
Click the above to follow us!
Is PLC Programming Challenging? Remember These 5 ‘Universal Templates’ for Beginners!
I remember when I first entered the industry, standing in front of the PLC control cabinet, looking at the rows of wires and modules, my heart raced. At that time, facing the dense ladder diagrams felt like reading a foreign language. To be honest, that feeling was really frustrating, and it even made me doubt whether I had chosen the right career.
Looking back now, much of that pain stemmed from my lack of understanding of how to utilize the “template” as a powerful tool. Yes, you heard it right, in the world of PLC programming, templates are our “dimensionality reduction artifacts.” Mastering a few core templates is like having the “programming password,” allowing you to navigate seemingly complex control systems with ease.
Today, I will share several “universal templates” that I have accumulated over the years, especially for new friends just starting out. With these templates, you will find that PLC programming is not as difficult as it seems!
Why Are Templates Indispensable in PLC Programming?
At this point, some friends might ask: Why use templates? Can’t we just learn programming directly?
I used to think that way too, but after countless head-banging experiences, I realized one thing: 【In the field of industrial automation, efficiency is always the top priority】. And templates are precisely the best way to improve programming efficiency.
● Templates provide a standardized program structure, making team collaboration smoother.● Templates contain verified code blocks, significantly reducing the error rate.● Using templates can save a lot of time, eliminating the need to start from scratch every time.● Templates help beginners quickly understand the thought process and logic of PLC programming.
I remember once I took on an urgent task where the client required a program update for a small assembly line to be completed within two days. If I had to write it from scratch, I would have had to pull several all-nighters. Fortunately, I had ready-made templates on hand, and with just a few modifications to meet specific requirements, I completed it in a day. The client was satisfied, my boss was happy, and I didn’t end up exhausted. That’s the charm of templates!
Self-Latching Circuit Template – The Most Basic Yet Practical
There’s a joke in the industrial control field: An electrician who can’t write a self-latching circuit is not a good programmer. This seemingly simple template is the foundation of countless control systems.
A self-latching circuit simply means that pressing the start button runs the device and keeps it running; pressing it again stops the device. This function can be seen in almost all mechanical equipment.

The core of the self-latching circuit is the “memory” function, which allows the system to “remember” the last operation command.
When I was providing technical support at a beverage bottling plant, I found that their bottling machine frequently experienced downtime. After investigation, it turned out that their self-latching circuit did not account for power recovery, causing the equipment to fail to automatically return to its previous state after a sudden power outage. I used an improved version of the self-latching circuit template, adding a power-off memory function, and the problem was immediately resolved.
Flashing Circuit Template – A Tool for Visual Feedback
Have you noticed that almost all industrial devices have various flashing indicator lights? These seemingly simple flashing effects are actually the result of the flashing circuit template at work.
● Flashing circuits can intuitively display the operational status of the device.● Different flashing frequencies can indicate different operating modes or alarm levels.● Flashing signals are more likely to attract the operator’s attention than fixed signals.
The essence of the flashing circuit lies in the flexible application of timers; by controlling the on-off time of the timer, various complex flashing effects can be achieved.
Speaking of flashing circuits, I recall an interesting case. Once, I went to a factory for technical consultation and found their alarm system strange: all alarm lights flashed at the same frequency, regardless of whether it was a minor warning or a serious fault. The operators could not distinguish which issues needed immediate attention and which could be resolved later. I helped them design a tiered alarm system based on the flashing circuit template: minor issues flashed slowly, general faults flashed at medium speed, and serious faults flashed quickly. This simple improvement significantly enhanced their fault response efficiency.
Momentary and Interlocking Circuit – Ensuring Operational Flexibility
In automated production lines, equipment often requires two operating modes: manual momentary and automatic interlocking. The momentary interlocking circuit template was created for this purpose.
In momentary mode, pressing the button runs the device, and releasing it stops it; in interlocking mode, all devices run automatically in a preset logical sequence. This dual-mode operation is very practical during debugging and daily production.
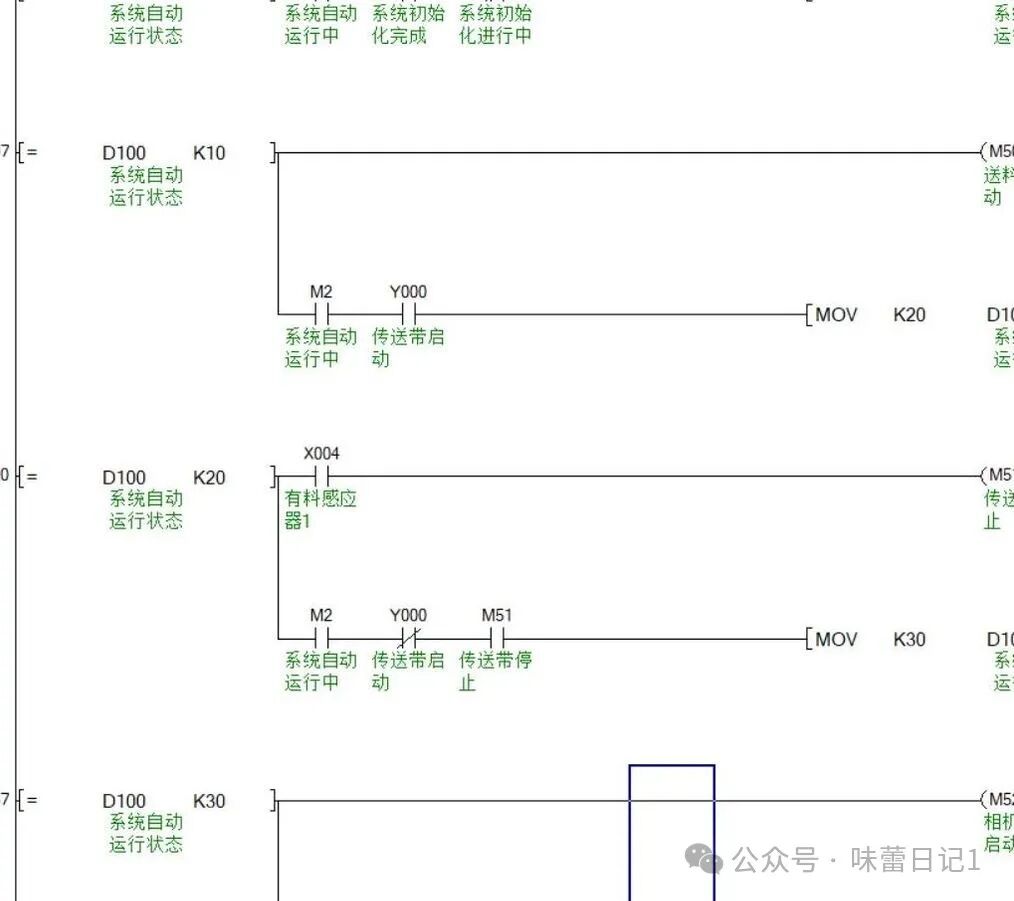
The key to the momentary interlocking circuit is the smooth transition between modes, ensuring that switching does not cause system confusion or safety issues.
Honestly, in my early projects, I once made a mistake due to improper handling of the momentary interlocking switch. It was a food packaging line, and when the operator switched from automatic to manual mode, the conveyor belt suddenly accelerated, causing all products to fall. Later, I used a more refined momentary interlocking template, adding buffering during mode switching, and the problem was resolved.
Delay On or Off – The Foundation of Timing Control
When it comes to PLC programming, we cannot overlook the delay function. The delay on or off template is a fundamental tool for handling timing control.
● Delay on: The action is executed after a delay once the signal arrives.● Delay off: The action stops after a delay once the signal disappears.
The essence of the delay template lies in the flexible control of the “time window,” allowing us to precisely grasp the timing rhythm in the automation process.
When I was providing technical support in a painting workshop, I encountered a problem: the painting robot often produced uneven paint surfaces when switching nozzles. After analysis, it turned out that there was not enough transition time between the switching signal and the actual action. I used the delay off template to add appropriate delays for each switch, and the paint quality immediately improved significantly.
Interlocking and Safety Circuit – Guardians of Safe Production
In the field of industrial automation, safety is always the top priority. The interlocking and safety circuit template is designed to ensure the safe operation of equipment.
Interlocking ensures that equipment starts and stops in the correct order; safety prevents conflicting commands from being executed simultaneously. The combination of these two functions can effectively prevent equipment damage and safety accidents.

The core of the interlocking safety circuit is “conditional judgment” and “priority handling,” allowing the system to make correct decisions under complex working conditions.
I remember once I participated in designing an automotive parts assembly line, which included multiple robotic arms and conveyor systems. Without strict interlocking control, the robotic arms could start grabbing workpieces while the conveyor belt was still moving, leading to collisions and damage. We applied a comprehensive interlocking template to ensure that each action could only be executed after the previous action was completed and confirmed safe. This production line has been running smoothly ever since, without any safety incidents.
The Pros and Cons of Using Templates
Having discussed the benefits of templates, I must objectively state: templates are not a panacea; they have both advantages and disadvantages.
The benefits are obvious: templates can significantly improve programming efficiency, reduce error rates, and help beginners get up to speed quickly. Especially when facing standardized, repetitive control tasks, using templates is a true multiplier of efficiency.
However, the drawbacks cannot be ignored: 【Over-reliance on templates can limit the development of programming thinking】, potentially leading to insufficient handling of non-standard issues. The industrial field is ever-changing, and simply applying templates cannot address all complex situations.
My suggestion is: beginners can start by using templates to familiarize themselves with the basic principles, and then gradually understand the programming concepts behind the templates, ultimately being able to flexibly apply or even create new templates suitable for specific problems. This is the true path to becoming a PLC programming expert.
A Real Comprehensive Case
To help everyone better understand the application of these templates, I will share a real case: a detection and classification system for good and bad products on a conveyor belt.
The entire process is as follows: products flow in from the left side, and when a material sensor detects a product, the conveyor belt stops, and a camera takes a picture for inspection; after the inspection is complete, the conveyor belt continues running until the product reaches the second sensor position; if the product is qualified, it passes directly; if not, a push cylinder will push it into the defective product collection box.
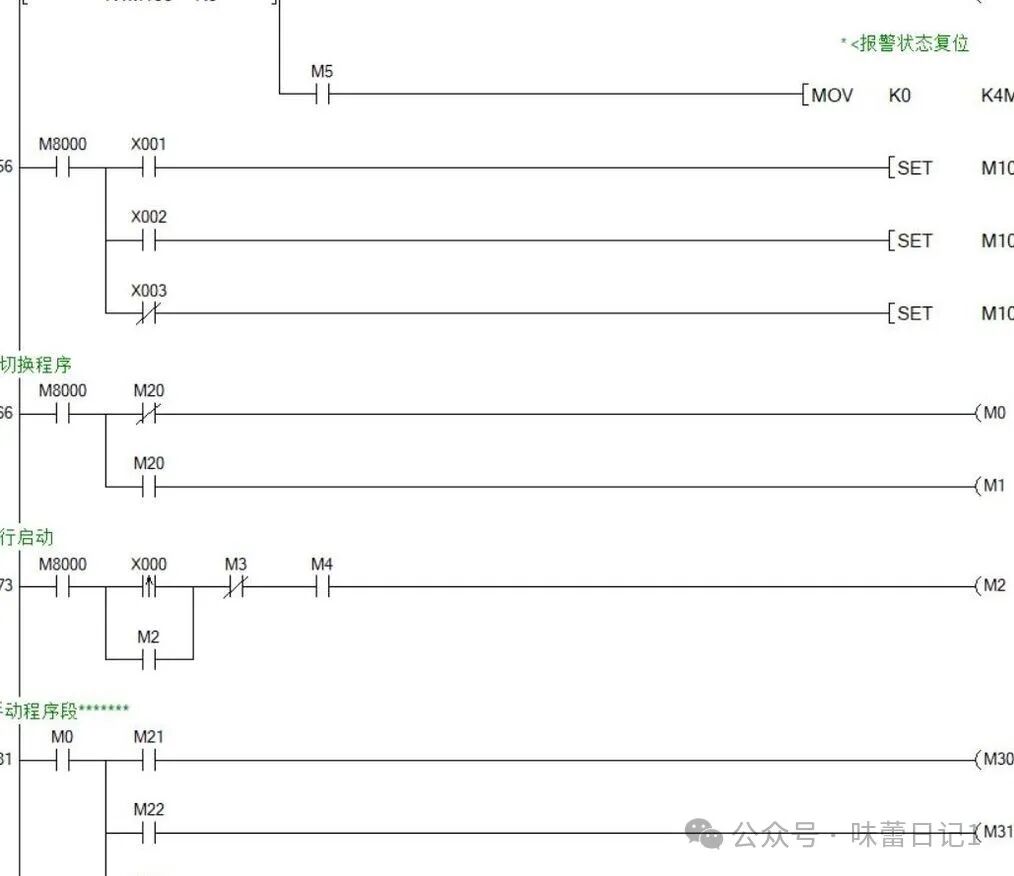
In implementing this system, I comprehensively applied multiple templates:● Self-latching circuit to control the start and stop of the conveyor belt.● Delay template to control the timing window for the camera to take pictures and analyze.● Interlocking ensured the safe collaboration of the conveyor belt and push cylinder.● Flashing circuit for indicating lights to show different statuses.
The entire program structure is clear, easy to maintain, and has a very low failure rate, which is the benefit of template-based programming.
In Conclusion
PLC programming may seem complex, but it actually follows certain rules. Mastering core templates means mastering the basic framework of programming. Practice makes perfect, and the flexible application of templates requires continuous practice and accumulation.
I hope the “universal templates” shared today can help friends who are learning PLC programming. Remember, 【templates are tools, not dogmas】. As you gain experience, you will gradually form your own programming style and template library.
By the way, what difficulties have you encountered while learning PLC programming? Do you have any practical templates you want to share? Feel free to leave a comment to exchange ideas; your experience might help others who are also learning!
If you found today’s sharing useful, don’t forget to like and share it so that more friends can benefit. I will also share more practical tips and case analyses on PLC programming in the future, so stay tuned!
What brand of PLC are you currently using? What troublesome issues have you encountered in programming? Let’s chat in the comments!
2:04