This article guide
ZigBee technology, as the most commonly used wireless technology in the field of the Internet of Things, is currently widely used in industries such as smart homes, intelligent agricultural management, and energy-saving applications. To facilitate everyone in utilizing ZigBee for project development, today we will share knowledge related to the ZigBee protocol stack and networking.
Figure 1 ZigBee Wireless Network Applications
The ZigBee protocol stack can be divided into four layers: Physical Layer (PHY), Medium Access Control Layer (MAC), Network Layer (NWK), and Application Layer (APL). As shown in Figure 2, the pink part is defined by IEEE standards, the light blue part is specified by the ZigBee Alliance, and the yellow part is defined by device manufacturers.
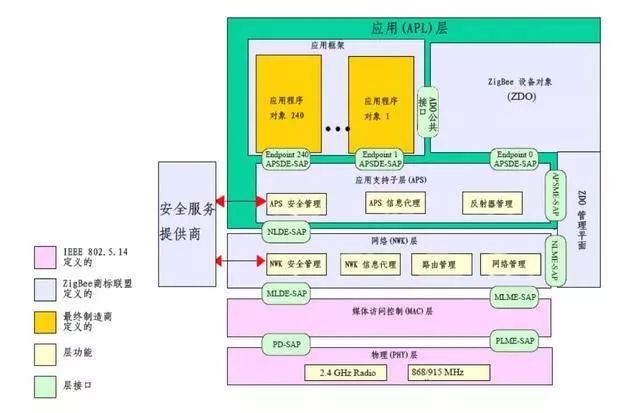
Figure 2 ZigBee Protocol Stack Diagram
The Physical Layer and MAC Layer of the ZigBee protocol stack are defined in the IEEE802.15.4 standard. The PHY layer (Physical Layer) specifies the frequency band used, as well as the encoding, modulation, spread spectrum, frequency modulation, and other wireless transmission technologies employed.
The main function of the MAC layer is to define the access control mechanism for the wireless channel, which specifies how devices take turns using the channel; without a MAC layer protocol, when there are many nodes, the lack of a regulated sending and receiving mechanism will lead to signal conflicts, making normal data transmission impossible.
The ZigBee protocol stack defines the network layer based on the 802.15.4 protocol. The main function of the network layer is to manage device connections and disconnections, the security mechanisms used during frame data transmission, and routing discovery and maintenance. In simple terms, it ensures networking between devices and data transmission between network nodes.
The standard ZigBee network protocol includes coordinators, routers, and terminal nodes. To establish a ZigBee network, in addition to the necessary coordinator, only a router or terminal node needs to be added.
Before starting standard ZigBee Pro network communication, if there is no routing table established to store jump paths, nodes cannot communicate. It is also necessary to periodically send network messages to check if nodes are abnormal. Thus, it can be seen that ZigBee Pro not only has a slow startup speed but also consumes a lot of bandwidth due to the periodic sending of network messages.
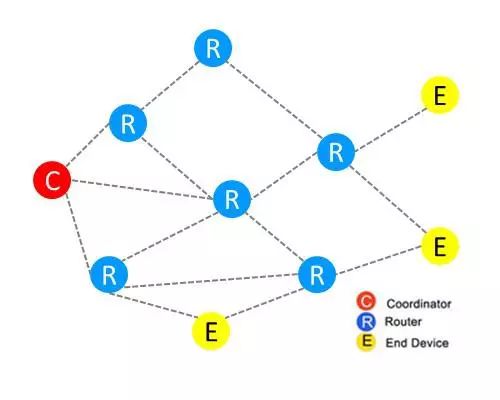
Figure 3 ZigBee Pro Networking Diagram
If any node in the network has peer-to-peer data transmission capabilities and does not require the coordinator to manage the network, then any node in the network can actively transmit data. This way, users do not need to worry about the specific network structure, making it evidently more convenient, and construction personnel do not need to understand related configurations.
Based on this, ZLG Zhiyuan Electronics, leveraging its deep accumulation of wireless technology and rich practical experience, has developed the FastZigBee transparent peer-to-peer network protocol based on the ZigBee protocol stack.
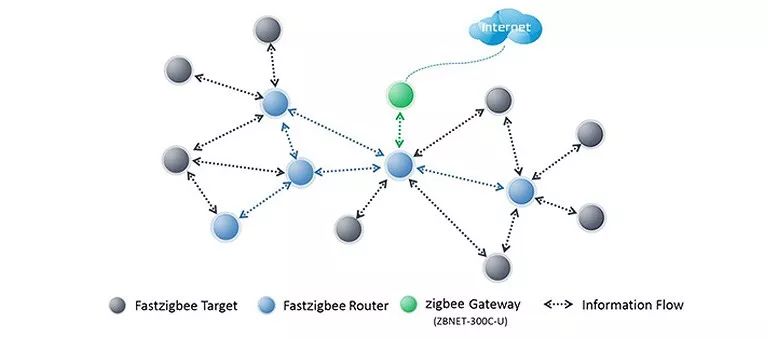
Figure 4 Zhiyuan Electronics FastZigBee Networking Diagram
Its advantages are as follows:
1. Zero delay startup: FastZigBee nodes do not need to wait for networking upon power-up and can directly output based on configuration information, minimizing wake-up startup time and power consumption;
2. Large node capacity: FastZigBee uses a 16-bit short address management method, theoretically allowing for a node capacity of up to 65,535 under the polling mechanism;
3. Completely transparent: FastZigBee employs transparent transmission, allowing users to create private protocol formats at will, without being limited to fixed third-party protocols;
4. No secondary development required: The FastZigBee networking protocol is embedded in the module, and can be configured using matching software or AT configuration commands, facilitating rapid networking communication.
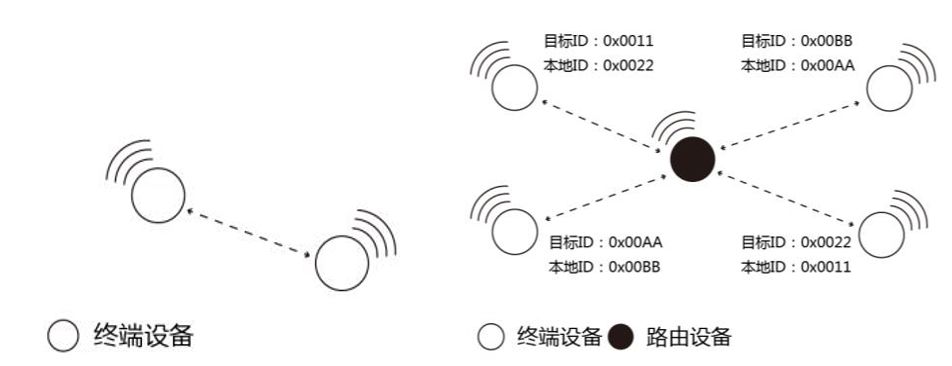
Figure 5 FastZigBee Point-to-Point and Multi-Point Communication Diagram
In general, when the number of nodes is not large, we can quickly complete the configuration using matching configuration tools. However, when the number of nodes reaches a certain level, configuring them one by one becomes very cumbersome. In this case, AT commands can be used to control the FastZigBee module to enter self-networking mode, quickly achieving dynamic networking on-site.
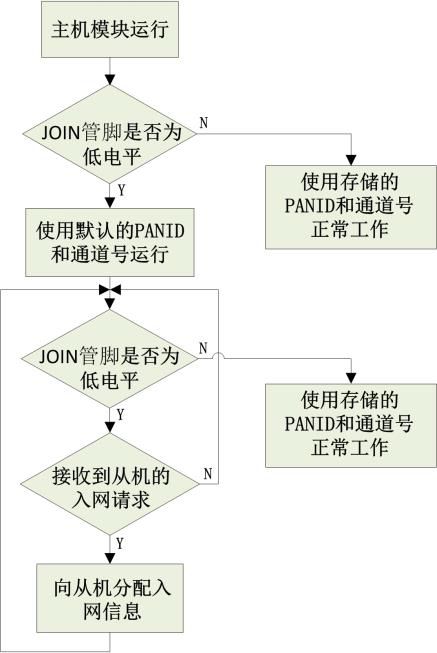
Figure 6 Host Module Self-Networking Process Diagram
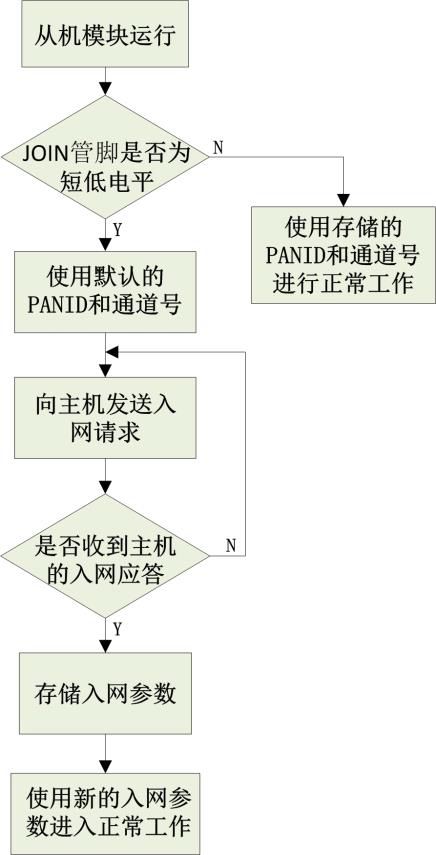
Figure 7 Slave Module Self-Networking Diagram
If updates are needed on-site in the future, changes to the number and layout of nodes in the local area network can also be controlled through commands, allowing the host module to re-acquire network parameters, while the slave module exits the previously joined network, and quickly completes the new network setup by re-entering self-networking.
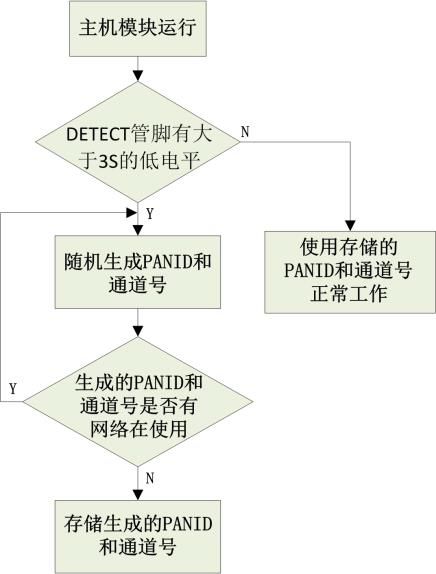
Figure 8 Host Reacquiring Network Parameters
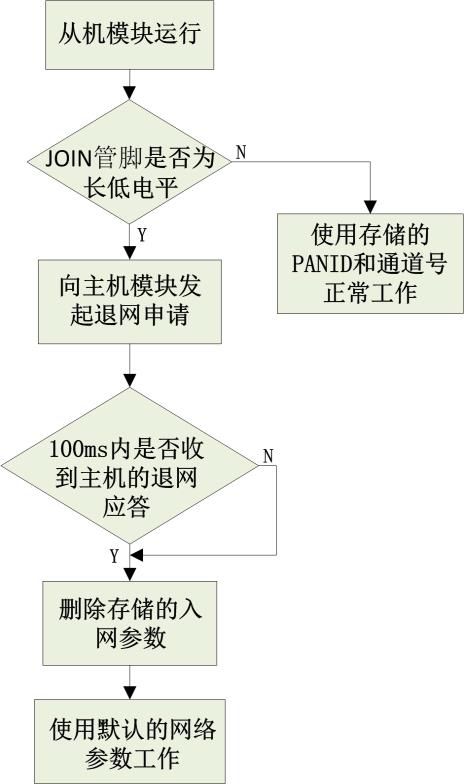
Figure 9 Slave Module Exit Network Operation
ZLG Zhiyuan Electronics has developed the AW516X series modules based on the NXP JN516X wireless microcontroller, which fully supports self-networking functionality. The AW516X series products significantly simplify the complex development process of wireless products, directly providing multiple user-configurable AD, IO, and PWM interfaces, allowing your products to enter the market at a lower cost and faster. Feel free to contact us for consultation!
Figure 10 AW516X Series Module Physical Diagram

Reply with the keyword 【Wireless Communication】 to view more related technical topics.
Official WeChat account introduction
Zhiyuan Electronics official WeChat account, a research and development testing sharing platform with 500 engineers, providing you with leading product technology and solutions in the electronics industry.
