1. What Is MQTT Protocol
The full name of MQTT protocol is Message Queuing Telemetry Transport, translated as Message Queue Telemetry Transport. It is a message protocol based on the publish-subscribe model under ISO standards, based on the TCP/IP protocol suite, designed to improve the performance of network device hardware and the network itself. MQTT is generally used in IoT, widely applied in industrial-grade application scenarios such as automotive, manufacturing, oil, and natural gas.

2. Features of the Protocol
-
Lightweight: The fixed header of an MQTT message is only 2 bytes, minimizing protocol exchange and overhead, making it suitable for resource-constrained devices and low-bandwidth network environments.
-
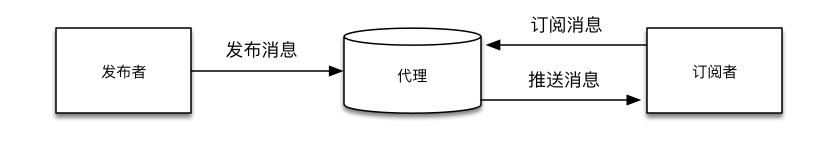
Publish/Subscribe Model: Utilizing a publish/subscribe messaging model, it provides one-to-many message publishing. Publishers and subscribers communicate through a message middleware, the MQTT Broker, decoupling both parties; the publisher does not need to know the specifics of the subscriber, nor does the subscriber need to understand the publisher’s information.
-
Three Levels of Message Quality of Service: QoS 0 indicates at most once, where messages may be lost; QoS 1 indicates at least once, where messages will be re-sent until confirmation is received; QoS 2 indicates exactly once, ensuring messages are received only once through a complex handshake and acknowledgment mechanism.
-
High Reliability: It ensures reliable message transmission in unreliable network environments, featuring message retransmission, last will and testament mechanisms, etc., ensuring messages are not lost or overlooked.
-
Strong Scalability: Supports various types of devices and application scenarios, meeting different business needs through flexible combinations of topics and messages.

3 Work Principles
-
Connection: The client establishes a TCP/IP connection with the Broker, which can use standard port 1883 for unencrypted communication or port 8883 for encrypted communication, employing SSL/TLS protocols for encryption.
-
Authentication: When the client sends a connection request to the Broker, it can perform identity verification, which can be done using plaintext username and password or SSL/TLS client certificates, etc.
-
Communication: The client can act as a publisher sending messages to the Broker or as a subscriber receiving messages from the Broker. Messages include a fixed header, optional variable header, message payload, and quality of service level. The Broker forwards messages to clients subscribed to the message’s topic.
-
Disconnection: After communication is complete, the client can disconnect from the Broker. If the connection is unexpectedly interrupted, the Broker can notify subscribers according to the last will mechanism.

4 Application Scenarios
-
Internet of Things: Widely used in smart homes, smart agriculture, smart transportation, etc., for data collection, monitoring, and control between devices. For example, in a smart home system, the MQTT protocol allows a mobile app to remotely control and monitor smart appliances, lighting, locks, and other devices.
-
Industrial Control and Remote Monitoring: Used in industrial automation to connect PLCs, sensors, remote terminal devices, etc., to achieve device status monitoring, fault alarms, remote control, and other functions, enhancing production efficiency and safety.
-
Instant Messaging and Real-time Data Transmission: Can be used to implement instant messaging applications like chat rooms and real-time message push; also suitable for applications requiring real-time data transmission, such as real-time stock quotes and weather data.
-
Real-time Location Tracking: Mobile devices can publish their location information to specific topics, allowing other users or systems to subscribe to these topics to obtain real-time location information, commonly used in fleet management and logistics tracking.

5 Comparison with Other Protocols
-
Comparison with HTTP: The HTTP protocol uses a request/response model, where the client must actively initiate a request to obtain data, whereas MQTT uses a publish/subscribe model that allows data to be pushed in real-time. The header information of the HTTP protocol is larger, while the MQTT message header is very small; HTTP is not suitable for low-power, low-bandwidth devices and networks, while MQTT is specifically designed for such environments.
-
Comparison with CoAP: CoAP is also a protocol designed for the Internet of Things, but it is based on UDP, while MQTT is based on TCP; CoAP is mainly used for simple data interaction between resource-constrained devices, while MQTT is more suitable for large-scale device connections and complex business scenarios.
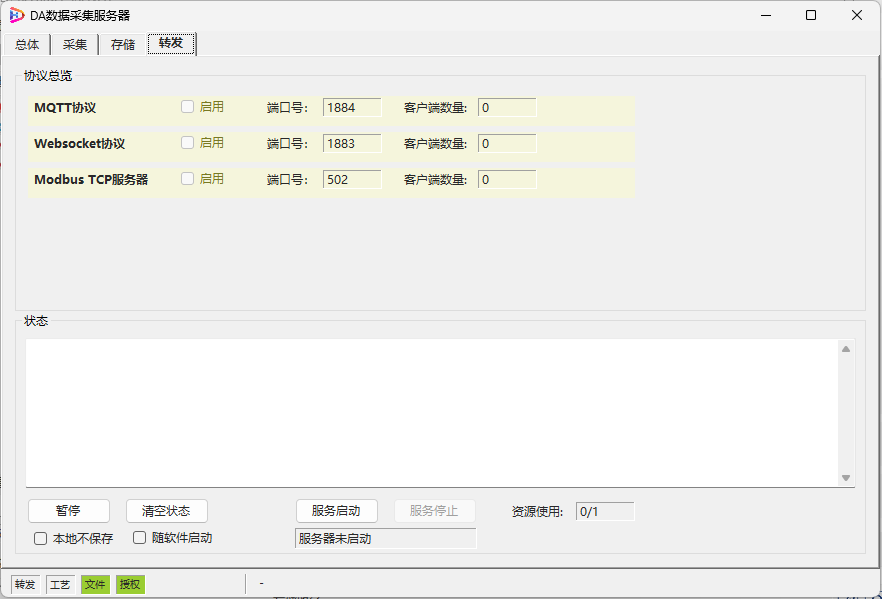
PLC-Recorder supports forwarding of multiple protocols: MQTT, Websocket, ModbusTCP. To enhance forwarding performance, the software has optimized the first two protocols. Please refer to the relevant sections of the software manual for details.