In the field of IoT development, Espressif’s ESP series chips hold a significant market share. Among them, the ESP8266 and ESP32 (along with their derivatives) are the most notable products. This article will compare them across multiple dimensions, including technical specifications, functional features, and applicable scenarios, to help you find the best choice for your project.
1
Hardware Specifications Showdown
Core Performance Differences
| Metric | ESP8266 | ESP32 (Basic Version) |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | Single-core Tensilica L106 (80MHz) | Dual-core Tensilica Xtensa (240MHz) |
| Memory Configuration | 32KB Instruction RAM + 80KB Data RAM | 520KB SRAM |
| Maximum Flash Memory | 4MB (requires external expansion) | 16MB (built-in for some models) |
| Computational Power | Approximately 60 DMIPS | Approximately 600 DMIPS |
The performance advantage of the ESP32 is evident, especially when handling complex tasks. For example, when running the same JSON data parsing code, the processing speed of the ESP32 is 5-8 times that of the ESP8266.
2
Peripheral and Function Comparison
Interface Resource Differences:
The peripheral configuration of the ESP8266 is relatively basic:
-
1 UART, 1 SPI, 1 I2C (software simulated)
-
Supports PWM, but can only output 8 channels simultaneously
-
Only 1 ADC (GPIO17), with low precision (0-1V range)
The ESP32 significantly enhances this:
-
3 UARTs, 4 SPIs, 2 I2Cs
-
16 PWM outputs, supports LEDc dimming
-
18 ADCs (12-bit precision), 2 DACs
-
Built-in Bluetooth Classic/BLE, infrared transceiver, Ethernet (for some models)
Practical Code Comparison:
ESP8266’s ADC usage limitations:

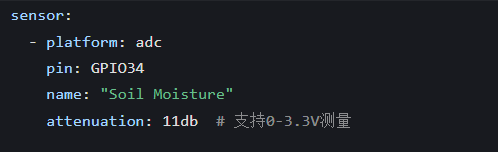
ESP32’s flexible configuration:
3
Power Consumption and Battery Life Performance
Power consumption comparison under the same operating mode:
| Mode | ESP8266 | ESP32 |
|---|---|---|
| Active Mode | ~120mA | ~80mA |
| Light Sleep | ~20mA | ~15mA |
| Deep Sleep | ~20μA | ~5μA |
The low power advantage of the ESP32 is particularly evident in battery-powered devices. For example, with the same capacity 18650 battery, when driving a temperature and humidity collection device:
-
ESP8266 can work for about 3-4 months
-
ESP32 can work for about 6-8 months
4
Development Experience and Ecosystem Support
The level of support from ESPHome for the two chips varies significantly:
ESP8266: Only supports basic functions, and some new components (like BLE gateways) are no longer compatible
ESP32: Supports all advanced features, including:
-
Native USB debugging (for some models)
-
More stable OTA upgrades
-
Supports WebServer and WebSocket
-
Built-in encryption engine
The official statement clearly indicates: ESP8266 no longer meets the “Made for ESPHome” standard, and future feature updates will prioritize the ESP32 series.
5
Purchase Recommendations and Applicable Scenarios
Situations to Prefer ESP8266:
-
Simple projects that only require basic Wi-Fi connectivity (like controlling a single LED)
-
Extremely limited budget, and already have a large stock of ESP8266 modules
-
Need to be compatible with existing hardware designed based on ESP8266
Recommended Situations to Choose ESP32:
New project development, especially when needing:
-
Bluetooth communication capabilities
-
Processing complex sensor data
-
Running machine learning models (like voice wake-up)
-
Multi-device interaction control
Transition Solutions
If you already have ESP8266 devices, you can extend their lifespan by:
-
Disabling unnecessary log outputs to reduce memory usage
-
Using restore_from_flash: true to save critical states
-
Adopting lightweight communication protocols (like MQTT lightweight mode)
However, in the long run, the ESP32-C3 is an ideal replacement for the ESP8266 — it is pin-compatible and costs only slightly more than 20 RMB, yet offers over 5 times the performance improvement.
6
Conclusion
The ESP8266, as a contributor to the popularization of IoT, is suitable for handling simple tasks and educational scenarios; while the ESP32 series, with its stronger performance, richer peripherals, and better power consumption, has become the first choice for new projects.
The core principle of technical selection: do not limit project scalability for the sake of saving a small amount of cost. Choosing the ESP32 may have a slightly higher initial investment, but it can avoid secondary development costs due to hardware limitations, ultimately proving to be more economical.

Click to identify and follow us
