
Many IoT projects fail primarily due to inaccurate project forecasts leading to excessively high operational costs.
One of the main factors contributing to this issue, and also a major contributor to device costs, is the volume of data transmitted. Therefore, choosing an efficient method for communication between IoT devices and applications can help alleviate this cost to some extent.
When the number of devices is small, the data volume is low, and power consumption is also minimal. However, when the total number of IoT devices increases to millions or even billions, the choice of network protocol becomes crucial. Costs can accumulate, and a small measure can save a significant portion of expenses.

MQTT-SN is an optimized version of the IoT communication protocol MQTT, specifically designed to operate efficiently in large-scale low-power IoT sensor networks.
In this issue, we introduce a protocol that can reduce costs in large-scale IoT: MQTT-SN.
 MQTT-SN (MQTT for Sensor Networks)
MQTT-SN (MQTT for Sensor Networks)
MQTT-SN (MQTT for Sensor Networks) is an extension of the widely adopted MQTT protocol, customized for sensor networks. It addresses the unique needs of resource-constrained devices, making it a key player in various IoT applications.MQTT-SN is a publish/subscribe messaging protocol designed for Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN), aimed at providing an application layer communication standard for non-TCP/IP embedded devices such as Zigbee and Bluetooth.So why not use MQTT directly?First, MQTT-SN is designed for efficiency. Compared to its parent protocol MQTT, the architecture of MQTT-SN has a more compact design. The message header is minimized, and topic names can be replaced with short topic IDs. The reduction in data volume means less bandwidth consumption and lower processing requirements for resource-limited devices. Secondly, to further reduce power consumption, MQTT-SN introduces a sleep mechanism. Devices can effectively shut down and receive queued messages upon restart. This greatly reduces power consumption and extends the battery life of battery-powered sensors.By addressing key issues such as power efficiency and scalability, MQTT-SN paves the way for robust and reliable communication in industrial IoT environments. As the industrial sector embraces automation and data-driven decision-making, MQTT-SN has become a powerful tool for driving innovation and ensuring the seamless operation of future smart factories.Additionally, to further save power and reduce data overhead, MQTT-SN adds another QoS mode based on the QoS modes used in MQTT. QoS mode -1: allows blind message sending, meaning devices can simply wake up and send messages without waiting for a response.Unlike MQTT, MQTT-SN does not rely on TCP/IP transmission. Instead, it is designed to be independent of the underlying network services. Therefore, any network that supports bidirectional transmission services between nodes and gateways should be able to support MQTT-SN.
Secondly, to further reduce power consumption, MQTT-SN introduces a sleep mechanism. Devices can effectively shut down and receive queued messages upon restart. This greatly reduces power consumption and extends the battery life of battery-powered sensors.By addressing key issues such as power efficiency and scalability, MQTT-SN paves the way for robust and reliable communication in industrial IoT environments. As the industrial sector embraces automation and data-driven decision-making, MQTT-SN has become a powerful tool for driving innovation and ensuring the seamless operation of future smart factories.Additionally, to further save power and reduce data overhead, MQTT-SN adds another QoS mode based on the QoS modes used in MQTT. QoS mode -1: allows blind message sending, meaning devices can simply wake up and send messages without waiting for a response.Unlike MQTT, MQTT-SN does not rely on TCP/IP transmission. Instead, it is designed to be independent of the underlying network services. Therefore, any network that supports bidirectional transmission services between nodes and gateways should be able to support MQTT-SN.
 MQTT-SN Architecture
MQTT-SN Architecture
Unlike the architecture of MQTT, MQTT-SN includes a Gateway routing mechanism:
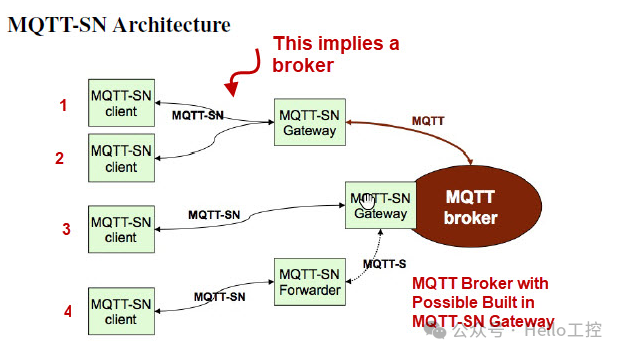
There are three common architectures in MQTT-SN protocol deployment:
- Clients and gateways are deployed in the same local area network (e.g., Zigbee) and communicate via the MQTT-SN protocol, with the gateway reporting data to the cloud MQTT broker via Ethernet and MQTT protocol.
- The MQTT Broker and MQTT-SN Gateway are integrated and deployed in the cloud. Clients communicate directly with the cloud MQTT-SN Gateway via UDP and MQTT-SN.
- The third deployment mode is similar to the first, with the difference being the interaction with the MQTT-SN gateway in the cloud using the MQTT-SN protocol.
Additionally, there are mainly two types of Gateways:
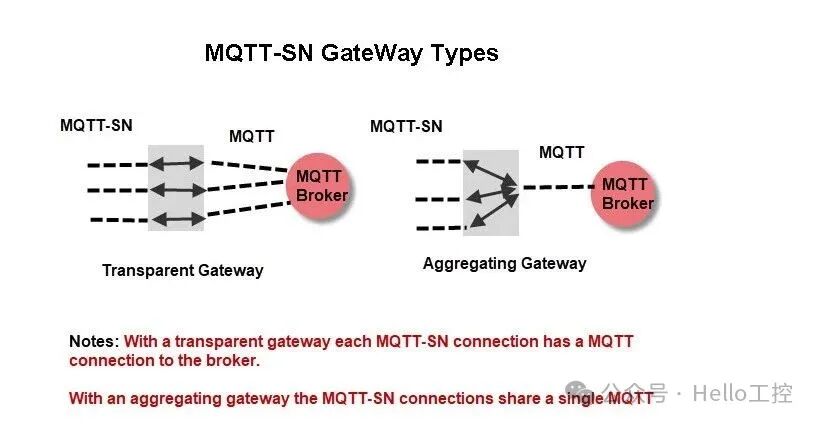
-
Transparent Gateway, where each MQTT-SN connection has a corresponding MQTT connection. This is the easiest type to implement.
-
Aggregating Gateway, where multiple MQTT-SN connections share a single MQTT connection.

Application Scenarios
The advantages of MQTT-SN in energy efficiency, scalability, and lightweight design make it a suitable choice for various industrial IoT applications. Here are several typical use cases:
-
Wireless Sensor Networks: In industrial environments, numerous sensors monitor temperature, pressure, vibration, and other critical parameters. The low data volume and sleep functionality of MQTT-SN are ideal for these battery-powered sensors, enabling them to transmit data efficiently while conserving battery life.
-
Smart Building Management: Buildings are increasingly integrating sensors to monitor energy consumption, occupancy, and environmental conditions. MQTT-SN facilitates efficient communication between these sensors and central control systems, enabling real-time data collection and optimization of building operations.
-
Predictive Maintenance: By continuously monitoring equipment health data (vibration, temperature), MQTT-SN can detect potential issues early. This allows for preventive maintenance measures to be taken, reducing downtime and associated costs.
-
Industrial Asset Tracking: Tracking the location and status of critical assets (such as tools, machinery, or inventory) within large facilities is crucial. MQTT-SN can handle data from low-power RFID tags or GNSS trackers, making it suitable for such applications.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: In applications such as environmental monitoring stations in pipelines or remote areas, MQTT-SN can efficiently communicate with battery-powered sensors, enabling real-time data collection and remote control functionalities.
Finally, for detailed steps on configuring and using MQTT-SN, please refer to the links below.
Reference Links:
-
http://www.steves-internet-guide.com/mqtt-sn/
-
https://www.u-blox.com/en/blogs/insights/mqtt-sn
-
https://docs.emqx.com/en/emqx/latest/gateway/mqttsn.html
-
https://www.hivemq.com/blog/mqtt-sn-smart-choice-for-iiot/
-
https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/connecting-mqtt-sn-devices-using-emqx

- 【Video Course】Codesys V3.5 Series Introduction Course(141 people have learned)
- 【Video Course】Codesys SoftMotion Basic Course(42 people have learned)
Comprehensive Free Resources for Codesys V3.5 Series
Top Ten Common Filtering Algorithms (ST Language)
What Does a PLC Integrated with Chat GPT Look Like?
Sharing the Top 10 PLC Programming Books of 2023
Customize Your Own CODESYS Motion Controller
MC_Power.status = FALSE, Can the Axis Still Move?
ST Language Learning Resource Compilation

——–END——–
 Like this article? Please share and “like” it
Like this article? Please share and “like” it  and “viewing
and “viewing  “
“