In industrial communication scenarios, both LoRa and ZigBee wireless communication technologies are widely used. However, during the application process, we often find ourselves confused about the calculation of their communication time. Today, let’s understand how their communication time is calculated together.
 Product Prototype
Product Prototype
GxCOM-NET is an intelligent LoRa | ZigBee data communication box independently developed and designed by ZLG Zhiyuan Electronics, empowering industrial communication applications. It has the following features:
 Introduction to Communication Time Principles
Introduction to Communication Time Principles
Taking the above-mentioned LoRa intelligent communication box GLCOM-NET as an example, here is a simple framework of wireless LoRa communication:
From the above diagram, we can clearly see that the process from data collection to transmission in the air involves four steps: “UART transmission + MCU packaging + SPI transmission + RF transmission”. It is important to note that the protocol also adds ACK time; different rate levels correspond to different ACK times, as detailed in the product documentation. Therefore, to calculate the unidirectional communication time, we only need to calculate the communication time for these four stages separately and then sum them up. Among them, “UART transmission” is related to the serial port baud rate setting; “MCU packaging” depends on the platform and software processing used; “SPI transmission” is very fast, so the time can be ignored; and the “RF transmission” time is related to the transmission rate setting of the RF module.
 Example of Communication Time Calculation
Example of Communication Time Calculation
Assuming we use GLCOM-NET 1 to collect data via serial port and send data to GLCOM-NET 2, which is 200 meters away, with a single data packet size of 50 bytes. The serial port baud rate is set to 115200bps; the transmission rate is set to 48kbps (at this rate level, the ACK time is 16ms); then the time for unidirectional communication to reach the other device is:
-
Serial communication: 50×8÷115200=1/288 (s)
-
MCU packaging: GLCOM-NET time is approximately 10ms (this time varies depending on the specific situation)
-
Air transmission: 50×8÷48000=1/120 (s)
-
Total time: 1/288+1/120+10+16≈37.80556 (ms)
In fact, we also need to add the communication time between devices; however, since wireless transmission between devices is at the speed of light and the distance is only 200 meters, this time can be completely ignored. We just need to understand the principle.
The above is a rough calculation of the communication time for wireless modules. Follow ZLG to learn more knowledge and insights!


 Product Prototype
Product Prototype
 Introduction to Communication Time Principles
Introduction to Communication Time Principles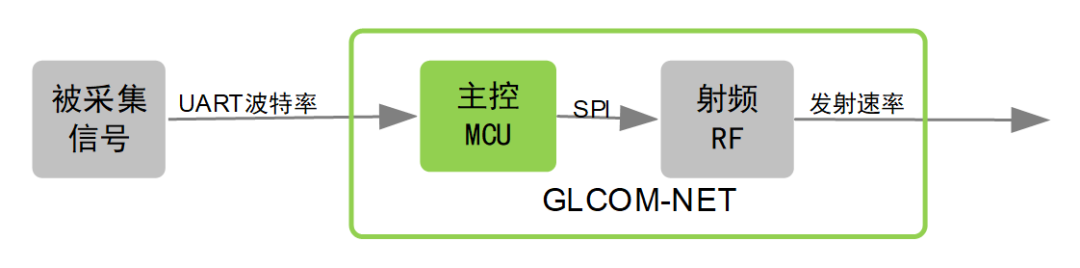
 Example of Communication Time Calculation
Example of Communication Time Calculation






