For the report, please contact customer service.
1. The development space for robots is vast, with major players entering to embrace a brilliant new era.
1.1. Robots are accelerating their penetration into various fields, with market space expected to grow significantly.
Globally, robots are hailed as “the crown jewel of the manufacturing industry,” and their research, development, manufacturing, and application are important indicators of a country’s technological innovation and high-end manufacturing level. They have become a crucial entry point for a new round of technological and industrial revolution. With the integration of technologies such as artificial intelligence, hardware, networks, and cloud computing, the intelligence and flexibility of robots are continuously improving, and their adaptive capabilities in various scenarios are becoming stronger, leading to accelerated penetration in various fields. As the population ages and labor supply tightens, policies are being strengthened to empower the development of the robot industry, with continuous investment and technological breakthroughs in areas like AI, leading to increased production efficiency and liberation of productivity. The era of “Robot+” is expected to arrive.
In the field of industrial robots, statistics from the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) show that in 2021, the global industrial robot market size reached $17.5 billion, with the installation volume hitting a historical high of 487,000 units, a year-on-year increase of 27%. With the continuous release of market demand and further popularization of industrial robots, the market size is expected to continue to grow, reaching $23 billion by 2024. Over the past five years, China’s industrial robot market has maintained a growth trend, with sizes of 58.517 billion and 66.588 billion yuan in 2022 and 2023 respectively. According to estimates from the Industrial Research Institute, it is expected to increase to 72.642 billion yuan by 2024. The production of industrial robots in China continues to grow, with a production volume of 429,500 units in 2023, and a cumulative production of 556,400 units in 2024, representing a year-on-year increase of 29.53%.
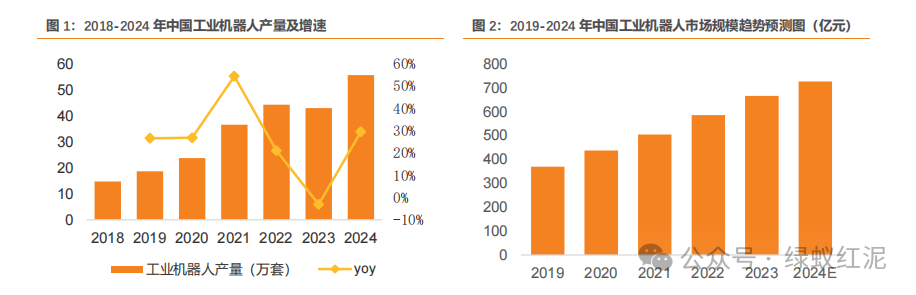
In the field of service robots, there has been significant support from national policies in recent years. In June 2024, the National Development and Reform Commission and other departments released measures to create new consumption scenarios and cultivate new growth points, proposing to expand the functions of intelligent robots in cleaning, entertainment, elderly care, education, and training, and to explore the development of humanoid robots based on large AI models. The introduction of relevant policies will provide a favorable production and operational environment for enterprises and accelerate the commercialization of service robots. By 2024, the production of service robots in China is expected to reach 10.519 million units, a year-on-year increase of 34.29%. Currently, in the service robot market, floor cleaning and ground cleaning robots hold the largest market share at 27.52%; logistics and mobile robots rank second with a market share of 23.26%; inspection robots account for 19.19%; while other service robots have a smaller market share.
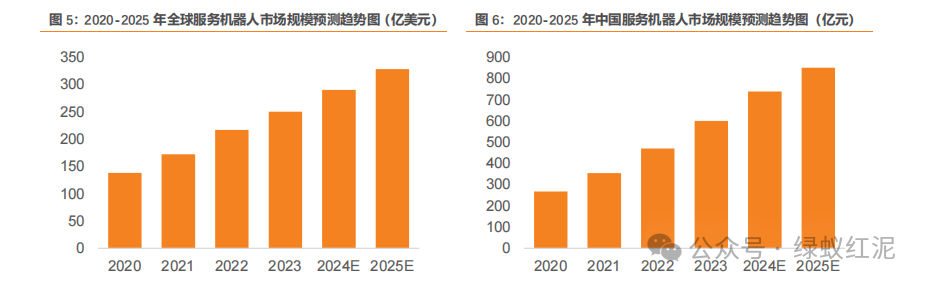
The increasing aging population and rising demand for medical, rehabilitation, and companionship services are driving the continuous expansion of the service robot market. According to the China Business Industry Research Institute, the global service robot market size was approximately $25 billion in 2023, a year-on-year increase of 15.21%, and is expected to reach $29 billion in 2024 and $32.8 billion in 2025. The service robot market in China was approximately 60 billion yuan in 2023, with an average annual compound growth rate of 32.41% over the past five years, and is expected to reach 73.8 billion yuan in 2024 and 85 billion yuan in 2025.
In the field of special robots, the performance of global special robots has continuously improved in recent years, significantly enhancing their operational capabilities in extreme environments and hazardous operations, promoting rapid development in applications such as space exploration, deep-sea exploration, and emergency rescue. In 2023, the global special robot market size reached $12 billion, with an average annual compound growth rate of 22.67% over the past five years, and is expected to reach $14 billion in 2024. Currently, the domestic special robot market is maintaining rapid development, with a significant demand for special robots in China to respond to earthquakes, floods, extreme weather, mining accidents, fires, and public safety events. As the localization of core components continues to accelerate, a large number of innovative enterprises in the special robot sector are emerging, enhancing product advantages and rapidly growing the industry scale. In 2023, the market size of special robots in China reached 20.3 billion yuan, with an average annual compound growth rate of 29.36%, and is expected to reach 24.6 billion yuan in 2024.
1.2. Major players are entering the market, ushering in a brilliant era for robots.
The China Electronics Society categorizes robots into three types: industrial robots, service robots, and special robots. Industrial robots are multi-joint mechanical arms or multi-degree-of-freedom machines designed for industrial applications, capable of automatically performing various tasks relying on their own power and control capabilities to achieve multiple functions. Service robots are advanced robots that integrate various high technologies to provide necessary services to humans in unstructured environments, possessing capabilities for perception, decision-making, and execution, and can interact naturally with humans. Special robots are primarily used to replace humans in high-risk environments and special working conditions, with the ability to adapt to complex environments.

Robots may become an important application direction for AI, focusing on industrial, medical, home service, and warehousing logistics scenarios. Multi-modal large models endow robots with a universal world model and semantic understanding capabilities, enabling them to “understand” the environment, “hear” human instructions, and plan reasonable action sequences, achieving scene generalization and task flexibility, making robots important application terminals for AI.
In the field of industrial manufacturing, embodied robots can utilize existing human work environments and tools to achieve “plug-and-play” labor supplementation. For example, the Zhiyuan Expedition A2-W humanoid robot can be used for flexible manufacturing, working alongside humans to perform tasks such as handling and patrolling. It is expected that within the next 5-10 years, embodied robots will gradually transition from assistants to main forces, taking on more night shifts, dangerous, or high-intensity work.
In the field of medical care, the use of robots can greatly reduce the burden on caregivers and improve service consistency. In recent years, general humanoid robots have begun to enter medical trial scenarios, with UBTECH’s “Cloud Sail” guiding patients to seek medical treatment; surgical robots like the Da Vinci system have been widely used in minimally invasive surgeries, improving surgical precision and stability. Additionally, nursing and companionship robots also have broad market prospects. In the future, surgical robots may take the lead in operating rooms, while humanoid robots may assist in nursing in hospital wards.
In the field of home services, there are currently simple home robots like Amazon’s Astro providing services such as patrolling and music playback, while delivery robots and educational companion robots are gradually becoming popular. With the improvement of large model brains, robotic hands, and mobility capabilities, domestic robots will be able to perform more tasks; with large-scale production and technological breakthroughs, the era of home robots may accelerate, bringing convenient and comfortable intelligent living to families.
In the field of warehousing logistics, the prosperity of e-commerce has driven the demand for automation in warehousing sorting, giving rise to a batch of general robots that can move freely in warehouses and perform handling tasks. The warehousing logistics environment is relatively controllable, and its application value is direct, making it a stronghold for the large-scale implementation of general robots. In the coming years, more logistics centers will introduce embodied robots to address peak e-commerce demands and labor shortages, achieving full-chain logistics automation, with humans taking on more monitoring and management roles.
1.3. The technology of industrial robots is maturing, and mass production of humanoid robots is expected to drive the upstream components.
The core components of humanoid robots mainly include motors, sensors, reducers, and screws. The upstream of the humanoid robot industry chain mainly consists of core components such as motors and reducers, as well as other components like cameras and bearings; the midstream involves the manufacturing of humanoid robot bodies, including major modules, built-in algorithm models and systems, and main components; the downstream includes system integration, product sales, and maintenance. The core components and key modules in the industry chain form the rotating joints, linear joints, dexterous hands, perception systems, and torso of humanoid robots. Taking Tesla’s Optimus Gen2 as an example, based on the production cost structure of components and the quantities used, the cost structure of mass-produced humanoid robots can be estimated, where the costs of motors, sensors, reducers, gears, and screws account for a significant proportion and are also the key core components of robots.
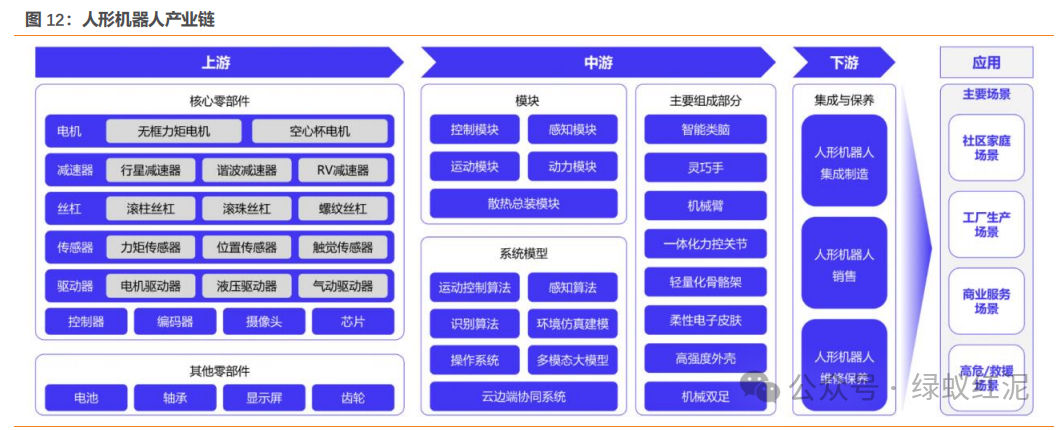
2. Electronic Skin: The Tactile Revolution of Humanoid Robots
2.1. The demand for natural interaction with smart devices is continuously growing, accelerating breakthroughs in the sensor field.
Electronic skin is an array-type flexible tactile sensor, made from flexible materials such as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), with sensitive materials like carbon nanotubes, graphene, and conductive polymers, fabricated using micro-nano processing technology. Electronic skin can be compared to the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue of human skin, divided into upper layers including flexible substrates (lightweight elastic materials like PI, PET) and protective packaging layers (waterproof and dustproof materials), a middle layer for the sensor layer that detects pressure, temperature, humidity, and chemicals for agile response, and a lower layer consisting of interface communication systems, circuits, and processors that transmit the data collected by the electronic skin back to the robot’s brain.
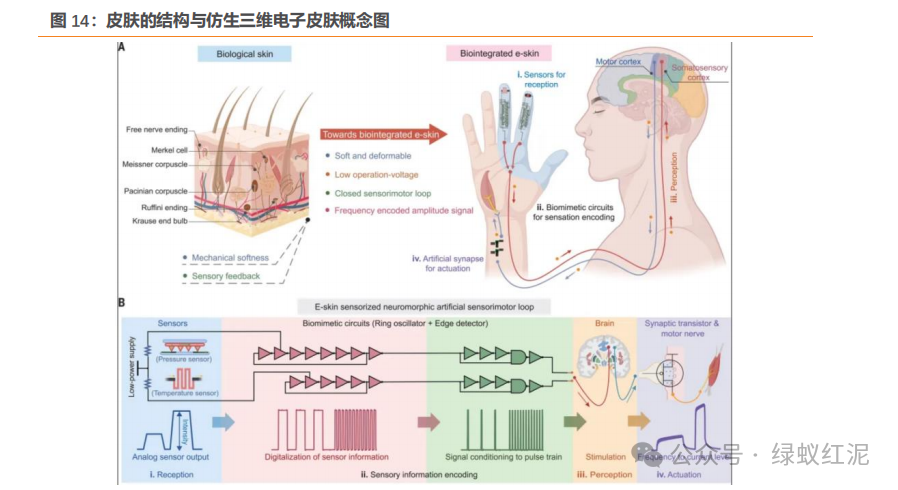
Currently, there are many technical breakthroughs and barriers in electronic skin technology. In terms of materials, it is necessary to achieve multi-modal perception such as pressure and temperature while also possessing flexibility, extensibility, and self-repair capabilities. The folding lifespan and biocompatibility of existing materials do not yet meet the demands for industrialization and large-scale production, necessitating breakthroughs in new composite materials.
In terms of manufacturing processes, flexible electronic devices need to maintain functional stability under tensile deformation, which requires high standards for both materials and processes, and also needs to address the challenges of dense electronic components facing external electromagnetic shielding. Achieving low-cost, high-efficiency large-scale production poses even higher challenges for process optimization.
In terms of the sensor layer, flexible tactile sensors play a crucial role in ensuring safe interaction and intelligent control between the robot’s dexterous hands and humans and the environment. Currently, there are five mainstream technical routes, including resistive, capacitive, piezoelectric, optical, and Hall effect types. Each route has its own barriers and advantages, and the industry has not yet formed a convergence at the technical route level.

3. Intelligent Communication and Computing Modules: The Core Driving Force for the Intelligence and Networking of the Robot Industry
3.1. Intelligent Module Innovation: The Integration of AI and Computing Power Drives Leapfrog Development in the Robot Industry
Communication modules are integrated circuit modules used to achieve data transmission between devices, typically embedded in various communication devices, responsible for receiving and sending signals, allowing devices to exchange data over 4G, 5G, WiFi, BLE, or other communication networks. As robots gradually enter the commercialization phase in various sub-fields such as industrial, medical, and service, wireless communication modules, as key components, will further expand the market. In March 2025, the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Economy and Information Technology publicly solicited opinions on the “Beijing 5G Large-Scale Application ‘Sailing’ Action Upgrade Plan (2025-2027) (Draft for Comments),” which mentioned pre-installing 5G modules for humanoid robots to enhance their collaborative adaptation capabilities with the industrial internet.
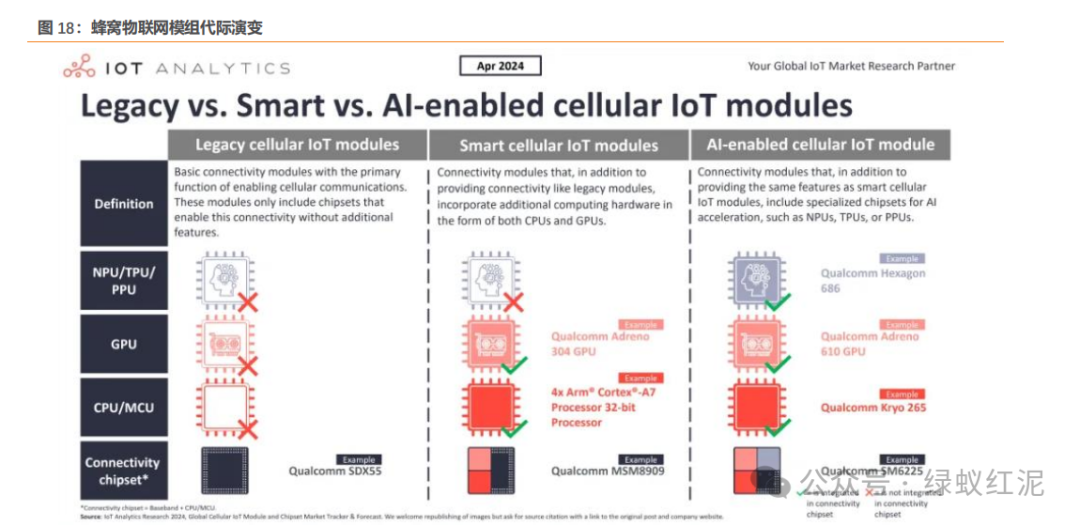
3.1.1. Quectel: High-Performance Intelligent Modules Drive AIoT Innovation and a New Era of Embodied Intelligent Interaction
High-performance intelligent modules drive AIoT industry innovation. Quectel has increased its investment in the computing module field since 2023, and has released high-performance edge computing intelligent modules SG885G, SG865W, SG368Z, which support both 5G and high-performance computing, as well as 5G intelligent modules SG560D, SG530C. Additionally, Quectel officially launched the QuecPi Alpha intelligent ecological development board for the global market at MWC 2025. This development board is built on the Leapdragon™ QCS6490 processor, compatible with various open-source operating systems, featuring high performance, rich multimedia capabilities, high integration, diverse interfaces, low power consumption, wide applicability, and low development costs, making it suitable for edge computing, robotics, industrial control, multimedia terminals, digital billboards, smart security, and industrial-grade PDAs, covering various industries in the AIoT field.
Edge large model solutions reshape embodied intelligent interaction experiences. Quectel’s edge large model solution is based on the high-performance AI intelligent module SG885G-WF, equipped with the Qualcomm QCS8550 platform, providing a comprehensive computing power of up to 48 TOPS, supporting mainstream large models in the industry such as Tongyi Qianwen and DeepSeek; in the field of voice interaction, it achieves seamless connection and efficient operation of the entire voice link, covering mainstream functions such as KWS voice wake-up, VAD voice detection, ASR voice recognition, and TTS voice broadcasting, helping users quickly achieve voice-based seamless interaction. With the support of this solution, embodied intelligent robots can achieve intention recognition within 1 second, with a decoding rate exceeding 15 tokens/s (the normal human speech rate is about 10 tokens/s), providing users with a more natural voice interaction and a more personalized service experience. Additionally, thanks to the high computing power of SG885G-WF, Quectel’s “large model + AI robot” solution can provide complete AI performance even in offline mode. This solution has already been implemented in various scenarios such as medical care, industrial manufacturing, intelligent customer service, reception guidance, and retail.

3.1.2. Gree: Launching the Full-Stack “Nebula” Series Modules to Empower Diverse Development in the Robot Industry

3.1.3. Meige Intelligent: Leading High-Performance AI Modules, Driving the Development of Embodied Intelligent Robots

3.2. Industrial Communication + Robots: Neural Networks and Motion Control, Autonomous Protocols Open New Spaces for Communication Chips
EtherCAT global node deployment is growing against the trend. EtherCAT is a high-performance industrial network system based on Ethernet but faster and more efficient. According to the latest data released by the EtherCAT Technology Group (ETG) on April 3, 2025, the number of globally deployed EtherCAT nodes has exceeded 88 million, with an increase of 11 million nodes in 2024, a year-on-year growth rate of 14.3%. This growth has occurred despite a decline in chip sales due to semiconductor inventory backlogs and increasing geopolitical risks.
From “communication protocol” to “industrial nervous system”, EtherCAT has the following technical advantages: 1) Speed. This is the primary reason EtherCAT has become the preferred protocol for motion control applications, capable of transmitting data at ultra-high speeds with cycle times as low as 12.5 microseconds, allowing users to enjoy fast and precise control of system movements. 2) High efficiency and low cost. EtherCAT adopts a “daisy chain” topology, making it a highly efficient protocol. This topology reduces the required wiring, simplifying the entire communication network. 3) Real-time capability. The EtherCAT communication protocol provides deterministic and reliable communication, demonstrating better device synchronization capabilities with sub-microsecond accuracy. 4) Flexibility. EtherCAT supports different network topologies and data transmission modes, making it easier to integrate into various types of motion control systems.
In the field of motion control, EtherCAT is becoming the core communication protocol for humanoid robots. Among various communication bus technologies, EtherCAT stands out with its excellent performance advantages, becoming an important communication solution in the field of humanoid robots. The clock synchronization of the EtherCAT bus can achieve nanosecond-level precision, enabling control of each joint’s position, speed, and torque, ensuring that robots can quickly and accurately execute decisions and achieve coordinated movement of all joints. The four major global robot manufacturers have adopted EtherCAT bus communication.
3.2.1. Chuangyao Technology: EtherCAT Chips and RISC-V Architecture Collaborate to Empower a New Ecological System for Embodied Intelligence in Industry
Chuangyao Technology focuses on the research, design, and sales of core communication chips, providing application solutions and technical support. It is one of the few integrated circuit design companies in China with both physical layer core communication algorithms and full-process design capabilities for large SoC chips. The company is a supplier of broadband access network communication core chips and power line carrier communication chips, gradually expanding into the new generation of short-range wireless and industrial interconnection fields.
Chuangyao Technology’s EtherCAT slave control chips have achieved small batch shipments. Chuangyao Technology has established cooperative relationships with customers by obtaining authorization from Beckhoff, using EtherCAT slave chips as a starting point. The chips are mainly used for industrial robot servo motor drives and distributed I/O modules, featuring low latency and nanosecond-level precise synchronization, with a very flexible topology.

4. Intelligent Controllers: The “Little Brain” of Robots, Empowering Motion Planning, Command Transmission, and Data Processing in Humanoid Robots
4.1. As a core component of robots, the intelligent controller market is continuously growing.
Intelligent controllers are control units in electronic products, devices, and systems, controlling them to complete specific functions. Based on automatic control theory, intelligent controllers integrate various technologies such as automatic control, microelectronics, power electronics, sensing, and communication, merging program control, information detection, resource scheduling, and output execution to enhance the intelligence level of terminal products. Intelligent controllers are widely used in home appliances, automotive electronics, power tools, industrial control, information communication, medical health, and new energy fields.
AI technology and humanoid robot applications are accelerating development, and the intelligent controller market is poised for broad prospects. With the accelerated iteration of AI technology and the continuous expansion of application scenarios for humanoid robots, controllers, as an important part of the humanoid robot industry chain, will see broader development space. According to Frost & Sullivan’s forecast, the global intelligent controller market size is expected to grow from $1,227.5 billion in 2015 to $1,959.9 billion in 2024, with a compound growth rate of 5%, while China’s intelligent controller market size is expected to grow from 1,169.5 billion yuan to 3,806.1 billion yuan, with a compound growth rate of 14%, indicating that the market boundaries for intelligent controllers may continue to expand.
Specifically, intelligent controllers empower humanoid robots in the following three aspects: 1) Motion planning and control. Controllers can plan and control the robot’s movements, achieving mutual conversion between the robot’s operational spatial coordinates and joint space coordinates, completing high-speed servo interpolation calculations and servo motion control to ensure the precision and response speed of robot movements. 2) Action command issuance and transmission. As the center for issuing and transmitting robot action commands, controllers can convey the operator’s instructions to the robot and ensure that the robot performs corresponding actions according to the instructions. 3) Data processing and transmission. Controllers can process and transmit data from components such as sensors, reducing the deviation between the actual movement trajectory of the robot and the expected target, ensuring the movement accuracy of the robot.
4.2. Progress of Related Enterprises
4.2.1. Topband Co., Ltd.: Driving Humanoid Robots and Multi-Field Intelligent Control Solutions with Innovative Hollow Cup Motor Technology
Topband Co., Ltd. was established in 1996 and is a global leader in intelligent control solutions. The company mainly engages in the research, production, and sales of intelligent controllers, with products primarily applied in home appliances, power tools, garden tools, switch power supplies, personal care, automotive electronics, industrial control, and gas control, possessing a large operational scale and strong comprehensive capabilities. Major clients include Midea, Supor, TCL, Joyoung, Pentium, Whirlpool, Haier, Rongshida, and Little Swan. The company’s core competitiveness lies in its platform-based technological innovation capabilities, partner-based customer service capabilities, and systematic rapid response capabilities, providing leading customized solutions for tools and home appliances, digital energy, and intelligent vehicles, as well as robots.
4.2.2. Heertai: Innovating Touch-Sensitive Human Interface Technology, Leading Tactile Interaction Solutions
Heertai was established in 2000 and is a supplier of intelligent controller solutions, with its main business involving the research, production, sales, and intelligent product platform services of intelligent controllers and terminal solutions in fields such as home appliances, power tools, automotive electronics, and intelligent products. The company adheres to a business positioning of “three highs” (high-end technology, high-end products, high-end markets) and a customer-centric service philosophy, continuously exploring new markets and customers. Major clients include Electrolux, Whirlpool, Xiaomi, Haier Smart Home, Volvo, BYD, NIO, and Xpeng. At the same time, the company acquired Chengchang Technology to enter the phased array T/R chip market; invested in Beijing Yuanluo Technology to further expand its layout in humanoid robots, artificial intelligence, and large models, actively exploring cooperation opportunities with the company based on the planning and needs of the humanoid robot field.
5. Inertial Navigation Measurement Units: The Core Driving Force for Efficient Autonomous Movement in Humanoid Robots
5.1. Inertial Navigation: Autonomous Positioning and High-Precision Perception Drive the Advancement of Humanoid Robots
Inertial navigation systems and their core components, inertial measurement units, achieve three-dimensional spatial positioning through autonomous measurement. Inertial navigation systems (INS) are autonomous navigation systems that use inertial sensors, reference directions, and initial position information to determine the position, direction, and speed of a carrier in inertial space. The IMU (inertial measurement unit) is the core sensor for attitude measurement and inertial navigation technology, generally composed of two or more accelerometers and gyroscopes, capable of measuring the angular velocity and acceleration of an object in three-dimensional space. Through error compensation and inertial navigation calculations, the IMU can ultimately output important navigation information such as the coordinate changes and speed of the carrier relative to the initial position. Inertial navigation can be divided into platform-based inertial navigation systems and strapdown inertial navigation systems based on whether there is a physical platform. Strapdown systems have advantages such as compact structure, high reliability, lightweight, small size, low power consumption, easy maintenance, and low cost, making them the mainstream technology for civilian inertial navigation.
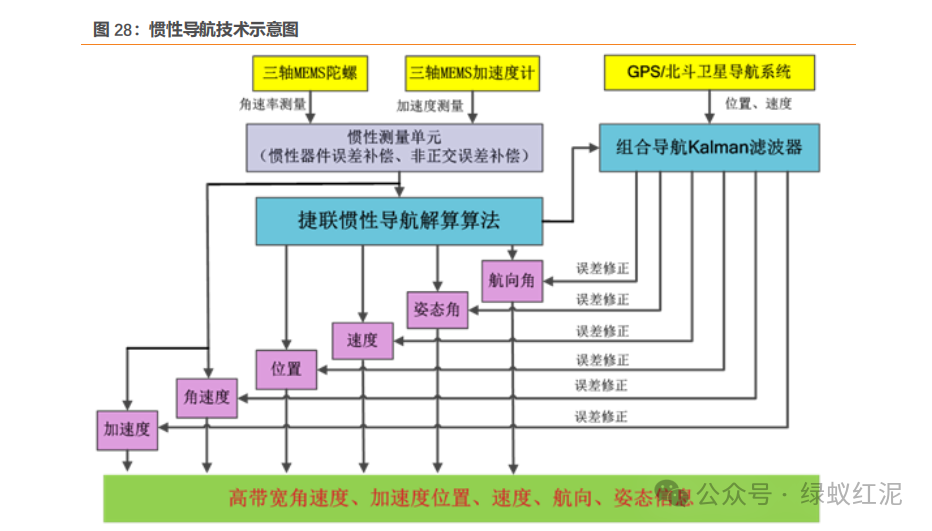
5.2. Huace Navigation: Leading Inertial Navigation Technology, Building an Intelligent World with Precise Spatial Information
Huace Navigation was established in 2003, focusing on the research, manufacturing, integration, and industrial application of core technologies and products related to high-precision navigation and positioning. It is one of the leading enterprises in China’s high-precision satellite navigation and positioning industry. The company has built two core technological moats: a high-precision positioning chip technology platform and a global star-ground integrated enhancement network service platform, possessing complete algorithmic capabilities in high-precision GNSS, three-dimensional point cloud and aerial surveying, GNSS signal processing and chipization, and autonomous driving perception and decision control. Its products are mainly applied in four major sectors: resources and public utilities, construction and infrastructure, geographic spatial information, and robotics and autonomous driving.
6. Operating Systems: The Nervous Network of the Machine World
6.1. Industrial Operating Systems: Real-Time Embedded Architectures Empowering Embodied Intelligence, Breaking the Technical Monopoly of Domestic Alliances
Based on real-time, embedded, and general architectures, providing standardized support for core links of embodied intelligence. As the “brain” of intelligent devices, operating systems are the first layer of software covering hardware, used to manage and schedule computer hardware and software resources. Industrial operating systems are the general data foundation and unified technical ecological environment for industrial internet platforms, big data platforms, and artificial intelligence platforms, growing from automation technology. Operating systems in the field of embodied intelligence can provide strong support for core links such as embodied perception, embodied planning, and embodied execution, promoting the formation of unified factual standards at the level of components and communication protocols, accelerating the integration and development of the industry.
Establishing the “Industrial Operating System Alliance” to promote domestic substitution of key technologies. As a core key technology, industrial operating systems have long been dominated by foreign products. In January 2024, seven departments, including the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, released implementation opinions on promoting future industrial innovation and development, pointing out the need to develop the next generation of operating systems and build a secure and reliable digital foundation. At the 2024 National Industrial Software Conference, the National Intelligent Control Technology Innovation Center, the National Intelligent Design and CNC Technology Innovation Center, and the National Key Laboratory of Industrial Control Technology, along with 26 research institutes and enterprises, jointly initiated the establishment of the “Industrial Intelligent Operating System Alliance.” The establishment of the alliance will gather core forces from upstream and downstream enterprises in the industry chain, accelerating breakthroughs in key technologies and enhancing the core competitiveness of China’s industrial sector.
6.2. Dongtu Technology: Building a Self-Controlled Industrial Operating System, Exploring New Boundaries in Industrial Technology
7. Military Informationization: AI Unmanned Technology Driving National Defense Upgrades
7.1. Unmanned Operations: AI Technology Empowering Land, Sea, and Air Coordination
7.2. Haige Communication: Leading Full-Frequency Communication and Beidou Navigation, Creating a New Benchmark for National Defense with Unmanned Systems
Haige Communication was established in 2000 and is the first stock of China’s military industry to go public. The company’s business mainly covers four fields: “wireless communication, Beidou navigation, aerospace, and intelligent ecology,” and it is a leading enterprise in the development of wireless communication with full-frequency coverage and the entire industrial chain layout of Beidou navigation equipment. In the trend of intelligence and unmanned systems, the company is strategically laying out unmanned systems and humanoid robots from the perspective of industrial chain construction and positioning, possessing first-mover and core technological advantages in the industry. Its main products include aerial unmanned platforms (drones), ground unmanned platforms (unmanned vehicles, robots), bionic platforms, interactive terminals, and core components.
8. Other Embodied Intelligence Fields
8.1. Xiechuang Data: Full-Stack Intelligence + Heterogeneous Computing Power, Accelerating the Layout of AI Hardware and Embodied Intelligence
Using technological innovation and computing power services as engines to continuously promote the upgrade of the intelligent IoT industry. Xiechuang Data was established in November 2005, based on a development strategy oriented towards AI demand, continuously advancing five major business lines: smart storage, intelligent IoT, cloud services, computing servers, and server remanufacturing, gradually building a three-in-one industrial model of “intelligent terminals + computing infrastructure + cloud services.” The company has a strong shareholder background, with the actual controller Geng Kangming having long served at Foxconn (now Industrial Fulian), deeply involved in building the consumer electronics manufacturing system, possessing rich supply chain management and large-scale production experience. The second-largest shareholder, PCL, is indirectly controlled by the publicly listed company Qianwei Precision Industry Co., Ltd. in Taiwan, which has a deep industrial background and can provide resources and support for the company’s business development.
Building an IoT cloud platform to empower multi-scenario applications. Xiechuang Data continues to build its own IoT cloud system and cloud platform, expanding its business from intelligent terminal production to technical services in edge computing and cloud services, successfully covering rich application scenarios such as smart home and wearable devices, intelligent security terminals, VSaaS video cloud services, intelligent cloud IoT integrated machines, coffee machines, and its own IoT cloud system, achieving strong integrated service capabilities.
9. Conclusion
The robot industry has broad prospects, and the value of upstream component enterprises is becoming prominent. Robot technology is experiencing leapfrog development, with industrial, service, special, and humanoid robots accelerating their penetration into all scenarios of production and life. In B-end applications, industrial robots are driving the upgrade of intelligent manufacturing, service robots are empowering vertical fields such as medical care, logistics, and security, and special robots are assisting in operations in extreme environments. The C-end market focuses on family services, health monitoring, educational companionship, and other needs, with humanoid robots opening new spaces for emotional interaction and complex task execution through their versatility. Under the catalysis of factors such as technological innovation (breakthroughs in AI large models, core components, and embodied intelligent algorithms), policy support (various policy supports and funding from all levels of government), market demand expansion (the aging population and rising labor costs leading to surging demand for elderly care and medical assistance), and capital promotion (high enthusiasm in the capital market and increased investments from technology giants), 2025 is expected to become a key node for the commercialization of robots, transitioning the industry from technology validation to large-scale implementation.
Upstream core component enterprises are the core driving force of the industry chain. The performance and cost of core components of humanoid robots, such as motors, reducers, electronic skin, communication modules, intelligent controllers, and inertial navigation units, directly determine the competitiveness and popularization speed of robot products. Currently, the iteration of benchmark products like Tesla’s Optimus and UBTECH’s Walker has validated the strategic value of upstream components. In the future, as the scenarios for robots diversify and demand grows rapidly, upstream enterprises will benefit first from order growth and technological premiums. It is recommended to focus on component suppliers with technological barriers, mass production capabilities, and customer stickiness to seize the dividends of the “Robot+” era.