▲Click above Leiphone to follow

By | Dazhuang Lu
From Leiphone (leiphone-sz)

Leiphone reports: On September 18, the 2018 World Artificial Intelligence Conference – Edge Intelligence Forum was held in Shanghai, themed “Edge Computing, Intelligent Future”, and is one of the important thematic forums of the 2018 World Artificial Intelligence Conference.
Yukai Yu, founder and CEO of Horizon Robotics, emphasized in his speech that humanity is transitioning from the era of big data to the era of big computing. The trend of edge computing is a result of the global internet technology trend of “long separation must unite, long unity must separate”.
“In the PC era, all computing was done on computers, which is local computing. With the development of the internet, data gradually shifted to the cloud, and computing slowly concentrated in the cloud. However, since the beginning of the mobile internet and now with the arrival of the IoT era, we are seeing another trend – more computing is migrating from the central to the edge.”
He also predicted that by 2025, the computing power that can be purchased for every thousand dollars will equate to 1000T, sufficient to support the computational needs of level 5 autonomous driving. If software systems that match this are developed further, true level 5 autonomous driving will become possible by 2030. Interestingly, the trend in technology shows that 1000T of computing power is roughly equivalent to the computing power of the human brain, which is a noteworthy development result of Moore’s Law.
Below is the full text of Yu Kai’s speech, sharing Horizon’s work and thoughts on edge computing, edited by Leiphone (with omissions):
Today, we are here to discuss edge intelligence and edge computing – an industry consensus that is increasingly gaining attention.
Cities are very important scenarios for artificial intelligence, where there is traffic, driving, and a large amount of human-machine interaction. Computing must occur in scenarios with data explosions, and currently, the places where data is generated and exploded in large quantities are cities.
The importance of edge computing lies in its ability to make urban life safer and better.
More Computing is Migrating from Central to Edge
The future development of AI will inevitably promote the construction of smart cities. Edge computing will cover every day of life – from home to the road, in work scenarios. Undoubtedly, this will generate a large amount of scenarios and data.
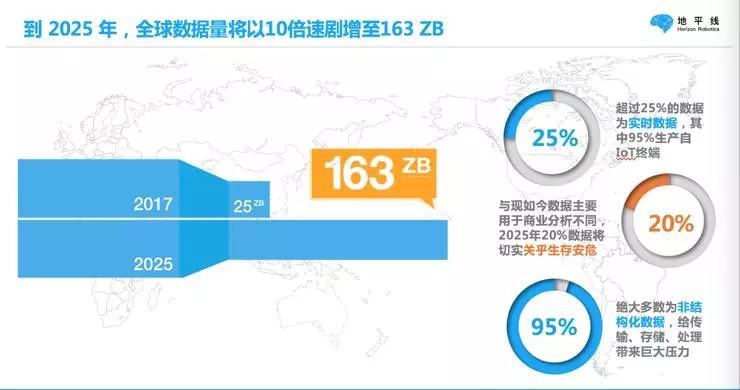
According to a report, it is estimated that by 2025, the global data volume will increase tenfold to 163ZB, which far exceeds the data reserves of any internet company today.
Long separation must unite, long unity must separate, and this is also happening in computing.
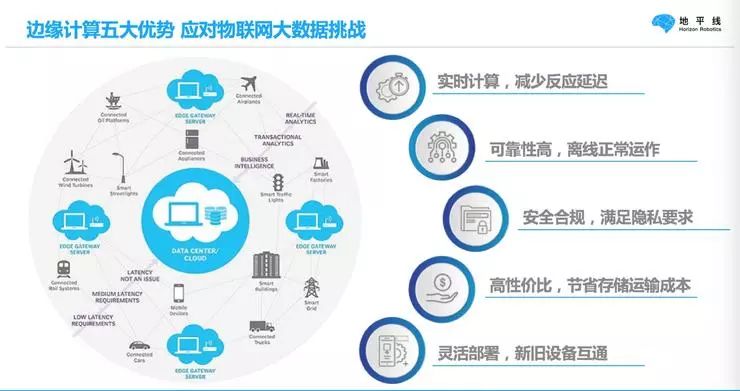
In the PC era, all computing was done on computers, which is local edge computing. Later, with the development of the internet, data gradually shifted to the cloud, and computing slowly transitioned to cloud computing. From the mobile internet to the current IoT era, we see another trend where more computing is migrating from the central to the edge. The benefits of this include real-time performance and reliability, allowing devices to operate normally even when offline.
For example, when an autonomous vehicle runs on the road and goes through a tunnel with no signal, how can it drive automatically? It must rely on edge computing that does not depend on the network and cloud. Many security companies currently rely on WIFI for processing, but they are greatly affected by signal and bandwidth, necessitating edge computing.
The core point here is that a large amount of computation must occur at the edge, not in data centers. Data centers require powerful power supply systems and are often built in places like Inner Mongolia where electricity demand is relatively low. Edge computing, however, requires low energy consumption, which places very high demands on edge computing processors.
The AI processors for edge computing can be said to be the core technological foundation for today’s smart cities and autonomous driving.
Five Advantages of Edge Computing
Do we emphasize edge computing to mean that our computing power is discounted? Not at all.
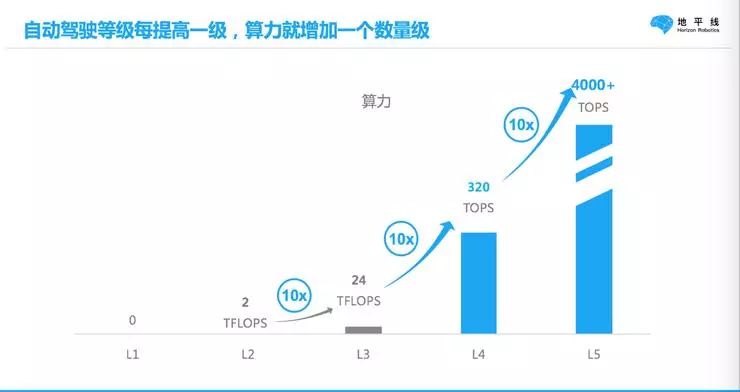
Take autonomous driving as an example; autonomous driving is divided into levels from Level 0 to Level 5, with Level 5 being full-time, all-condition, and all-scenario autonomous driving. There is an interesting trend here: every time autonomous driving advances a level, its computational requirements increase by an order of magnitude.
For instance, the current stage in the industry is Level 3 autonomous driving, with the corresponding industrial AI processors at around 10T of computing power. Level 4 autonomous driving requires hundreds of T, and for full Level 5 autonomous driving, it needs to reach 1000T.
What does this mean? Let’s briefly review Moore’s Law. Over the past century, the computing power that can be bought for every thousand dollars has followed this growth curve (as shown in the image above).
Today, the computing power equivalent to a thousand dollars is about the same as that of an iPhone. Since 2017, Moore’s Law has undergone new changes because our physical processes have started to change, with the industry recently tackling processes like five nanometers. However, continuing to push forward will become increasingly difficult, as atoms are 0.1 nanometers, and humanity has already approached the atomic limit in chip manufacturing processes, meaning physical processes cannot continue to advance Moore’s Law.