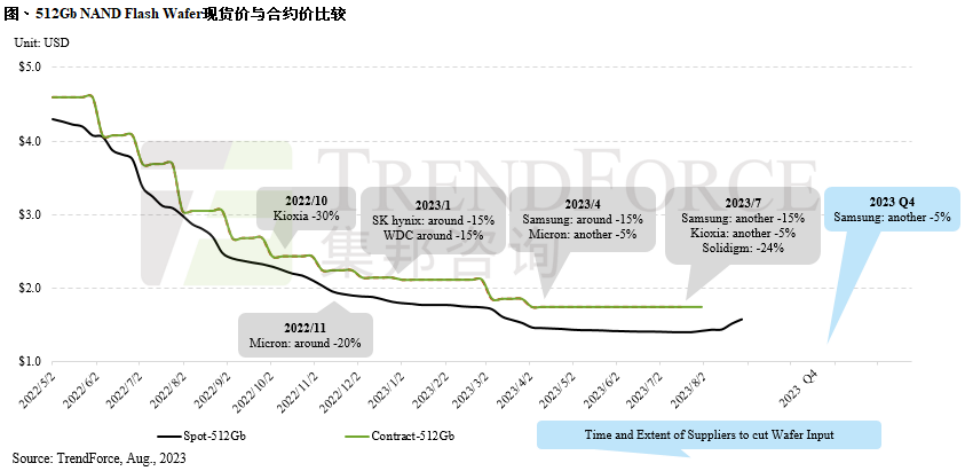
ADATA also stated that due to the production cut effects from upstream storage manufacturers and inventory levels approaching reasonable levels, following the bottoming out of DRAM spot prices in Q2, the attitude of NAND Flash suppliers to raise prices became clear in August, and NAND Flash spot prices began to stop falling and recover, prompting most customers to actively replenish inventory, with the company’s revenue performance also showing a significant recovery. Short-term price increase in the spot marketPreviously, TrendForce indicated that the recent spot market prices for NAND Flash particles have been driven by successful increases in wafer contract prices, with some items experiencing more active inquiry demand. This is mainly due to the further agreements made by NAND Flash manufacturers with some key Chinese module manufacturers for new wafer orders in late August, successfully raising the 512Gb wafer contract price by about 10%, with other manufacturers also following suit to increase prices for similar products, indicating that manufacturers are unwilling to transact at lower prices, thus driving a short-term price increase in the wafer spot market. However, since the related procurement orders are based on price increases from the supply side, whether there is actual end-user order support remains to be seen.TrendForce believes that since sellers currently hold the dominant power in raising prices for wafer and related NAND Flash products, short-term market price fluctuations are inevitable. In Q4, Korean manufacturers will continue to increase NAND Flash production cuts to stabilize prices, but in contrast to actual end-user demand, buyers remain conservative or even pessimistic about future demand outlook. Even if procurement prices are forced to rise, it is still difficult to stimulate an increase in order volume, so whether this round of wafer spot market price increases can continue remains to be observed.
Short-term price increase in the spot marketPreviously, TrendForce indicated that the recent spot market prices for NAND Flash particles have been driven by successful increases in wafer contract prices, with some items experiencing more active inquiry demand. This is mainly due to the further agreements made by NAND Flash manufacturers with some key Chinese module manufacturers for new wafer orders in late August, successfully raising the 512Gb wafer contract price by about 10%, with other manufacturers also following suit to increase prices for similar products, indicating that manufacturers are unwilling to transact at lower prices, thus driving a short-term price increase in the wafer spot market. However, since the related procurement orders are based on price increases from the supply side, whether there is actual end-user order support remains to be seen.TrendForce believes that since sellers currently hold the dominant power in raising prices for wafer and related NAND Flash products, short-term market price fluctuations are inevitable. In Q4, Korean manufacturers will continue to increase NAND Flash production cuts to stabilize prices, but in contrast to actual end-user demand, buyers remain conservative or even pessimistic about future demand outlook. Even if procurement prices are forced to rise, it is still difficult to stimulate an increase in order volume, so whether this round of wafer spot market price increases can continue remains to be observed.
TrendForce expects that in 2024, manufacturers will continue their production cut strategies for DRAM and NAND Flash, especially for NAND Flash, which is experiencing severe losses. It is estimated that in the first half of 2024, the visibility of demand in the consumer electronics market will remain unclear, and capital expenditures for general-purpose servers will continue to be squeezed by AI servers, resulting in relatively weak demand. Given that the baseline for 2023 is already low, and some storage product prices have reached relatively low points, it is estimated that the year-on-year growth rate of demand bits for DRAM and NAND Flash will be 13.0% and 16.0%, respectively.In the PC sector, the average growth rate of PC DRAM capacity is expected to be about 12.4% year-on-year, mainly due to the expectation that in 2024, with the mass production of Intel’s new CPU Meteor Lake models, which only support DDR5 and LPDDR5, DDR5 will become mainstream in the second half of 2024. The growth of PC Client SSDs is not as strong as that of PC DRAM, with an average growth rate of about 8%-10% year-on-year.In the server sector, the average growth rate of Server DRAM capacity is expected to reach 17.3%, mainly benefiting from the generational transition of server platforms, the increased reliance of CSP on matching RAM with CPU cores, and the high demand for computing power from AI servers. The average growth rate of Enterprise SSD capacity is expected to be about 14.7%. For CSP, as the shipment of processors supporting PCIe 5.0 increases, the OEM’s inventory is expected to return to normal by early next year, and subsequent procurement of 8TB products will increase. As for server brands, benefiting from the significant drop in NAND Flash prices, the capacity of 16TB will continue to rise, while the contribution from AI servers is minimal.In the smartphone sector, due to the impact of the global economic downturn, the production volume growth rate in 2024 is expected to be only about 2.2%. TrendForce believes this is the main reason dragging down the growth of demand bits. The continuous decline in storage prices over several quarters has initiated a competition among brands in hardware, thus it is estimated that the average capacity of smartphones will increase by about 14.3% in 2023, and in 2024, as the average selling price of Mobile DRAM remains at relatively low levels, this trend is expected to continue, with the annual single-device capacity potentially growing by 7.9%.*Disclaimer:This article is the original author’s creation.The content of the article represents their personal views, and our reposting is for sharing and discussion purposes only, not representing our endorsement or agreement. If there are any objections, please contact us.