
Data is the “lifeblood” of modern society. Although fiber optics can transmit data at 200,000 kilometers per second (two-thirds of the speed of light in a vacuum), delays are inevitable in long-distance transmission.
For example, a signal sent from Beijing takes at least 0.1 seconds to reach Chile, which is about 20,000 kilometers away. Although this delay is almost negligible, in an upcoming world of interconnected devices, even the slightest data delay can have a significant impact on certain industries, such as remote surgery, stock trading, and autonomous driving.
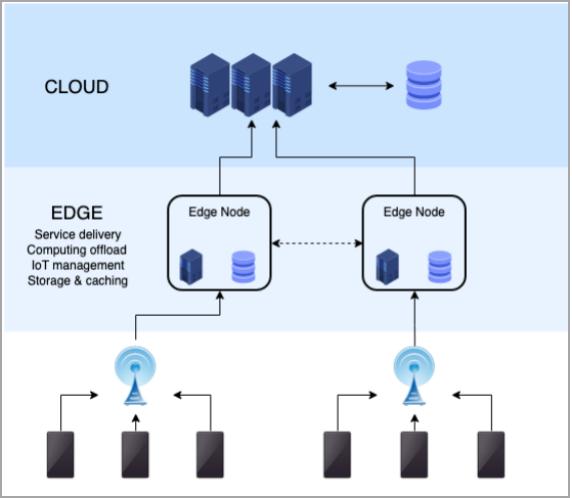
Therefore, reducing the distance of data transmission has become an urgent need. This demand has also driven data storage and computation to shift towards intelligent device terminals, leading to the emergence of edge computing.
How can we understand edge computing? What are its advantages? What promising applications can we expect? Let’s enjoy the exploration:
+
How to Understand Edge Computing Through the Nervous System?
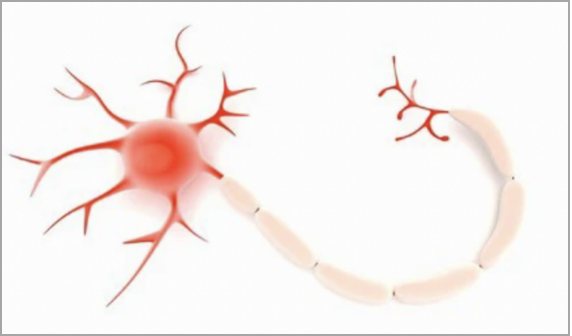
+
The Era of Data Explosion
Four Major Advantages of Edge Computing
High Speed
Edge computing devices in IoT can process data locally or at nearby edge data centers. Since the information collected does not need to be transmitted to traditional cloud facilities, it can significantly enhance the response speed of smart devices. For instance, in the field of facial recognition, the response time of edge computing is reduced from 900ms to 169ms, even faster than the human response time for recognizing faces (370-620ms).
Security
Edge computing decentralizes data processing, storage, and applications across a wide range of devices and data centers, making it difficult for a single attack to compromise the entire network. On the other hand, traditional cloud computing transmits private data collected from wearable devices, medical devices, and industrial manufacturing to data centers over long paths, which can easily lead to data loss or information leakage. By storing and processing data at the edge, this risk can be effectively mitigated. Additionally, the ownership of the collected data will shift from service providers to end users.
Low Bandwidth Requirements
Edge computing reduces the amount of data transmitted to cloud centers through local processing, thereby lowering the demand for network bandwidth. This feature is particularly important in bandwidth-constrained scenarios, such as poor signal conditions on airplanes or in mountainous areas.
Scalability
Edge computing provides a cost-effective scalability path, allowing companies to expand their computing capabilities through a combination of IoT devices and edge data centers.
+
Sky and Sea
Edge Computing Opens Up More Application Scenarios

+
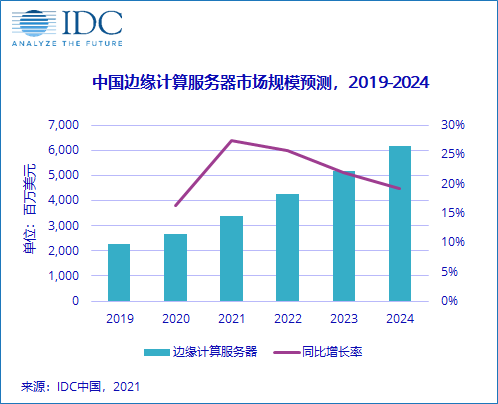
Broad Market
Rapid Development of Edge Computing in China
+
References
-
What is Edge Computing? Understand It All at Once
-
Huaxin Consulting: “Approaching Edge Computing”
-
Lenovo Group Senior Vice President Rui Yong: Intelligent Edge Computing, Bringing AI to Your “Side”
-
Economic Observer: Edge Computing, New Opportunity in the 5G Era
-
The Edge Computing Infrastructure
+
Previous Recommendations

THE END

