At the end of this article, there are 55 practical case materials.
Introduction: When we learnPLC programming, why does it take us much longer to develop programs than others? It could be due to our unfamiliarity with the software or not using the right methods. The following programming and debugging methods can significantly improve our work efficiency!
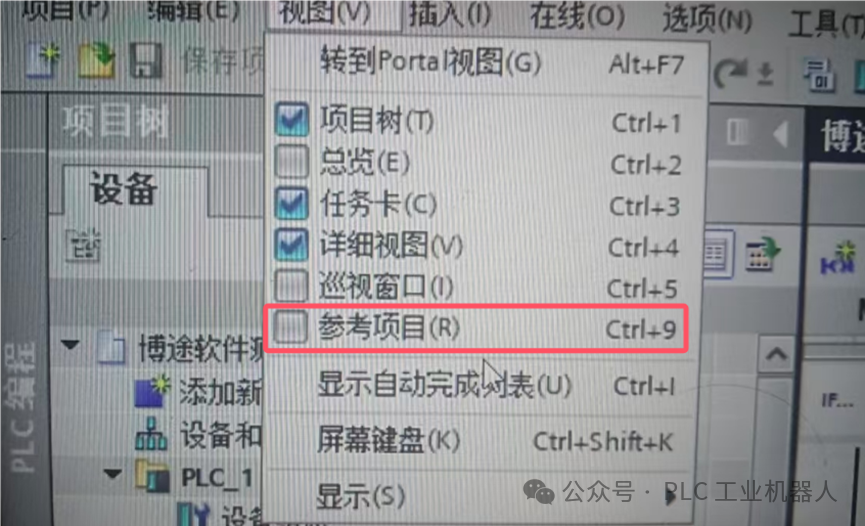
Method1: Use of Reference Projects
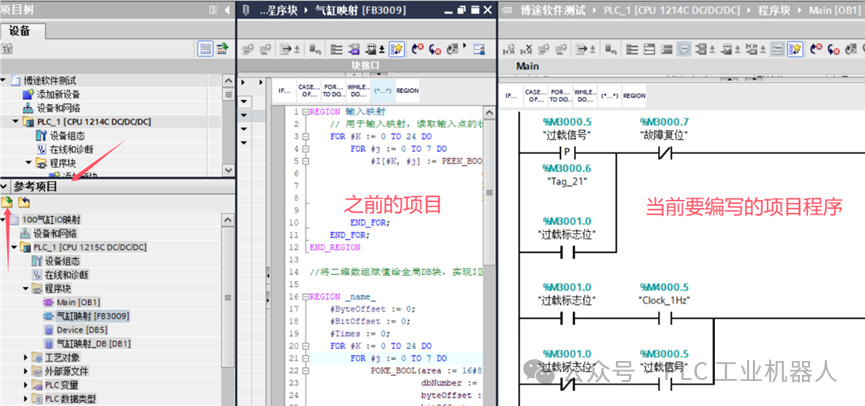
When we are writing programs, we need to refer to others’ or our previously written project programs. We can use the “Reference Project” feature in the software, which allows us to drag and drop previous project programs into the current project, making it very convenient!
Method2: Use of Project Libraries
Once we have written and encapsulated a program, we don’t want to waste that encapsulation. We hope to use it in other projects next time, such as the “Cylinder” program, “Analog” program, “Servo Control” program, etc. We can use the “Project Library” feature to save it, allowing us to use it directly next time and iterate on the original program. This iterative approach will make you increasingly proficient!
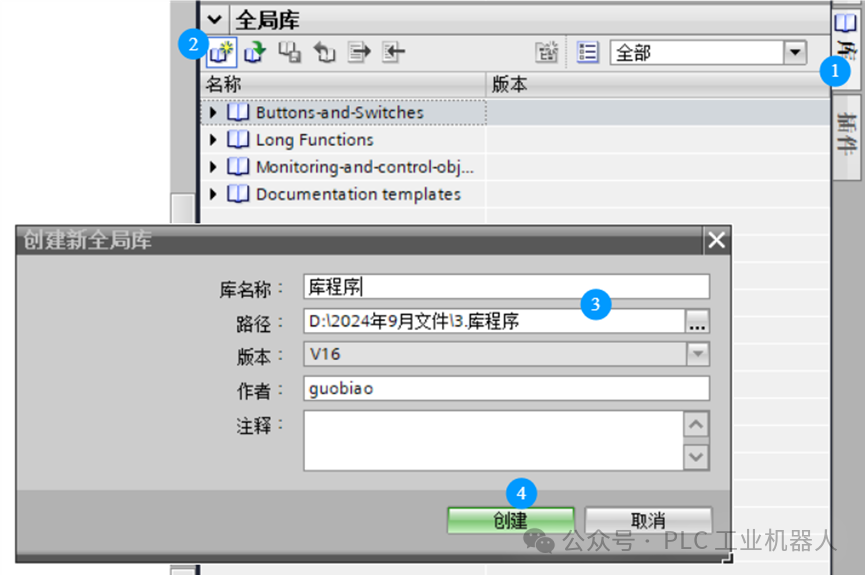
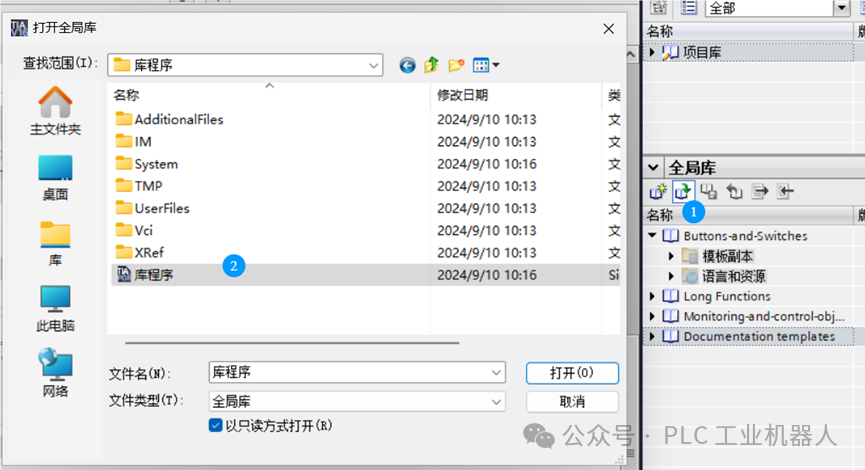
1)Create a “Library”, name it appropriately, and change the storage path.
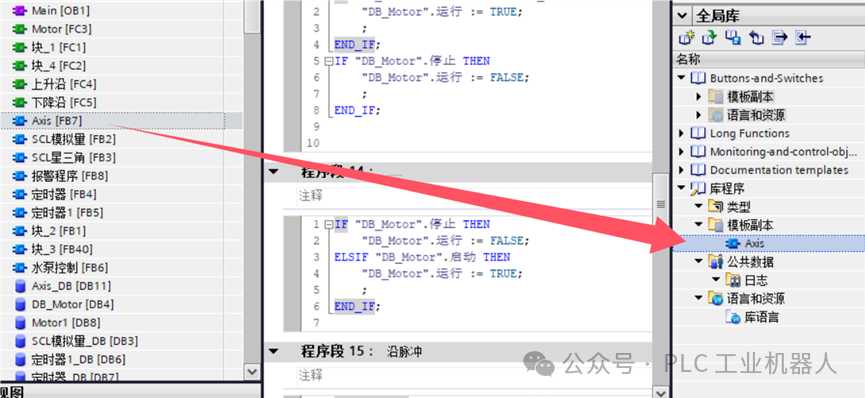
2)Drag the writtenFB program block into the global library
3)Open in other projects: just find the storage path.
Method3: Use of Call Structures
When we write or look at programs written by others, once the program blocks become numerous, their calling relationships become complex. We can use the “Call Structure” feature to quickly clarify the programming framework.
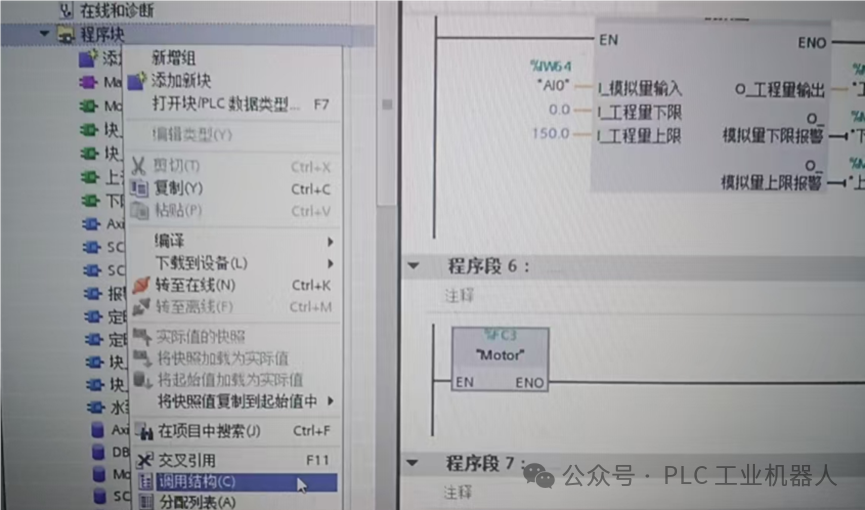
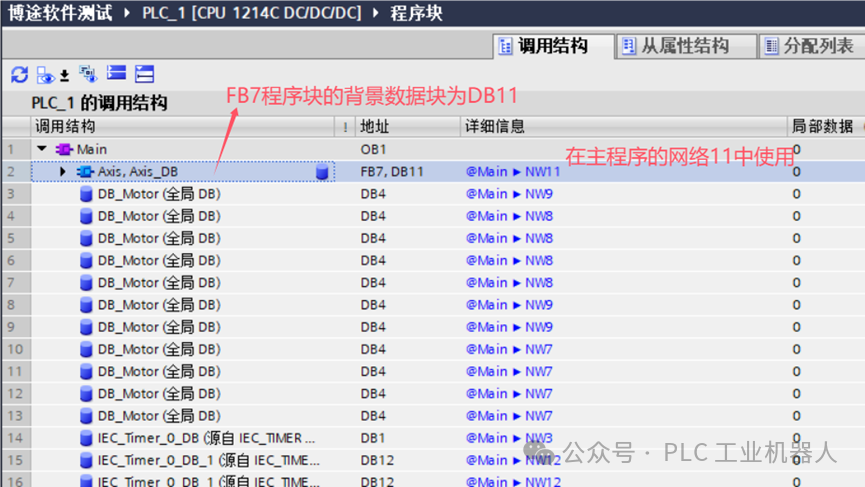
The “Subordinate Structure” is exactly the opposite of the “Call Structure”. The following diagram showsOB1 callingFC3, and thenFC3 callingFC5 program blocks.
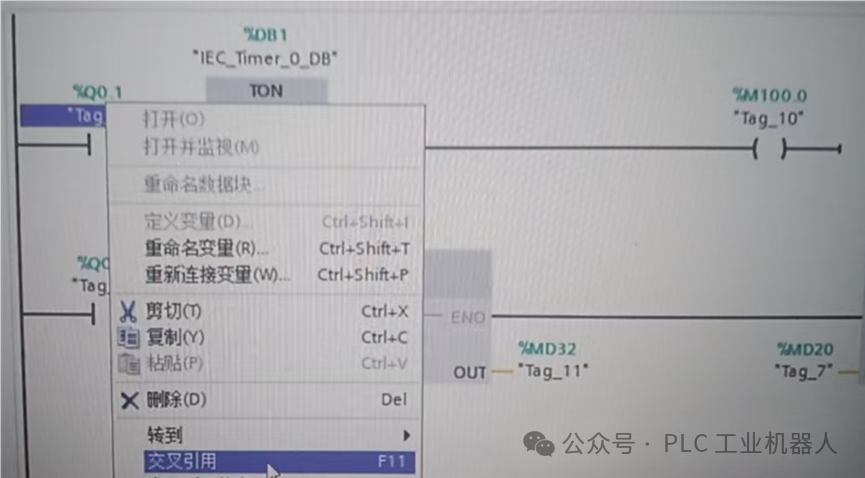
Method4: Use of Cross-References
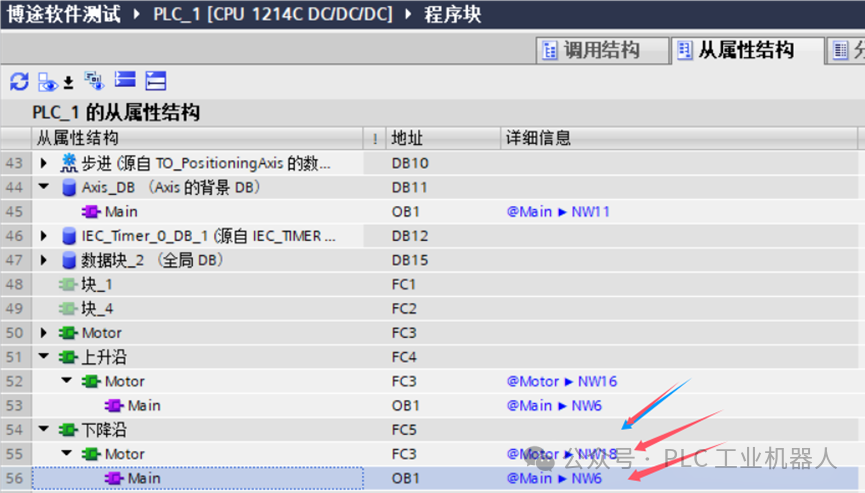
When we write programs, if the same address is used in multiple program segments and we cannot quickly find its address, we can use the “Cross-Reference” feature to quickly locate the usage position.
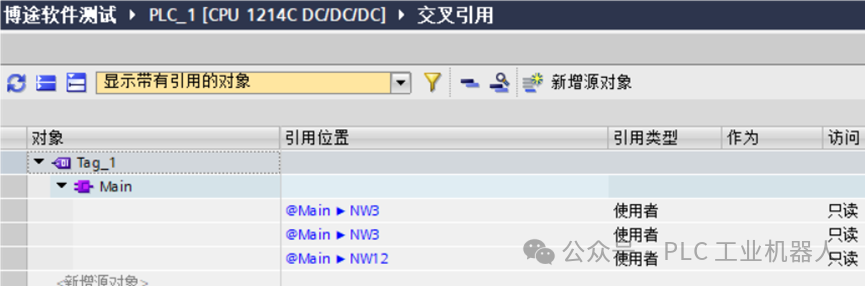
The following shows where the address “Q0.1” is used, specifically in network3 and network12 of the main program.
Recently, many friends have asked for case books, saying that reading articles on mobile is not very convenient. I took some time to organize all 55 practical cases, which are quite typical, including cylinder control programs, alarm programs, program frameworks, motion control program encapsulation, analog control of frequency converters, communication, and other practical cases.If you need them, you can add me on WeChat: biao467524527. If you can’t add me, feel free to message me!


Previous Recommendations
You are not unable to program PLCs; you may just be missing a perspective!
Automatic rotation program for 8 water pumps (faults automatically skipped)
A comprehensive guide to understanding FB programming with and without parameters
SCL programming case for Modbus TCP communication between 1200 and 200SMART (200SMART as client)
SCL programming case for controlling servo motors
A step-by-step guide to writing Modbus RTU communication programs
SCL programming case for controlling frequency converters with two PLCs using S7 communication
Comparison of ladder diagram and SCL for motor forward start and reverse stop programs
Resolving PLC communication faults is not difficult; the key is to find the right method!
How to achieve efficient programming using scan cycles and arrays
PLC communication techniques with Taiyuan frequency converters using Modbus RTU
Three conversion programs in PLC programming that you must master!
Three PLC programs that beginners must master
How to quickly complete PLC programming projects in one article?
The two most important instructions in learning SCL language, have you mastered them?
Comparison of the latest features of 200SMART and 1200 PLC
200SMART PLC has finally improved this feature
Preview of new features in the latest version of SMART and 1200 PLC!
Learn Modbus RTU communication through one case
1200 PLC programming for weight detection and packaging control program