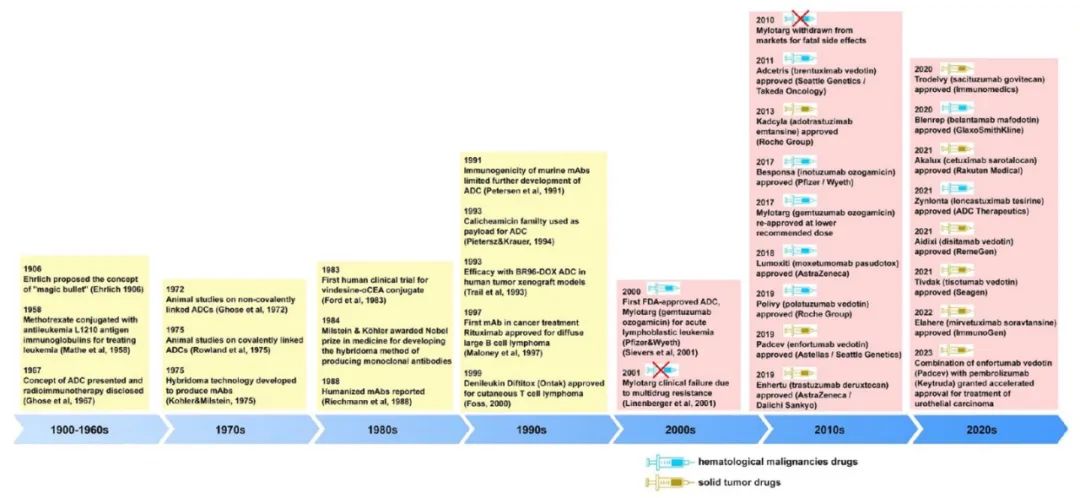
Periodically, major pharmaceutical media and authoritative journals summarize the development of ADCs. Recently, a review on ADCs published by the internationally renowned journal ACS caught our attention. As a member of CAS (American Chemical Society), Janet M. Sasso’s team innovatively used patents and articles related to ADCs within CAS as data for multidimensional analysis, presenting us with the evolution of ADCs.

CAS is the largest collection of published scientific articles, based on which Janet M. Sasso’s team created a new conceptual map of ADCs (Figure 1). The article discusses the evolution of key concepts in the field, major technologies, and their development pipeline, including research focuses of companies, disease targets, development stages, as well as publication and investment trends.
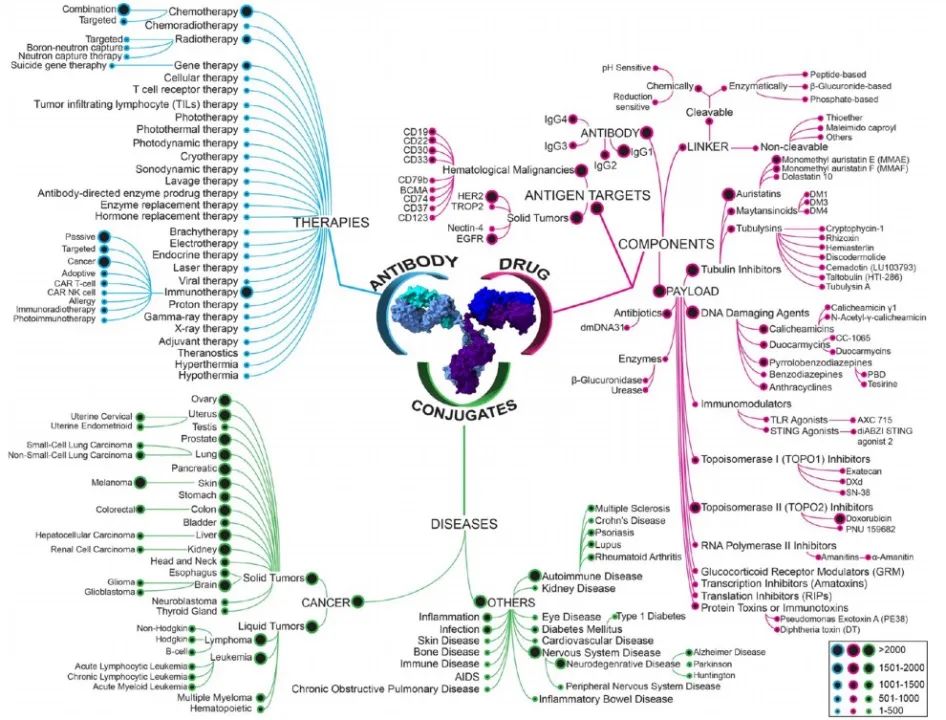
Figure 1: Conceptual Map of ADCs
01
Optimization and Progress Directions of ADCs
ADCs combine the targeting ability of monoclonal antibodies with the cytotoxicity of drugs, minimizing damage to healthy cells and reducing systemic toxicity, which is significant for cancer treatment. In the past decade, ADCs have made tremendous progress in optimizing the selection of cytotoxic drugs, conjugation strategies, better-targeting antigens, and improving antibody engineering.
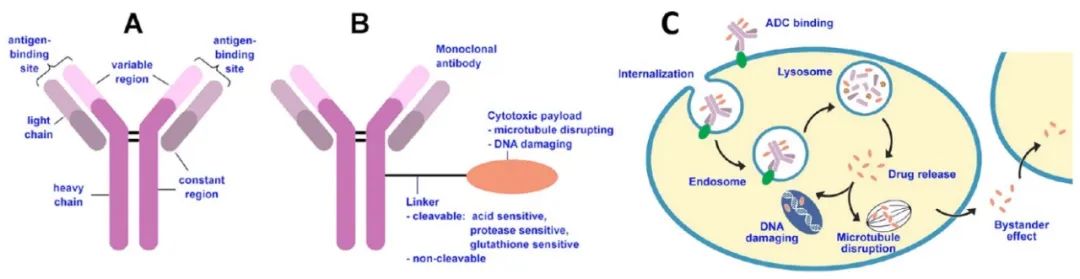
1.1 Selection/Optimization of Antibodies
Most marketed ADCs use the IgG1 backbone, but the heterogeneity of antibodies during systemic administration is a long-standing and significant issue.Improvements and innovations in antibody forms are expected to enhance target specificity, improve tissue permeability, engage the immune system, and reduce systemic toxicity. For example: Nanobody-enhanced ADCs improve therapeutic efficacy; Bispecific antibodies in ADCs can simultaneously target tumor-specific antigens and immune cells, promoting immune-mediated cancer cell killing; Trispecific antibodies are designed to bind to three different targets and antigens, providing higher targeting specificity. Additionally, there are dual-site antibodies, site-specific antibody conjugates, peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs).
1.2 Linker
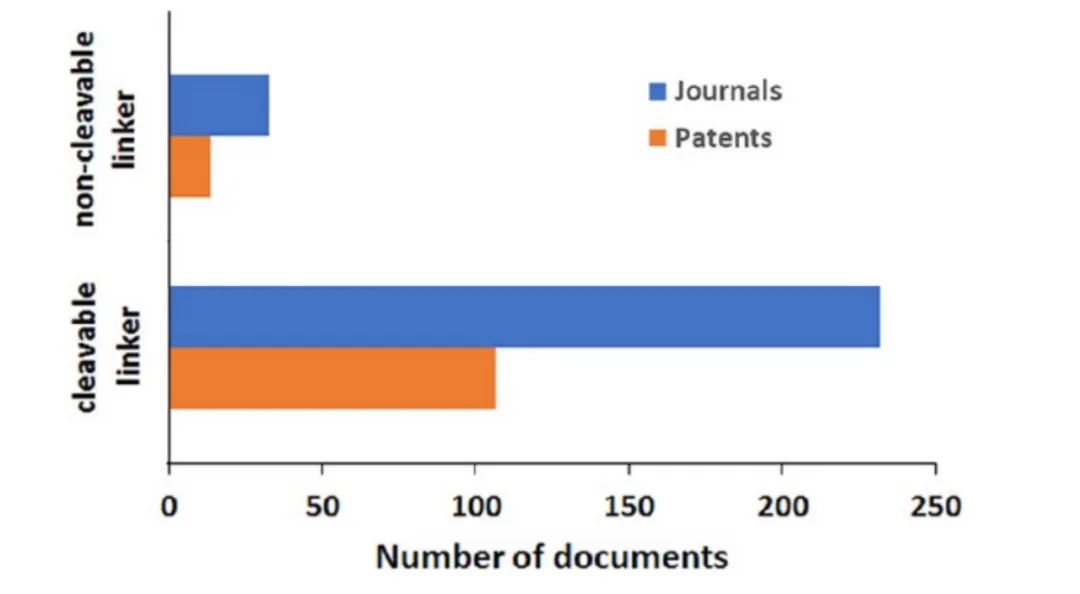
Linkers are divided into cleavable and non-cleavable types. Cleavable linkers are cleaved by acid, reductants, or enzymes; non-cleavable linkers only become active after antibody internalization and hydrolysis. Recently, branched linkers have been designed for ADCs to achieve high drug-antibody ratios (DAR).
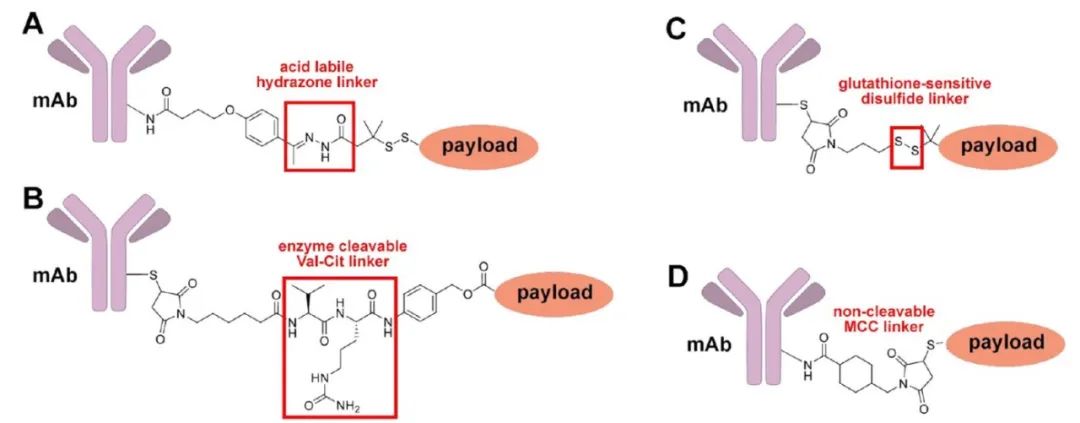
1.3 Payload
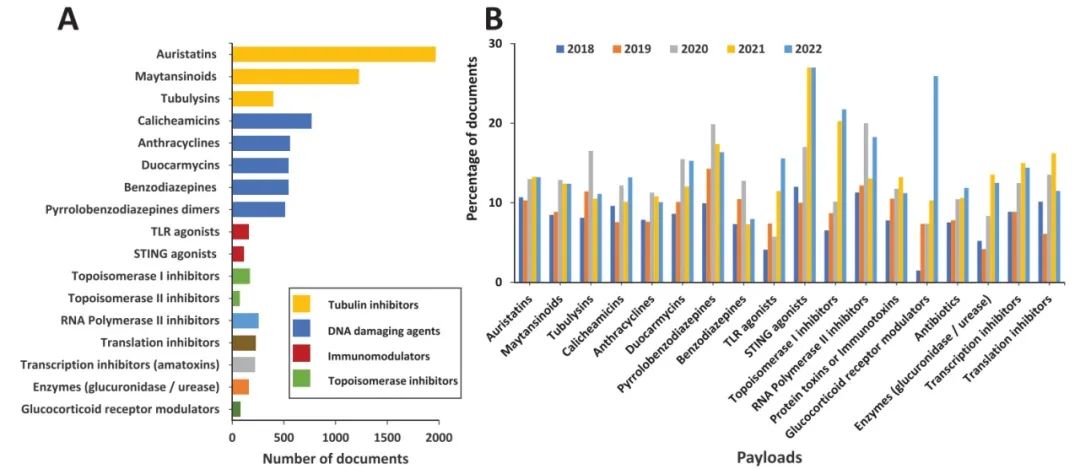
Payloads must behighly toxic and stable. Auristatins, maytansinoids, camptothecin and its analogs, pyrrolobenzodiazepines, Calicheamicin, etc., can serve as payloads.
1.4 Conjugation Methods for ADCs
Conjugation methods must not disrupt the activity or stability of the drug or antibody. Conjugation should be performed efficiently, with high yield, and should also be selective and predictable.
1.5 Selection/Optimization of Target Antigens
The efficacy of ADCs depends on the expression level of the target antigen.The most commonly used antigen targets are CD19, ERBB2, HER2, CD22, CD30, CD33, CD79b, and MSLN. Recently, ADCs have been developed to simultaneously target immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-L1 or B7-H3, preventing immune suppression by directly binding to immune checkpoint molecules while carrying cytotoxic payloads.
1.6 Combination Therapy
1.7 Companion Diagnostics
Selecting the most suitable patients for treatment based on target gene expression levels or other predictive biomarkers can improve clinical outcomes of ADC therapies.
02
Insights into the ADC Research Landscape from CAS
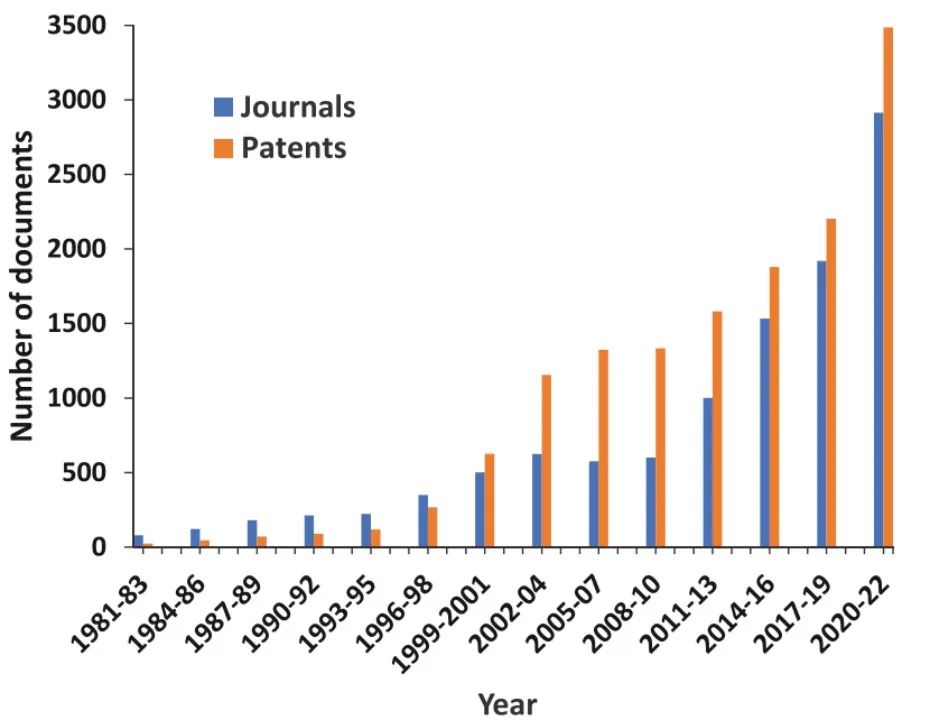
CAS has over 25,000 scientific publications related to ADC research and development (mainly journal articles and patents). After 2000, the number of patents exceeded that of journal articles (Figure 5). This correlates closely with the accumulation of scientific knowledge and its subsequent translation into patents.
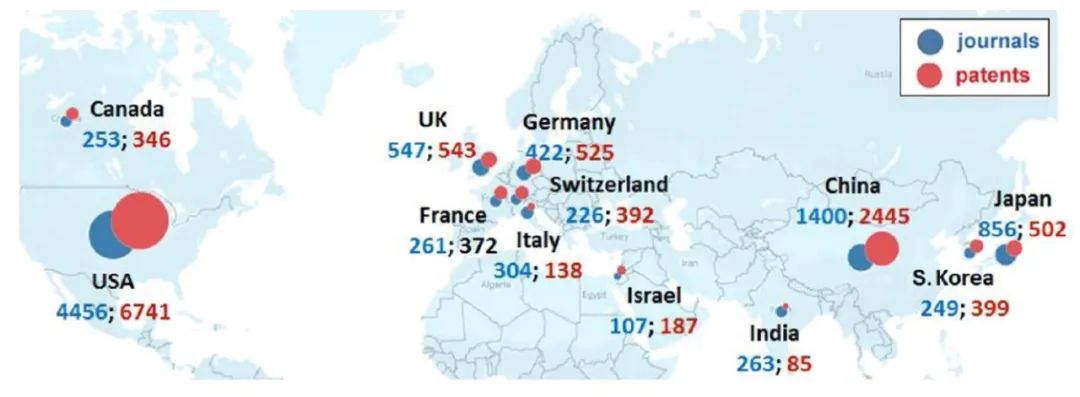
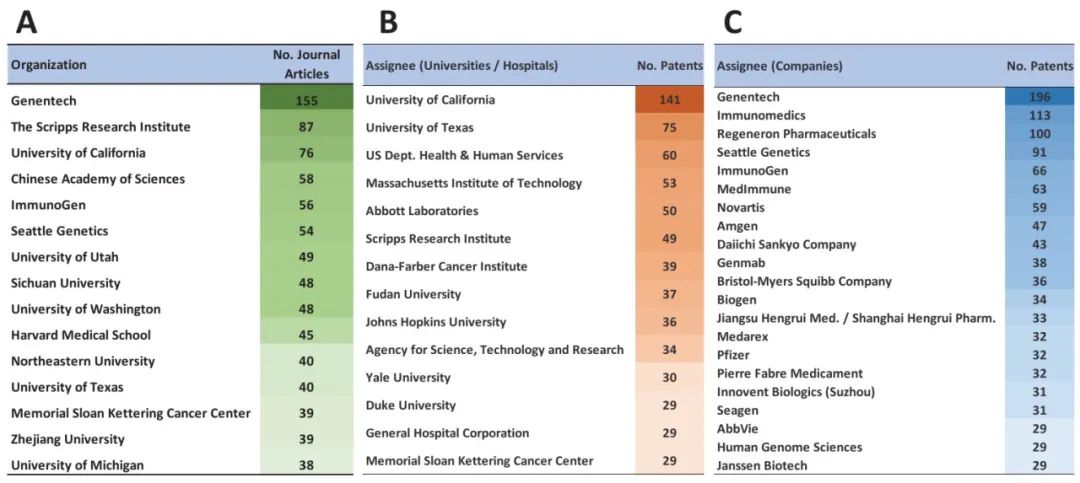
Ranking of countries and organizations by the number of journal articles and patents related to ADCs: The US, China, and Japan rank in the top three, with patent applications mainly led by enterprises (Figures 6, 7).
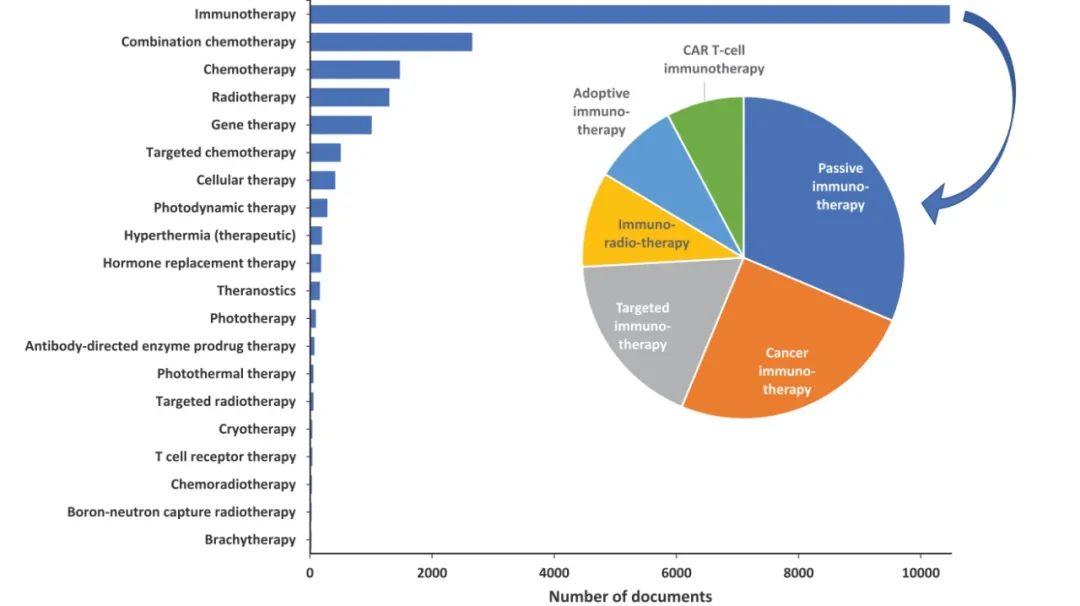
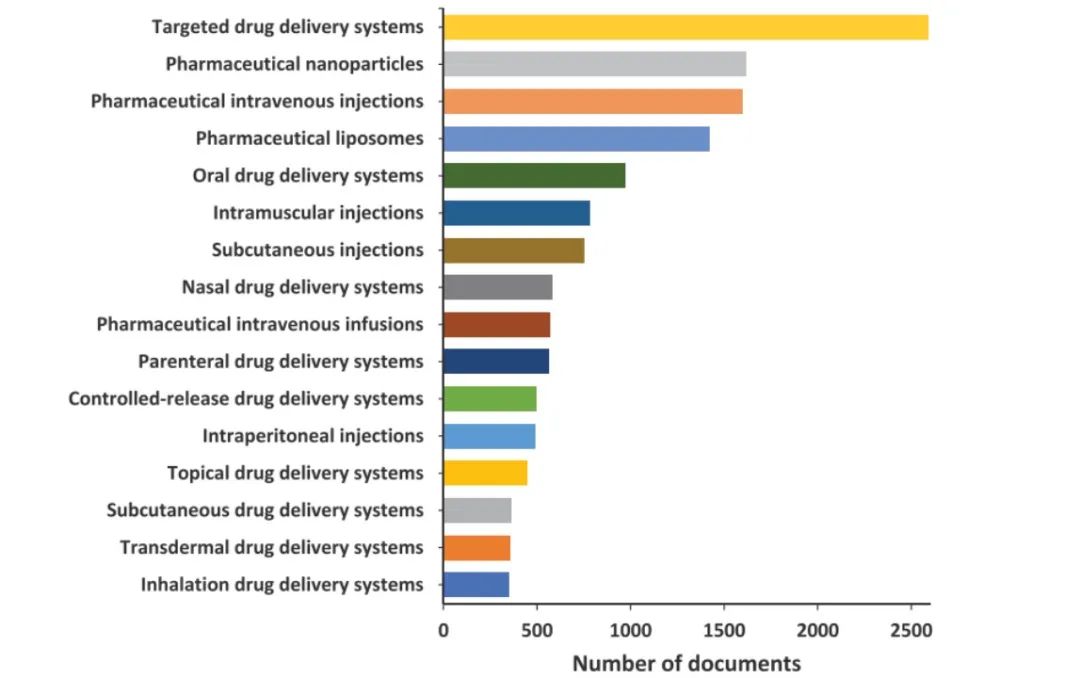
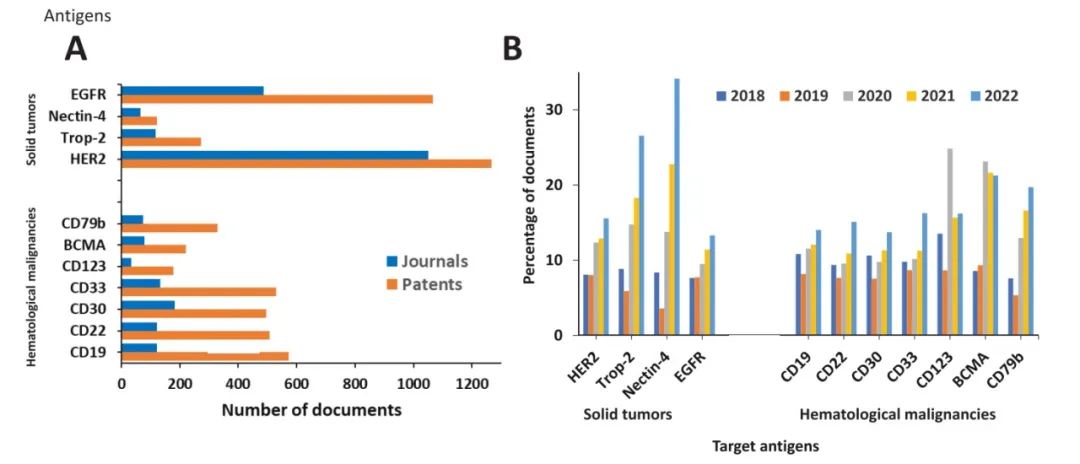
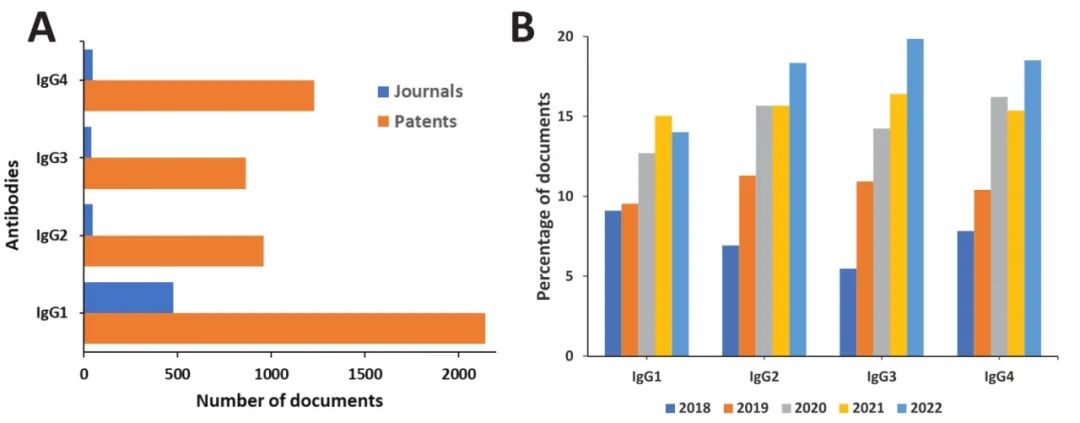
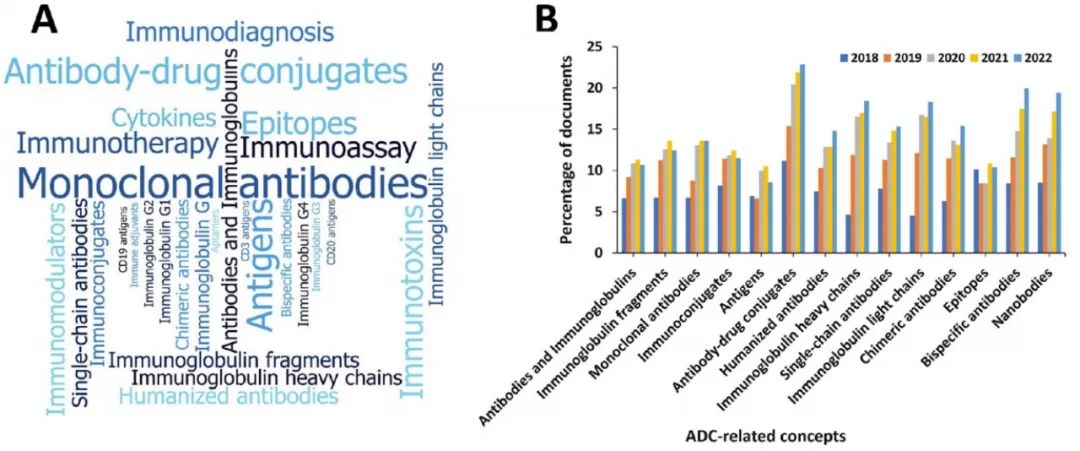
Distribution and Trends of ADC-related Concepts in Literature: Combination immunotherapy with ADCs accounts for the most literature (Figure 9); the most common delivery system for ADCs is the nanoparticle-targeted intravenous delivery system (Figure 10); the payloads used in ADCs are primarily auristatins and calicheamicins (Figure 11); HER2 and EGFR remain the most widely explored target antigens in solid tumors, while Trop-2 and Nectin-4 antigens have shown steady growth over the past five years (Figure 12); the most commonly used IgG subtypes in cancer immunotherapy are IgG1 and IgG4, while the applications of IgG2 and IgG3 in ADCs have grown faster than those of IgG1 (Figure 13); the preferred linker type in therapeutic ADCs is cleavable linkers (Figure 14).
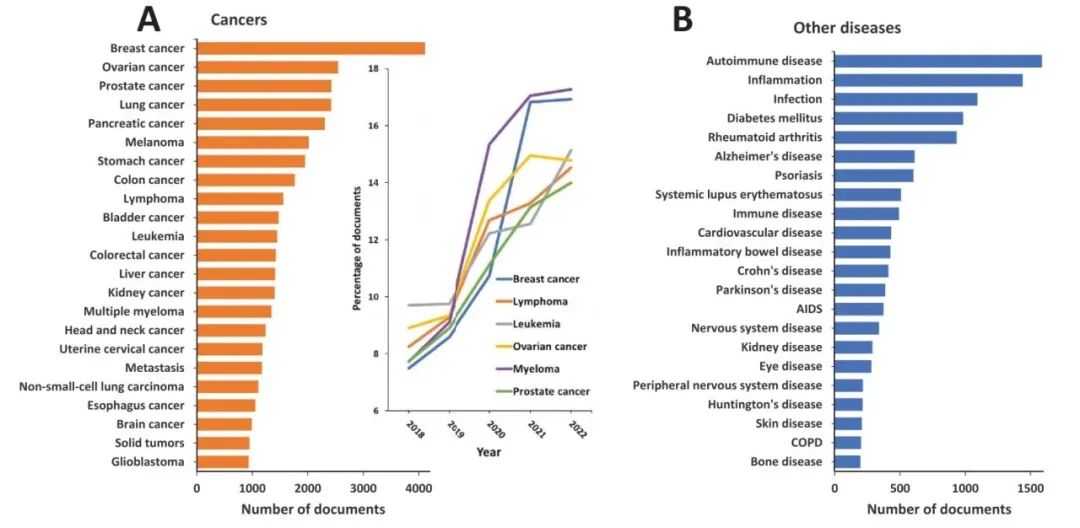
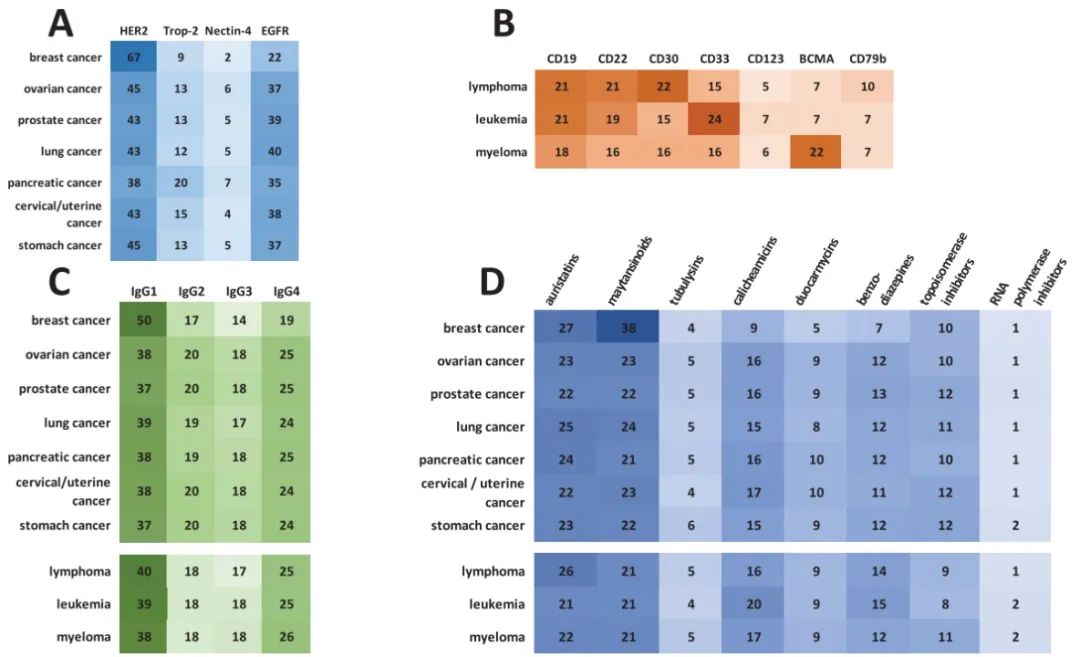
Correlation Between Various Cancers and ADC Target Antigens, ADC Antibodies, and ADC Payloads: The strongest correlation is between breast cancer and HER2, lymphoma with CD19, CD22, and CD30, leukemia with CD33 and CD19, and multiple myeloma with BCMA; the strongest correlation is between breast cancer and maytansinoids, followed by lymphoma and auristatins.
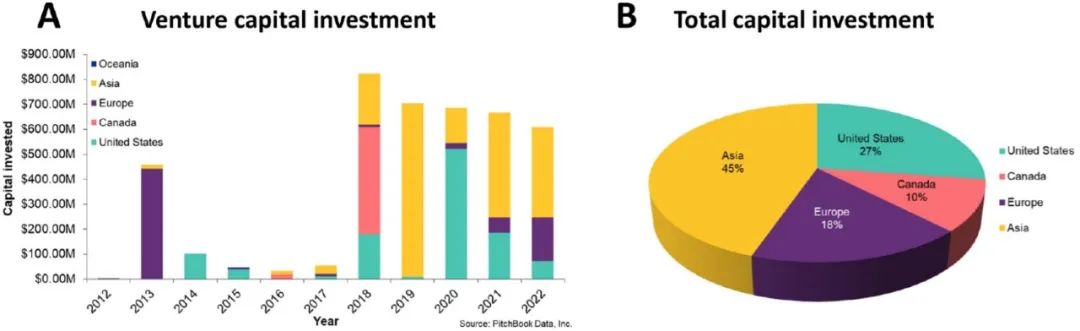
Business Investment in the ADC Field has been enthusiastic: In 2018, capital investment in the ADC field surged, and the investment enthusiasm for ADCs has remained strong in the following years, with amounts exceeding $60 billion. Globally, most of the investment comes from Asia, followed by the US, with the rest from Europe and Canada (Figure 17).
03
Conclusion
To provide effective ADC therapies for patients, continuous advancements in antibody engineering, linker technology, payload design, and tumor biology are necessary. At the same time, collaboration among researchers, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory agencies is essential. The conclusions drawn by the author from the analysis of CAS content not only validate our known ADC-related content but also supplement us with new insights, allowing us to interpret the ADC field from a broader, global perspective.
In summary, ADCs are a very promising therapeutic approach.
Recent Events
March 8-9, XDC Unbreakable! 2024 BiG ADC Thematic Seminar
Keywords: Expansion of clinical indications; target & project initiation; bispecific ADC; combination strategies; next-generation linker-payload; nuclear medicine
▼

▼

