Source: IoT Space Station
Author: Jian Lai
Published by IoT Think Tank
Please indicate the source when reprinting
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) is developing rapidly. While cloud computing has driven the development of IoT, edge computing provides more powerful insights and analysis of the collected data. With technological advancements, edge computing will help you better manage and significantly improve IoT operations.
Cloud computing and edge computing are shaping the future of the Internet of Things (IoT). This combination brings stability to the connected devices within IoT networks and addresses latency issues by processing data closer to the source.
Cloud computing has significantly changed the way data is processed, especially for big data. By leveraging the computing power of the cloud, IoT has achieved leapfrog development, allowing us to acquire, store, and process data without the need to configure computing resources and manage them.
Billions of smart devices are installed annually in the IoT, with estimates suggesting over 20 billion smart devices will be installed by 2020. With a large number of devices connected to the IoT, the volume of data being processed has been increasing. We are facing the challenge of processing and analyzing this data, especially when near real-time processing is required. Cloud computing alone cannot help process such vast datasets and provide real-time responses.
Decoding Edge Computing
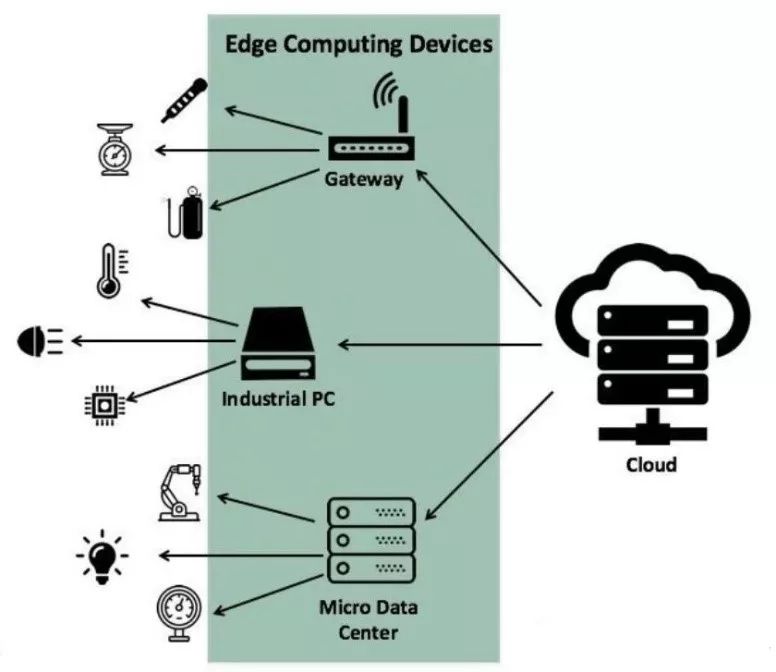
According to the International Data Corporation (IDC), edge computing is a mesh network of micro data centers that can process or store critical data locally and push all received data to a central data center or cloud repository.
In short, edge computing can process and analyze data closer to the source of data generation.
Smart devices installed and connected in an edge computing environment can handle critical task data and respond in real-time, rather than sending all data over the network to the cloud and waiting for a response. The devices themselves act like a mini data center, and because basic analysis is performed on the device, latency is nearly zero. With this new capability, data processing becomes decentralized, and network traffic is greatly reduced. The cloud can collect this data later for a second round of evaluation, processing, and in-depth analysis.
Benefits of Edge Computing for IoT
Utilizing edge computing brings many benefits to IoT devices, such as near-zero latency, reduced network load, increased resilience, reduced data exposure, and lower data management costs. Let’s take a closer look at these:
Near-Zero Latency:
Near-zero latency is the biggest advantage of edge computing. The time interval between data collection, processing, and action is almost real-time. This is a critical requirement for IoT devices in mission-critical situations. A very good example is self-driving cars.
Google estimates that their self-driving cars generate about 1GB of data every second! Rapid processing of such large amounts of data is needed for the car to stay on the correct path and avoid collisions. Imagine if this data were collected, sent to the cloud, processed there, and then sent back to the car. Even though the entire process might be completed in a few seconds, it could be too late, and the car may have already encountered a collision. The best solution in this scenario is to use edge computing to analyze the data from the sensors themselves and then send it to the cloud for further analysis.
Edge computing is also critical in the healthcare industry. Latency is particularly crucial in healthcare, where devices are connected to heart rate monitors or pacemakers, and even slight delays could determine life or death for patients.
Reduced Network Load:
Cisco estimates that by 2020, the amount of data processed by IoT devices will reach nearly 7.5 Zettabytes (1ZB = 1,000,000,000,000 GB)! This is a massive amount of data on the internet highway, which could lead to increased network congestion, especially in areas with weak connections. By using edge computing, most of the traffic load will be handled by processing data at the source rather than sending all data over the network, significantly improving network congestion.
Enhanced Resilience:
With the decentralized architecture provided by edge computing, other connected devices in the network become more resilient. Compare this to a single virtual machine failure in the cloud, which could impact thousands or even millions of IoT devices connected to the network. Even if one device fails, it does not affect other devices, and they remain active and operational.
Reduced Data Exposure:
Edge computing reduces the amount of data sent over the network. This also helps reduce the risk of data breaches during transmission. In some cases, sensitive and critical data collected by smart devices (such as Payment Card Industry (PCI) and Personally Identifiable Information (PII)) does not need to be transmitted at all. This helps avoid many privacy, legal, and security complexities, especially when different regulations apply to this data in each country, and processing data closer to its source is beneficial. By further encrypting the data and controlling access, we can make it more secure against known threats.
Lower Data Management Costs:
Using edge computing can significantly reduce storage costs in the cloud, as we are not storing everything in the cloud. This also helps manage data effectively due to the relatively small amount. Only aggregated data that requires deeper analysis will be sent to the cloud, where it will then be analyzed and inferred.
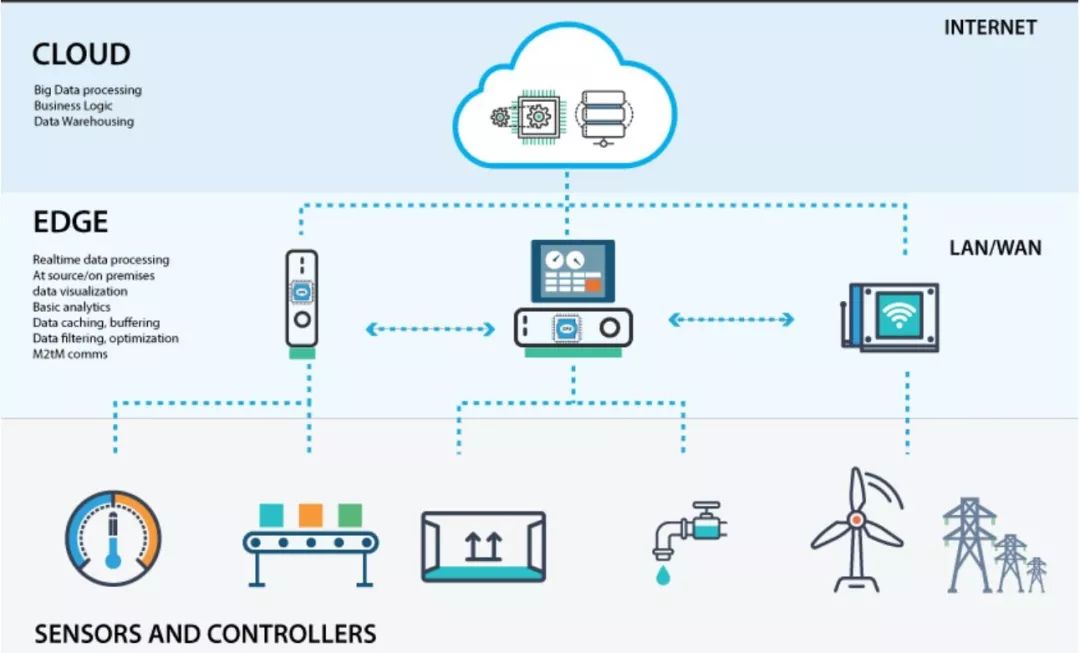
Edge Computing and Cloud Working Together to Achieve IoT
We have seen how edge computing benefits IoT, so let’s analyze why edge computing cannot completely replace cloud computing.
To meet all the requirements and demands of IoT devices, edge computing and cloud computing need to work together. All data from smart devices and sensors still needs to be aggregated in the cloud, which requires deeper analysis to extract meaningful insights. Cloud computing still plays a critical role in making IoT devices smarter and better.
Looking back at the example of Google’s self-driving cars.
After collecting all the vehicle data and analyzing it in the cloud, Google can propose best practices and driving algorithms that will improve navigation and make the vehicles perform optimally when visiting a location for the first time.
Major freight companies in the U.S. and Europe have already benefited from this approach, saving significant costs. They place sensors in their fleets and collect various data, including engine performance, tires, fuel levels, transmissions, and batteries. Processing this data at the edge is not useful; instead, all this data is sent to the cloud. After in-depth analysis, companies can issue alerts about obtaining the best driving routes, when to replace old parts, when fuel is low, when to replace faulty transmissions, etc., thereby improving and saving on maintenance, repair, and operational costs.
With the immense computing power provided by the cloud, it makes sense to let it do the heavy lifting on vast and cumbersome datasets. Most of the time, the centralization of cloud computing outperforms the decentralized nature of edge computing in terms of speed, cost, and scalability. Therefore, to fully meet the primary demands of IoT, which are low latency and big data processing, we see that edge computing and cloud computing need to work in coordination. Edge is responsible for real-time analysis and response, while the cloud handles the heavy lifting and processing of datasets to enhance the functionality of these smart devices.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things will develop rapidly in the coming years. While cloud computing drives the development of IoT, edge computing provides more powerful insights and analysis of the collected data. With technological advancements, it will help you better manage and significantly improve IoT operations.
Previous Hot Articles (Click on the title to read directly):
-
“How Difficult Is It to Make a Smart Lock for Shared Bicycles?”
-
“Cognitive Computing, Blockchain IoT, IoT Security… Those Who Understand Will Control the Future”
-
“[Heavy Release] 2017-2018 China IoT Industry Panorama Report – The IoT Has Started a Deep Transformation of the Industry”
-
“[Heavy] IoT Industry Panorama Report, Leading the Way in Domestic IoT Industry Two-Dimensional Perspective”
-
“A Cartoon Explains: Besides WiFi and Bluetooth, What Else Can the Recently Popular NB-IoT Do?”
-
“A Cartoon Explains: Behind NB-IoT, What Is the LoRa Everyone Is Talking About?”