Recently, Intel announced plans to spin off its Programmable Solutions Group (PSG) into an independent company, with an IPO expected in the next two to three years. In the announcement, Intel stated that PSG is expected to begin independent operations on January 1 of next year, during which Intel will continue to provide support. Intel also mentioned that it will report PSG as an independent business unit when releasing its Q1 2024 financial results.
In 2015, Intel acquired Altera, then a leading company in the FPGA field, for $16.7 billion, subsequently forming the current PSG division. One of PSG’s key responsibilities has been to drive innovation and development in FPGA technology. According to statistics from Iam Cutress, PSG generates approximately $500 million in revenue for Intel each quarter.
FPGAs are a type of semi-custom circuit chip in the ASIC domain, known for their hardware programmability, high integration, strong parallel computing capabilities, and low latency, earning them the nickname “universal chips.” FPGAs play a significant role in consumer electronics, communications, and industrial applications, and they also have promising applications in the currently trending fields of intelligent connected vehicles and AI. Intel’s decision to spin off PSG reflects its long-term optimism about the self-sustaining capabilities of this business segment. While this move appears to be an internal operational policy adjustment, it is likely to bring about changes in the landscape of the relatively small but rapidly growing FPGA market.
Optimistic about FPGAs, granting more “independence” to the business
Third-party data indicates that the FPGA market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of over 9% from 2023 to 2027, increasing from $8 billion to $11.5 billion. Undoubtedly, Intel’s actions are also driven by the enormous potential of the FPGA market. Li Yang, a researcher at Tsinghua University’s Intelligent Micro Systems Institute, told China Electronics News that after the spin-off, Intel will be able to leverage more external resources on top of its existing resources to enhance the competitiveness of its FPGA business.
Global FPGA Market Size Estimation (in hundreds of millions of dollars)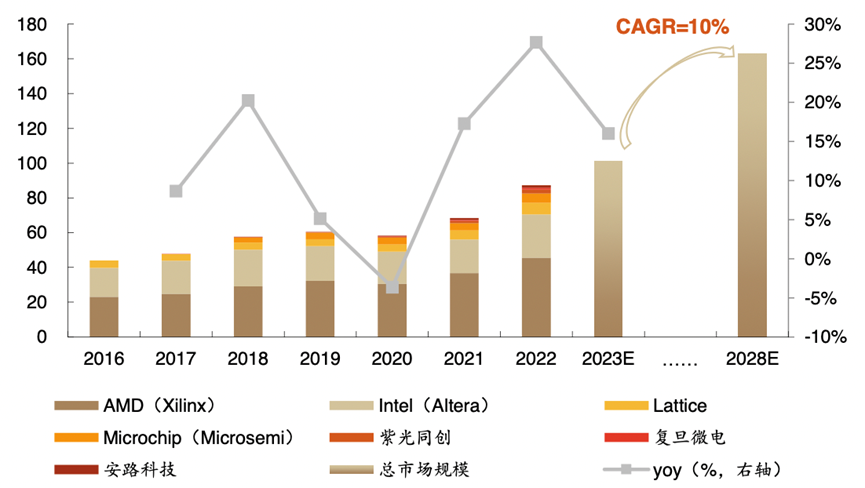
Data Source: Estimated based on public information
In this announcement, Intel stated that operating PSG as an independent business will provide the necessary autonomy and flexibility for PSG, accelerating its development and enabling it to compete more effectively in the FPGA industry, serving multiple markets including data centers, communications, industrial, automotive, and aerospace.
Additionally, Intel’s announcement indicated that even after the spin-off, the two companies will maintain strategic alignment, including PSG continuing its collaboration with Intel Foundry Services (IFS), and both companies will jointly address the challenges posed by the FPGA market. Furthermore, due to the success of PSG’s Supply Resilience program pilot, the collaboration with IFS will allow PSG to ensure stability and predictability in the supply process based on customer demand, making the supply chain more resilient. This means that PSG’s foundry partnerships will not be limited to just Intel’s IFS but may also include external foundries like TSMC.
Almost simultaneously, Intel also announced the addition of a new member to its Agilex FPGA product line—the Agilex 3 series, which will continue to expand PSG’s product offerings. Previously, Intel planned to release 15 new FPGA products in 2023, and as of now, it has launched a total of 11 products, surpassing the total number of FPGA products Intel has released in previous years. In the Q2 2023 earnings call, Intel disclosed that its PSG business unit’s revenue grew by 35% year-over-year, achieving a historic high for three consecutive quarters.
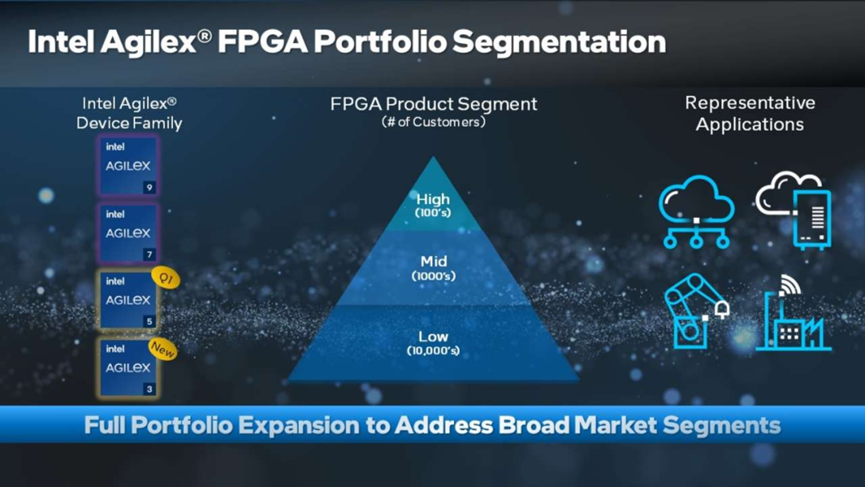
Intel Agilex FPGA Product Line Planning Diagram
With Intel’s spin-off of PSG, the independent FPGA model is expected to rise again. After the FPGA market matured, it once exhibited a “two large, two small” market structure, with Xilinx, Altera, Lattice, and Microsemi as the main players, while other smaller companies were distributed throughout the market. Among them, Xilinx and Altera held a monopoly on FPGA technology and market, while Lattice and Microsemi had certain market shares due to their unique low power consumption and high reliability.
In 2015, Altera was acquired by Intel for $16.7 billion; in 2018, Microchip acquired Microsemi for $8 billion; and in 2022, AMD announced the completion of its acquisition of the largest FPGA manufacturer, Xilinx, through an all-stock transaction, with the deal valued at $35 billion based on the stock prices at that time. With AMD’s announcement of completing the acquisition of Xilinx, independent FPGA companies have become scarce in the field. Meanwhile, to meet the demands of high-performance computing, data centers, and cloud computing workloads, semiconductor giants that acquired FPGA manufacturers have also adopted a “CPU + GPU + FPGA” hybrid XPU architecture, pushing FPGA acceleration into the era of heterogeneous systems, suggesting that the independent FPGA model may also face changes in technology and application.
However, Intel’s move to spin off PSG and take it public may change this trend.
Potential for Market Changes, PSG Also Faces Challenges
The demand for FPGAs primarily comes from data centers, communications, industrial, automotive, and aerospace sectors, which have high requirements for FPGA performance, efficiency, flexibility, and programmability. Li Yang believes that if PSG can provide superior FPGA products and solutions that meet the needs of various industries and customers, it may be able to establish a solid foothold in the market.
Moreover, Li Yang stated that after the spin-off, PSG will become an independent business entity, allowing it to adjust its product strategy and market positioning more flexibly to adapt to different application scenarios and technological changes. With greater flexibility, PSG will also find it easier to establish partnerships with other chip manufacturers or partners to provide more diverse solutions. “If PSG can formulate wise strategies and maintain good cooperation with Intel or other companies, it is very likely to make independent FPGAs a force to be reckoned with in the market again,” Li Yang said.
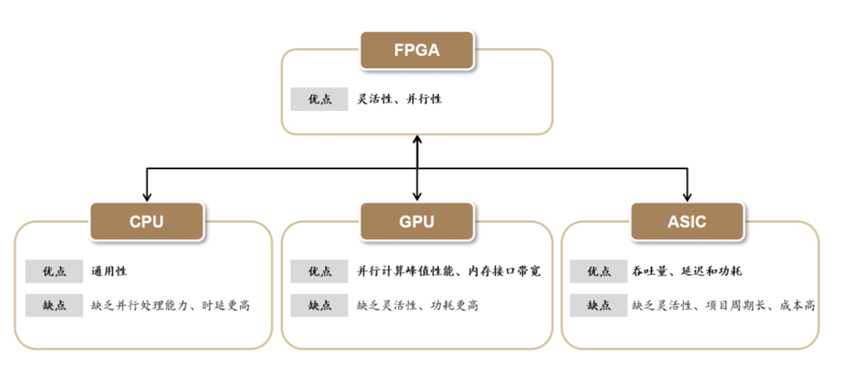
Comparison of FPGAs with Other Logic Chips (Source: Compiled from public information)
Industry experts told China Electronics News that the spin-off of Intel’s PSG division undoubtedly adds a strong competitor to other FPGA companies, which may significantly impact the market.
Firstly, market competition will intensify. The spin-off of Intel’s PSG division will make it an independent business entity, competing with existing FPGA market participants, which may lead to greater competitive pressure on other FPGA suppliers. Secondly, more resources will be invested. By spinning off the PSG division, more external resources can be directed towards the development and innovation of this business area, enhancing its competitiveness in the FPGA market and potentially accelerating industry development. Thirdly, new collaboration opportunities may arise. As an independent business entity, PSG may be more proactive in collaborating with other companies and institutions to promote further development in the FPGA market. Fourthly, market consolidation may occur. With the spin-off of Intel’s PSG division and intensified market competition, the FPGA market may experience a trend of consolidation. Some smaller FPGA suppliers may be acquired or merged, while larger FPGA suppliers may increase their market share through expanded production capacity and technological innovation. Fifthly, technological innovation may be stimulated. The spin-off of Intel’s PSG division may encourage other FPGA suppliers to increase their investment in technological innovation and R&D to maintain their market competitiveness. This will help drive further development of FPGA technology and create more business opportunities.
However, the FPGA market today has changed significantly compared to before Altera’s acquisition in 2015, and PSG’s brand influence and market share cannot be compared to the Altera era. Therefore, for PSG to establish a foothold in the ever-changing market, it needs to deeply understand market demands and competitive dynamics and formulate development strategies that align with market trends.
Stability and competitiveness of the supply chain are also key factors. Although Intel emphasized the continued collaboration between PSG and IFS in its announcement, ensuring stability and competitiveness in the supply chain also requires diversification. Therefore, PSG needs to establish good relationships with external suppliers like TSMC to ensure product quality and stability.
Further Reading:Two Departments Join Forces to Launch the 2023 Smart Manufacturing System Solution InitiativeThe World’s First! Tsinghua University Develops a Memristor Chip for In-Memory ComputingAuthor丨Shen CongEditor丨Zhang XinyiDesigner丨MariaSupervisor丨Lian Xiaodong