1. Overall Course Introduction
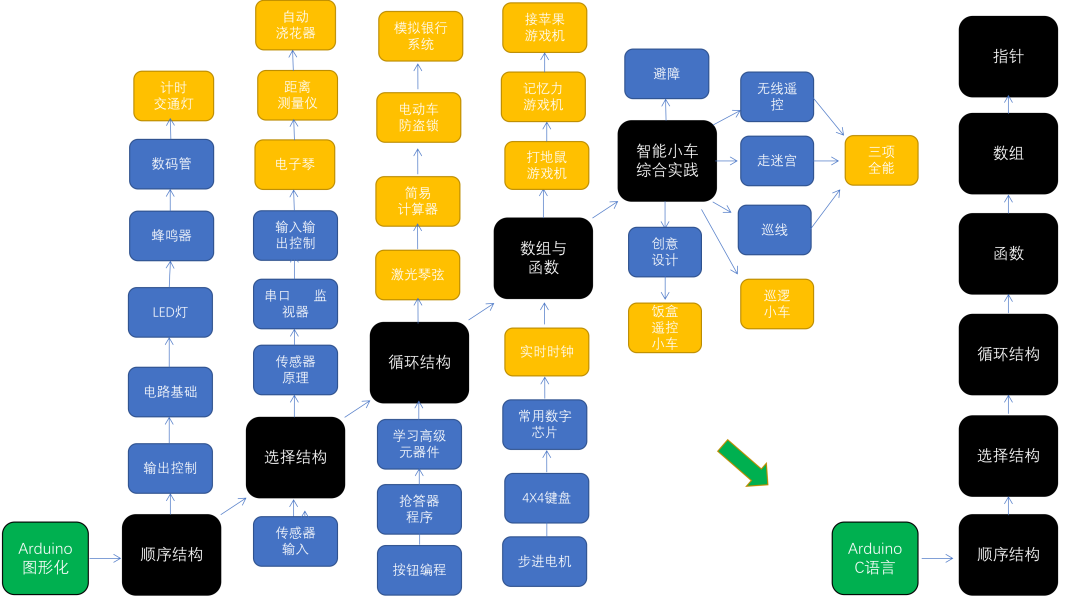
Knowledge Framework
Applicable Age:Suitable for children in the fourth grade and above; for third graders, learning should be adjusted based on the child’s ability.
Course Design Philosophy:
1. The entire course is centered around programming design concepts, emphasizing hardware fundamentals and programming thinking.
2. Periodic practical projects can enhance children’s sense of achievement and increase the fun of the course.
Course Content Arrangement:
1. The black parts in the knowledge framework represent the main knowledge, the blue parts represent branches, and the yellow parts represent fruits (project outcomes). The core content focuses on programming design, starting with graphical programming, and the last 15 classes will concentrate on C language coding. Based on the main programming concepts, hardware learning will begin with basic output components, then move to sensors, and finally to advanced components such as dot matrix screens, displays, 4×4 keypads, stepper motors, and common digital chips: decoders, latches, shift registers, and clock chips. The last part of the graphical course includes comprehensive practice with smart cars, allowing children to consolidate previously learned hardware and programming skills. Additionally, controlling robots to perform tasks can enhance children’s debugging and problem-solving abilities.
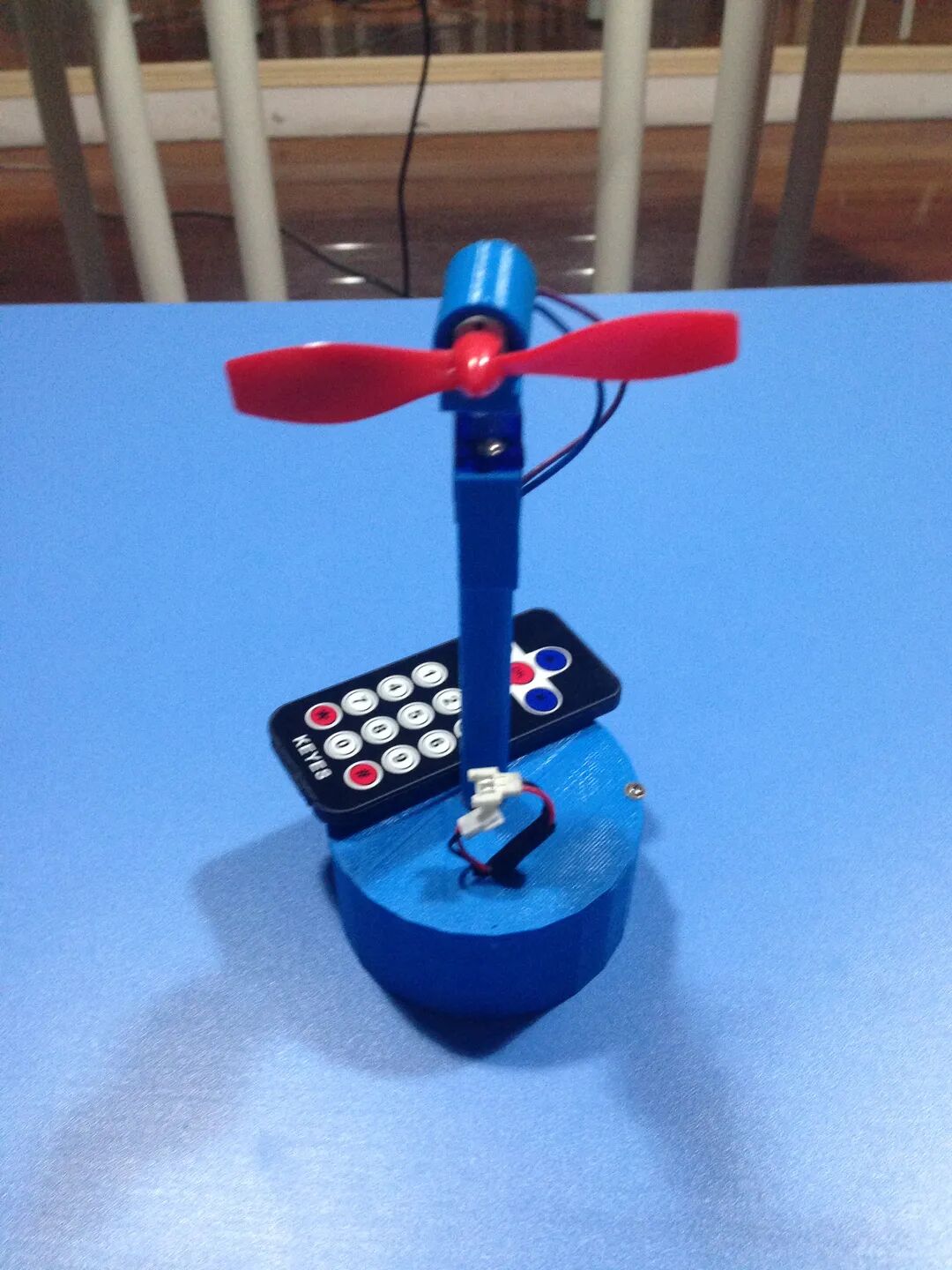
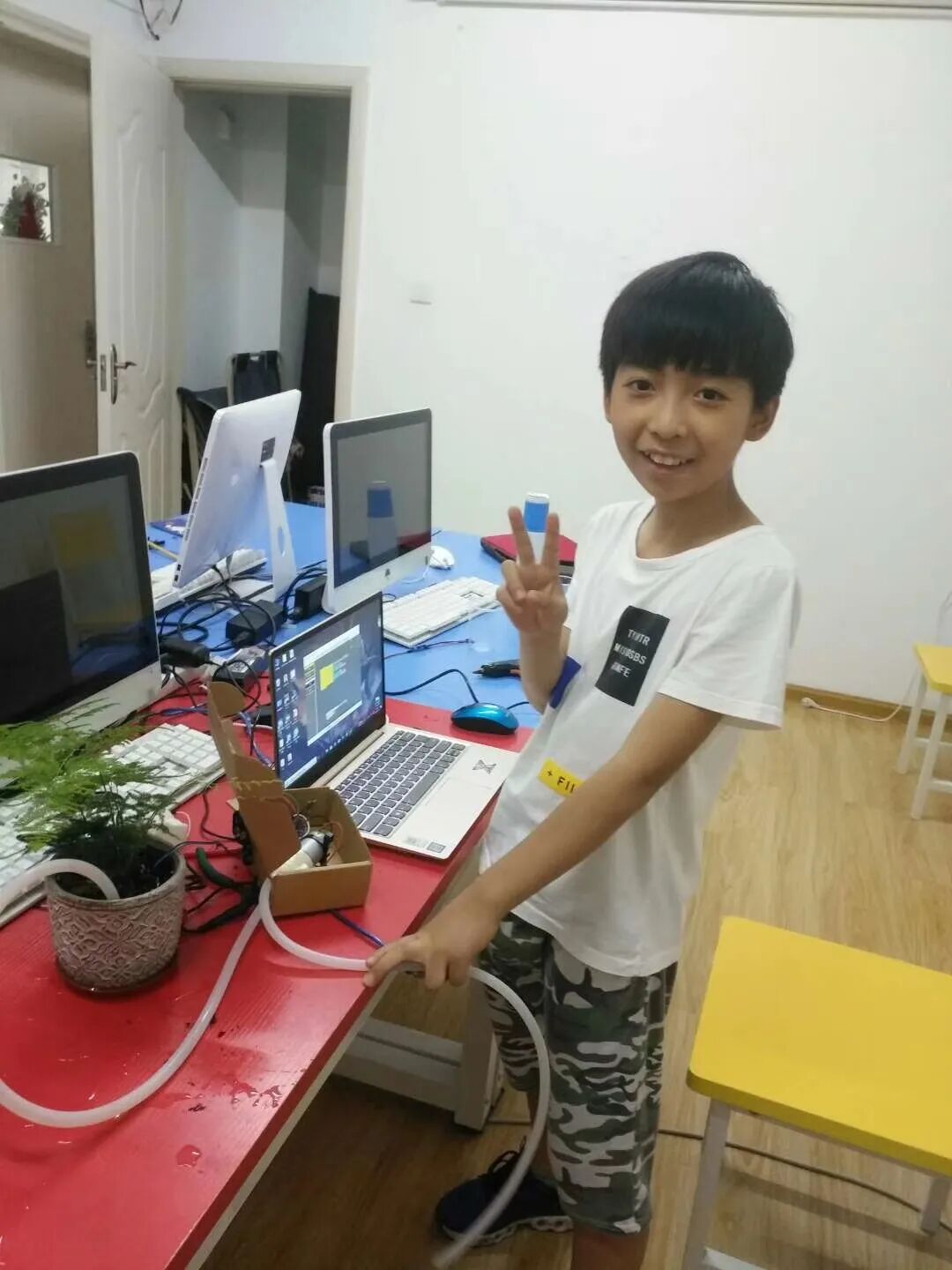


2. Projects included in the course: countdown traffic light, digital dice, electronic piano, remote-controlled oscillating fan, automatic speed fan, welcoming robot, distance measuring instrument, piggy bank, automatic watering device, laser string instrument, electric vehicle anti-theft device, simulated banking system, whack-a-mole game machine, memory game machine, apple-picking game machine, real-time clock, etc. The comprehensive practice tasks for the smart car include: obstacle avoidance, remote control, maze navigation, fall prevention, line following, patrolling, and creative design.
Class Planning:A total of 80 classes, offline teaching can be planned for two years.
The following link is our video tutorial, for reference only.

Listen
To
The
 2. Complete Course Directory
2. Complete Course Directory 3. Course Objectives for Each Lesson
3. Course Objectives for Each Lesson
|
Serial Number |
Course Name |
Course Objectives |
|
1 |
Light Up LED |
1. Understand Arduino 2. Basic knowledge of circuits 3. Build a circuit to light up an LED |
|
2 |
Blinking LED |
1. Principle of LED blinking 2. Write a program to blink the LED 3. SOS signal light |
|
3 |
Flowing Lights |
1. Master the wiring and layout of flowing lights 2. Master the programming method for flowing lights |
|
4 |
Buzzer |
1. Basic knowledge of sound 2. Understand active and passive buzzers 3. Programming control methods for buzzers |
|
5 |
Air Raid Siren |
1. Learn the for loop program structure 2. Understand the role of variables in programs |
|
6 |
Music Master |
1. Basic knowledge of music notation 2. Programming to control the buzzer to play music 3. Understand the concept of subroutines |
|
7 |
Digital Tube |
1. Internal principles of digital tubes. 2. Distinguish between common cathode and common anode digital tubes. 3. Wiring and programming methods for digital tubes. 4. Control the digital tube to dynamically display from 0 to 9 |
|
8 |
Countdown Traffic Light |
1. Understand the delay program module 2. Encapsulation of subroutines |
|
9 |
Light-Controlled LED |
1. Understand the function and role of sensors 2. Learn to program to process external signal input 3. Complete the experiment with light-controlled LED |
|
10 |
Serial Monitor (Part 1) |
1. Understand serial ports and serial monitors 2. Working principle of serial monitors 3. Use the serial monitor to test sensor values |
|
11 |
Serial Monitor (Part 2) |
1. Send signals via serial port to control Arduino output 2. Understand the characteristics of Arduino output latching |
|
12 |
Breathing Light |
1. Input and output of signals 2. Difference between digital and analog signals. 3. Complete the breathing light using PWM output. |
|
13 |
Circuit Basics |
1. Composition of circuits, understanding circuit schematics 2. Circuit states: closed circuit, open circuit, short circuit 3. Circuit connection forms: series and parallel circuits |
|
14 |
Button Sensor |
1. Principle of button circuit connection and disconnection. 2. Internal circuit principles of button sensors 3. Implement button control of LED lights |
|
15 |
Digital Dice |
1. Functional analysis of dice 2. Write a program for electronic dice 3. Summarize the thought process for creating the project |
|
16 |
Electronic Piano |
1. Analyze the functions of the electronic piano 2. Programming design ideas for the electronic piano 3. Difference between multiple “if” and “if-else” statements |
|
17 |
Potentiometer Principle |
1. Applications of potentiometers in life 2. Adjusting the brightness of LED lights with potentiometers 3. Using potentiometers as sensors |
|
18 |
RGB Color Light |
1. Principle of the three primary colors of light 2. Test the common terminal of RGB color lights 3. Control the color of the light emitted by the RGB light |
|
19 |
Crazy Motor |
1. Basic principles of motors 2. Control the speed and direction of the motor 3. Create a potentiometer-controlled fan |
|
20 |
Infrared Remote Control |
1. Applications of infrared remote control in life. 2. Test the key values of the infrared remote control. 3. Create fans with various switching methods. |
|
21 |
Remote-Controlled Oscillating Fan |
1. Basic principles of servo motors 2. Wiring and programming of servo motors 3. Program design for remote-controlled oscillating fans |
|
22 |
Creative Fan |
1. Principle of ultrasonic sensor distance measurement 2. Wiring and programming of ultrasonic sensors. 3. Ultrasonic automatic speed fan. |
|
23 |
Welcoming Robot |
1. Control servo motors with ultrasonic sensors 2. Create a “Big White Welcoming Robot” |
|
24 |
Four-Digit Digital Tube Principle |
1. Internal composition of four-digit digital tubes 2. Principles of dynamic display for digital tubes 3. Wiring and programming for four-digit digital tubes |
|
25 |
Distance Measuring Instrument |
1. Application of four-digit digital tube modules 2. Learn to extract the various weights of a number 3. Create a distance measuring instrument |
|
26 |
Coin Counter |
1. How to use counting sensors 2. Design the program for the coin counting box 3. Learn to use EEPROM in programs |
|
27 |
LED Dot Matrix Indicator |
1. Applications of LED dot matrices in life 2. Internal structure and principles of LED dot matrices 3. Control LED dot matrices to display various patterns |
|
28 |
Rock-Paper-Scissors Game Machine |
1. Use LED dot matrices to draw patterns 2. Use LED dot matrices to display animations 3. Design the rock-paper-scissors game machine |
|
29 |
Automatic Watering Machine |
1. Working principle of relays 2. Build a relay output circuit 3. Create an automatic watering device |
|
30 |
Laser String Instrument |
1. Learn to make a light sensor 2. Difference between “if” modules and “when” loop modules 3. Create a laser harp |
|
31 |
Smart Button (Part 1) |
1. Wiring and programming of buttons 2. Program design with variables as “intermediaries” 3. Design the “Smart Button” program |
|
32 |
Smart Button (Part 2) |
1. Design the program for multi-level buttons 2. Specific execution process of the smart button program 3. Learn to detect if the button is released |
|
33 |
Quiz Buzzer |
1. Application scenarios for quiz buzzers 2. Write the basic program for the quiz buzzer 3. Use “when loop” to control program execution |
|
34 |
Remote-Controlled Oscillating Fan (Advanced) |
1. Three types of loops in programs 2. Design a counting loop with while loops 3. Exiting loop programs 4. Advanced version of infrared remote-controlled oscillating fan |
|
35 |
Electric Vehicle Anti-Theft Device |
1. Functions of the electric vehicle anti-theft device 2. Learn to use a four-channel wireless remote control kit. 3. Design the anti-theft device using two different programs |
|
36 |
Timer Stopwatch |
1. Real-time display of variables on digital tubes 2. Program for the smart button 3. Create loops and exit loops |
|
37 |
Digital Tube Clock |
1. Real-time display of variables on digital tubes 2. Usage of variable classification tags |
|
38 |
Guess the Number Game Machine |
1. Use digital tubes for input display 2. Multiple “if” judgment programs 3. Determine if the button is long-pressed and if it times out |
|
39 |
Simple Calculator |
1. Use digital tubes for input display 2. Multiple “if” judgment programs 3. Learn to debug and improve program bugs |
|
40 |
1602 LCD Display |
1. LCDs and their working principles 2. Differences between parallel and serial communication 3. Wiring and programming of LCD1602 |
|
41 |
Simulated Banking System |
1. How to use the LCD1602 display 2. Learn to use programs to solve practical problems |
|
42 |
Whack-a-Mole Game Machine (Part 1) |
1. Familiarize with the use of Mixly software 2. Use of multiple choice structures and when loop structures 3. Use of OLED displays |
|
43 |
Whack-a-Mole Game Machine (Part 2) |
1. Basic concept of interrupts 2. Use timer interrupts to solve problems 3. Design variables in programs based on project requirements |
|
44 |
Breathing Flowing Light |
1. Working process of breathing flowing lights 2. Write the program for breathing flowing lights 3. Use arrays to store data |
|
45 |
Memory Game Machine |
1. Learn to define variables based on project requirements 2. Learn to use arrays to solve program problems 3. Further practice for loops on arrays |
|
46 |
Electronic Password Lock |
1. Review the digital tube display program 2. Complete password input with digital tubes and buttons 3. Further practice storing and retrieving array data |
|
47 |
Bean Game Machine |
1. Use of 8*8 dot matrix screens 2. Storing and retrieving array data 3. Use of timer interrupt programs |
|
48 |
Detailed Explanation of Program Functions |
1. Program functions and their roles 2. Four types of program functions 3. Write functions to simplify programs |
|
49 |
Matrix Keyboard Usage |
1. Principles of 4*4 matrix keyboards 2. Use scanning methods to detect matrix keyboards 3. Use line inversion methods to detect matrix keyboards |
|
50 |
Control of Stepper Motors |
1. Principles and applications of stepper motors 2. Wiring and programming control of stepper motors 3. Control stepper motors with different excitation methods |
|
51 |
Decoder Chip 74HC138 |
1. Master binary addition and subtraction 2. Learn about the 74HC138 decoder 3. Principles of cascading two decoder chips |
|
52 |
Shift Register Chip 74HC595 |
1. Functions and pin wiring of the 74HC595 chip 2. Principles of serial input and output of data in the 595 chip |
|
53 |
Latch Chip 74HC573 |
1. Functions and pin wiring of the 74HC573 chip 2. Principles of serial input and output of data in the 573 chip 3. Use two chips to achieve pin multiplexing on the main control board |
|
54 |
Clock Chip DS1307 |
1. Functions and pin wiring of the DS130 chip 2. Data units and BCD codes in computers 3. Working process of reading and writing chips via I2C interface |
|
55 |
Assembly of Smart Cars |
1. Complete soldering of motor pin wires and switches 2. Complete assembly of the smart car |
|
56 |
Programming Control of Smart Cars |
1. Transistor switch circuits 2. Working principles of the L298N driver 3. Programming to control the movement of smart cars |
|
57 |
Mobile Remote-Controlled Car |
1. Bluetooth technology and Bluetooth serial modules 2. Understand the Bluetooth communication process 3. Realize mobile remote control of smart cars via Bluetooth serial |
|
58 |
Obstacle Avoidance for Smart Cars |
1. Common solutions for robot obstacle avoidance 2. Control the car to meet different obstacle avoidance needs |
|
59 |
Smart Car Maze Navigation |
1. Common algorithms for maze navigation 2. Write a program for the robot to navigate the maze 3. Learn to debug the car to complete different tasks |
|
60 |
Fall Prevention for Smart Cars |
1. Usage of line-following sensors 2. Implement fall prevention measures for the car |
|
61 |
Line-Following Car (Part 1) |
※※ Single Photoelectric Line-Following Strategy 1. Basic line-following 2. Line-following + off-line protection 3. Line-following + off-line protection + intersection judgment |
|
62 |
Line-Following Car (Part 2) |
※※ Double Photoelectric Line-Following Strategy 1. Basic line-following 2. Line-following + off-line protection 3. Line-following + off-line protection + intersection judgment |
|
63 |
Robot Triathlon |
※※ Triathlon: Remote Control, Maze Navigation, Line Following |
|
64 |
Automatic Patrolling Robot |
1. Function of servo-controlled ultrasonic platforms 2. Control the platform to detect obstacles in multiple directions 3. Design and create multi-directional obstacle-avoiding (patrolling) cars |
|
65 |
Communication Between Bluetooth Devices |
1. Serial communication between Arduino boards 2. Realize wireless communication between Arduinos 3. Create a PS2 joystick wireless remote-controlled car |
|
66 |
Lunch Box Remote-Controlled Robot |
1. Realize wireless communication between Arduinos 2. Understand the circuit working principles of the lunch box remote control 3. Design a lunch box remote control to control the smart car |
|
67 |
Introduction to Arduino Programming |
1. Framework of Arduino code programs 2. Common pin operation commands for Arduino 3. Common serial operation commands for Arduino |
|
68 |
Variables, Constants, Data Types |
1. Knowledge of computer memory and variables 2. Data types and variable types 3. Learn to define constants in programs |
|
69 |
Mathematical, Relational, and Logical Operations |
1. Basic mathematical operations in C language 2. Basic relational operations in C language 3. Basic logical operations in C language |
|
70 |
Conditional Judgments (Part 1) |
1. The three main structures of programs 2. if-else conditional judgment statements 3. Smart button program |
|
71 |
Conditional Judgments (Part 2) |
1. Use else if structure to handle multi-branch programs 2. How to use switch-case |
|
72 |
Practice – Rock-Paper-Scissors Game |
1. if-else judgment statements 2. switch-case statements |
|
73 |
Loops (Part 1) |
1. Loops in programs 2. How to use while loops 3. break and continue statements |
|
74 |
Loops (Part 2) |
1. for loop program structure 2. Nested structures of loops |
|
75 |
Practice – Perpetual Calendar |
※※ Project Function Overview: Users can input any year and month in the serial monitor, and the system will automatically print a calendar for that month, similar to the calendar in the Windows system. |
|
76 |
Functions |
1. Program functions and their roles. 2. Four types of program functions 3. Write functions to simplify programs |
|
77 |
Arrays |
1. Learn to create arrays 2. Access, modify, and traverse array elements 3. Sum, find the maximum value, and sort arrays |
|
78 |
Pointers |
1. Concept of pointers, learn to define pointers 2. Use * to dereference and & to get addresses 3. Use pointers to manipulate variables |
|
79 |
Arrays and Pointers (Part 1) |
1. Meaning of array names representing the starting address of the array 2. Manipulate arrays using pointers 3. Define pointer arrays, access addresses and contents in pointer arrays |
|
80 |
Arrays and Pointers (Part 2) |
1. Manipulate elements in two-dimensional arrays 2. Differences between two-dimensional arrays, pointer arrays, and array pointers 3. Usage and learning methods of Arduino libraries |
Resources included in the entire course::PPT materials, source code files, carefully recorded videos. All resources of this course will be available after course collaboration.
How to collaborate on the course? —>Learn about course collaboration details..
