One
Basic Analysis of Logical Reasoning
The number of logical reasoning questions remains stable at 40 each year, divided into graphic reasoning, definitional judgment, analogical reasoning, and logical judgment, with 10 questions for each type.
Two
Key Question Type Analysis
01
Graphic Reasoning
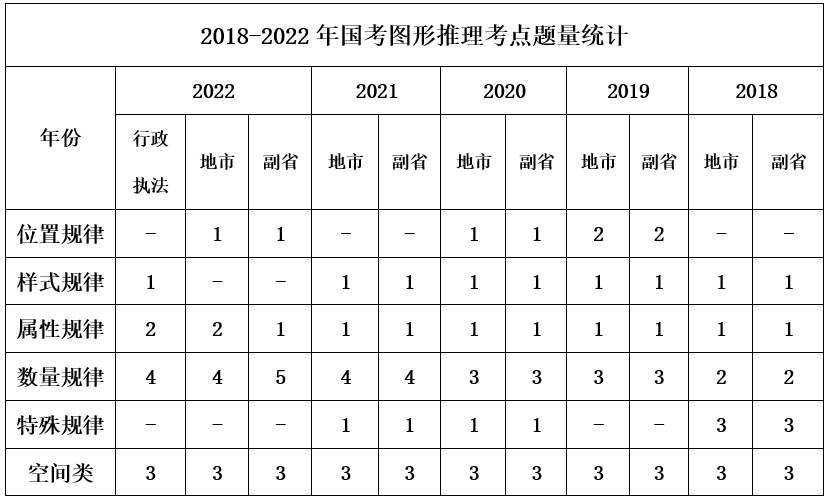
The graphic reasoning section covers a wide range of topics, mainly including two major types: plane and spatial.
Plane-type questions involve the examination of position patterns, style patterns, quantity patterns, attribute patterns, and special patterns. It mainly tests candidates’ familiarity with graphic features and corresponding topics. Among these, quantity patterns have the highest frequency, the most topics, and the greatest difficulty. Symmetry in attribute patterns has been a must-test topic for the past five years, and this topic has many detailed testing methods that need to be studied intensively.
Spatial-type questions include topics such as spatial reconstruction, three-view diagrams, three-dimensional assembly, and sectional views. Among these, spatial reconstruction and three-dimensional assembly are popular must-test topics, and candidates should focus on learning methods and techniques for these topics.
02
Definitional Judgment
In the past five years, the number of definitional judgment questions in the national exam has been consistently 10, with a very broad examination scope that includes not only philosophy, logic, sociology, psychology, education, and law, but also astronomy, mathematics, physics, chemistry, zoology, and botany. This indicates that candidates cannot master every discipline’s essential knowledge but should seek logical methods for defining concepts by breaking down definitions to answer questions.
Each definitional judgment question first defines the relevant concept, then lists four situations, requiring candidates to strictly select the answer that is most or least consistent with the definition. The question formats mainly include single definition and multiple definitions, with inquiry forms including belonging and not belonging. Two points need attention:
First, understand the question format: “belonging/not belonging” to the definition;
Second, when legal definitions appear, the difficulty of the question is generally higher.
03
Analogical Reasoning
In the past five years, there have been consistently 10 analogical reasoning questions, with testing formats including: two-word groups, three-word groups, and fill-in-the-blank. Common relationships between words include semantic relations, logical relations, and grammatical relations.
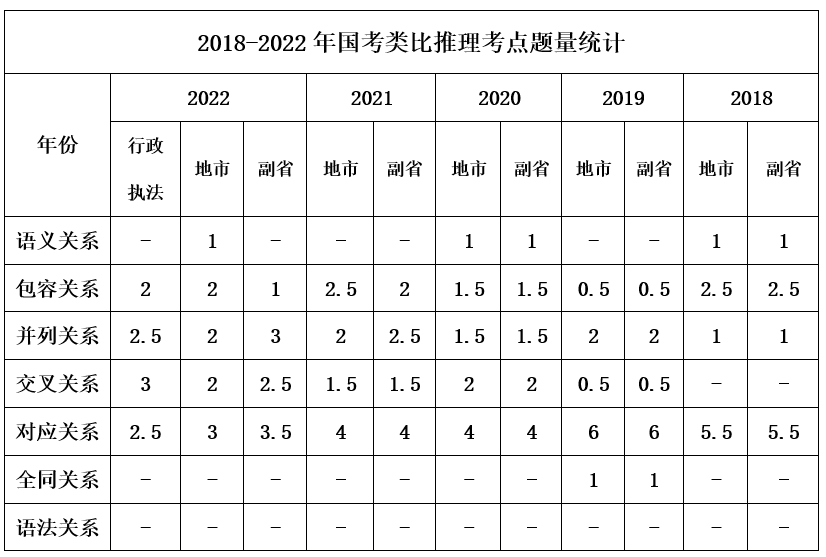
Analogical reasoning tests candidates’ mastery of relationships between words, with common relationships including semantic relations, logical relations, and grammatical relations. Logical relations include equivalence relations, parallel relations, inclusion relations, intersection relations, and corresponding relations. Among these, corresponding relations have the most varied topics and the largest proportion of questions, and each type of corresponding relation also involves secondary differentiation testing. Additionally, parallel relations, inclusion relations, and intersection relations are also key focuses in past exam questions, and candidates need to understand the connotations of these topics and be able to quickly distinguish them when they appear in the same question.
04
Logical Judgment
In the past five years, the number of logical judgment questions has been consistently 10. Before 2021, there were differences in the last five questions between city-level and deputy provincial-level exams, with city-level having one main material question with five sub-questions, testing combination and arrangement separately. In the 2022 new administrative enforcement category, the logical judgment topics are similar to those at the city level.
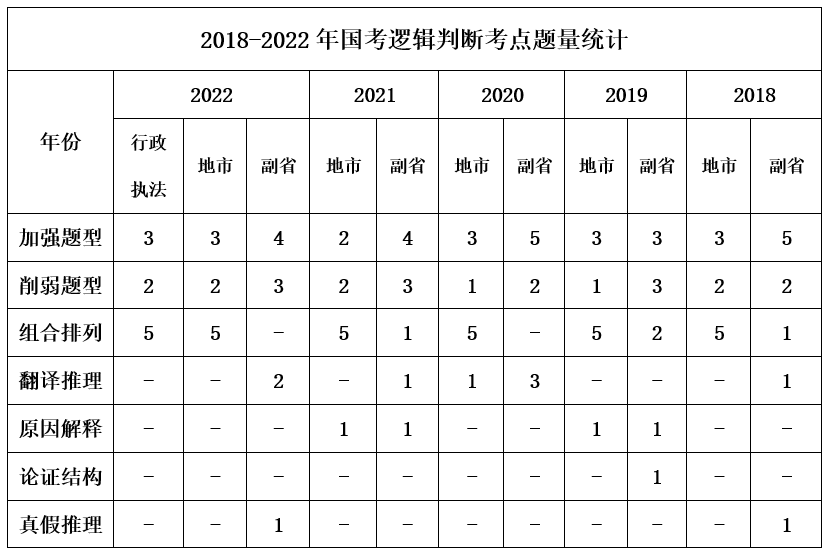
Logical judgment has the most and varied knowledge points among the four modules of logical reasoning, making it the most difficult question type. Therefore, when reviewing this section, all candidates should adhere to the three principles:
First, study each knowledge point thoroughly, ensuring no point is overlooked.
Second, focus on the knowledge points that are commonly tested/must-test.
Third, “niche”/”difficult” knowledge points can be skipped if they are not well understood.
Three
Commonly Mistaken Points
01
High-frequency Mistake: Points
In recent years, points have become a hot topic in our exams. Points are actually the first thought direction after excluding the line of inquiry. When there are many and chaotic lines in the graphic, we should prioritize considering points, especially when there are crossings, cutting points, and large branches. The number of points is a basic examination, and additionally, there are detailed upgrades in the examination of intersections of curves and straight lines, internal intersections of graphics, and intersections on borders.
02
High-frequency Mistake: Lines
For lines, curves and direct quantities are the basic reference checks. When we find that there are many curves and straight lines in the graphic, we should prioritize considering them. Additionally, we can consider specific directions, such as checking only vertical or horizontal lines, as well as the difference between curves and straight lines.
03
High-frequency Mistake: Angles
The examination of angles in the national exam is not very frequent, which is precisely why the probability of examination in the coming years will be higher. Last year, the national exam included angles tested in a very novel way, examining angles of 0, 45, 90, and 135 degrees in a fan-shaped format. When the question stem includes sharp angles, many triangles, jagged lines, small notches, fan shapes, or right angles, we should prioritize considering angles, especially right angles.
04
High-frequency Mistake: Surfaces
Surfaces are the easiest element to examine among quantity types. Based on the number of surfaces, if we cannot determine a unique answer, we should analyze the question stem. If the sizes of the surfaces of each graphic are relatively even, we should prioritize considering the shapes of the surfaces. If the sizes are uneven, we should consider whether the largest or smallest surface’s characteristics resemble the outer border, whether it is a center or axis-symmetric graphic, and the area size. Additionally, we can consider the number of identical surfaces.
05
High-frequency Mistake: Elements
When we find a large number of small patterns in the graphic, we should prioritize considering elements, such as rules. For regular patterns, consider the types and quantities of elements, and for irregular patterns, consider the number of independent parts. When thick lines appear, we should prioritize considering the number of parts. If each graphic contains two types of small elements, we should prioritize considering the operations of the elements.
This is a summary of the examination situation for the logical reasoning section of the national exam. If you find it helpful, feel free to bookmark it and review it more often!

2023 National Exam Written Test Gift Package
Scan the QR code below to receive it
▼ ▼ ▼

2023 National Exam Courses
Support the National Exam!
Scan the QR code below for consultation
▼ ▼ ▼

Past
Recommendations
Quick Look! 2023 National Exam Position Analysis
Quick Look! 2023 National Exam Situation!

LiRen Public Examination
/LiRen/
Sina Weibo|Jiangsu LiRen