
With the deepening trend of the Internet of Everything, the number of end devices such as smartphones and smart glasses is constantly increasing, causing the growth rate of data to far exceed the growth rate of network bandwidth; at the same time, the emergence of many new applications such as augmented reality and autonomous driving has raised higher demands on latency. Edge computing provides a unified platform of computing, networking, and storage resources at the network edge to serve users, allowing data to be processed timely and effectively near the source. This model differs from cloud computing, which requires all data to be transmitted to data centers, bypassing the bottlenecks of network bandwidth and latency, and has attracted widespread attention.
Understanding Edge Computing

In recent years, the rapid development of big data, cloud computing, and intelligent technologies has brought profound changes to the Internet industry and has raised new demands on computing models. The amount of data generated daily in the era of big data is surging, while data in the context of applications such as the Internet of Things is geographically dispersed, requiring higher standards for response time and security. Although cloud computing provides an efficient computing platform for big data processing, the current growth rate of network bandwidth lags far behind that of data, and the decline in bandwidth costs is much slower than that of hardware resources such as CPU and memory. Additionally, complex network environments make it difficult to achieve breakthroughs in network latency. Therefore, the traditional cloud computing model needs to address the two major bottlenecks of bandwidth and latency. In this context, edge computing has emerged and has gained widespread attention from researchers in the past two years.
Edge computing refers to the computing and storage resources at the network edge, which is closer to users in terms of both geographical and network distance compared to data centers. Edge computing leverages these resources to provide services at the network edge, allowing applications to process data near the source. From a bionic perspective, we can make this analogy: cloud computing is like the human brain, while edge computing is akin to the nerve endings. When a needle pricks the hand, the hand instinctively withdraws before the brain realizes it has been pricked, because the withdrawal process is a reflex directly processed by the nerve endings. This reflex accelerates human response times, preventing greater harm while allowing the brain to focus on higher-level thinking. The future is the era of the Internet of Everything, with Cisco predicting that by 2020, there will be 50 billion devices connected to the Internet. We cannot make cloud computing the “brain” for every device; edge computing allows devices to have their own “brains”.
To make it easier to understand, we can liken edge computing to a fascinating creature in the world— the octopus, which is the most intelligent among invertebrates. An octopus has a vast number of neurons, with 60% distributed in its eight arms (tentacles) and only 40% in its brain. It can escape and hunt with exceptional speed, and its eight arms never tangle, thanks to the octopus’s distributed computing-like “multiple small brains + one large brain”.
(Image source: Jiangnan Misty Rain Residence Blog)
Advantages of Edge Computing

When discussing edge computing, we cannot overlook cloud computing. Cloud computing services are centralized services where all data is transmitted over the network to a cloud computing center for processing. The high degree of centralization and integration of resources gives cloud computing high versatility. However, in the face of the explosive growth of IoT devices and data, the aggregation service based on the cloud computing model has gradually revealed its shortcomings in terms of real-time performance, network constraints, resource expenditure, and privacy protection.
Compared to cloud computing, edge computing better supports mobile computing and IoT applications, offering the following significant advantages:
1. Greatly alleviates pressure on network bandwidth and data centers.Cisco indicated in its Global Cloud Index from 2015-2020 that with the development of the Internet of Things, devices worldwide will generate 600ZB of data by 2020, of which only 10% is critical data, while the remaining 90% is temporary data that does not require long-term storage. Edge computing can fully leverage this characteristic by processing a large amount of temporary data at the network edge, thereby alleviating the pressure on network bandwidth and data centers.
2. Enhances real-time response.In the Internet of Everything scenario, applications have extremely high real-time requirements. Under the traditional cloud computing model, applications transmit data to the cloud computing center and then request processing results, which increases system latency. For example, in autonomous driving applications, a high-speed vehicle requires millisecond-level response times. If network issues increase system latency, it can lead to severe consequences. Edge computing processes data close to data producers, eliminating the need to request responses from the cloud computing center, significantly reducing system latency. The proliferation of gigabit wireless technology ensures network transmission speeds, making edge services more responsive than cloud services.
3. Protects privacy data and enhances data security.Data security in IoT applications has always been a critical issue. Surveys show that approximately 78% of users worry about their IoT data being used by third parties without authorization. In the cloud computing model, all data and applications are housed in data centers, making it difficult for users to control access and usage at a granular level. With the rise of smart homes, many households install network cameras indoors. If video data is directly uploaded to the cloud data center, not only will it consume bandwidth resources, but it will also increase the risk of leaking users’ private data. To address the data security issues in the existing cloud computing model, edge computing provides a better privacy protection mechanism for such sensitive data. On one hand, users’ source data is processed directly at the edge node before being uploaded to the cloud data center to protect and isolate sensitive data. On the other hand, a functional interface is established between the edge node and the cloud data, meaning that edge nodes only receive requests from the cloud computing center and feedback the processed results to the cloud computing center. This method significantly reduces the risk of privacy leaks.
However, edge computing does not replace cloud computing; it complements it. Many services that require global data support still rely on cloud computing. For instance, in e-commerce applications, users can operate their shopping carts at edge nodes for the fastest response times, while services such as product recommendations are more suited to the cloud, as they require global data support.
Applications of Edge Computing

Currently, edge computing applications are very widespread, especially suitable for application scenarios with special requirements such as low latency, high bandwidth, high reliability, massive connectivity, heterogeneous convergence, and local security and privacy protection.
Smart Cities
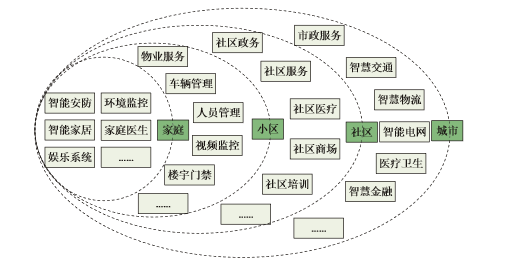
Smart cities utilize advanced information technology to achieve intelligent management and operation of cities. In 2016, Alibaba Cloud proposed the concept of “City Brain”, which essentially uses urban data resources to better manage cities. However, the data required for building smart cities is characterized by diverse sources and heterogeneity, and also involves issues of privacy and security for urban residents. Therefore, applying the edge computing model to process data at the network edge is a good solution.
Edge computing has rich application scenarios in the construction of smart cities. In urban road surface detection, sensors can be installed on streetlights to collect information about the urban surface, detecting environmental data such as air quality, light intensity, and noise levels. When streetlights malfunction, they can promptly notify maintenance personnel. In intelligent traffic systems, edge servers can run intelligent traffic control systems to obtain and analyze data in real time, controlling traffic lights based on current road conditions to alleviate vehicle congestion. In autonomous driving, uploading sensor data to the cloud computing center would increase the difficulty of real-time processing and be constrained by the network. Therefore, autonomous driving primarily relies on in-vehicle computing units to recognize traffic signals and obstacles and plan routes. EdgeOSc is a system-level operating system based on edge computing aimed at smart cities, consisting of three parts: the underlying data perception layer, the middle network interconnection layer, and the top data application management layer. This operating system can effectively manage multi-source data in smart cities, increasing the range and depth of data sharing to maximize the value of data in smart cities.
(Source: Applications and Prospects of Edge Computing in the IoT Field)
Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing is a typical application area of edge computing in the IoT, leveraging edge computing to promote the deep integration of IT and OT systems. Industrial robots are fundamental to achieving smart manufacturing, and in recent years, industrial robots have shown a booming trend in the Chinese market. According to statistics, the total consumption of industrial robots in the Chinese market reached 87,000 units in 2016, accounting for nearly one-third of global sales, making it the largest industrial robot market in the world. The application fields of industrial robots mainly focus on automotive manufacturing, 3C industries, logistics, metal processing, plastics, and chemicals, performing tasks such as handling, assembly, welding, and other work scenarios that require high automation/precision and safety levels. Industrial robots need to have the ability to respond to complex on-site environments and comprehensively analyze and judge based on current workflows, as well as collaborate with other robots to complete complex tasks. These require robots to be equipped with intelligent controllers to perform complex computational tasks. However, in factory environments where dozens or hundreds of robots are used, equipping each robot with a complex intelligent controller would increase costs. By adopting edge technology, the functions of intelligent controllers for industrial robots can be concentrated and deployed at edge nodes in the workshop, ensuring low latency while achieving centralized control and collaborative operation between robots, significantly reducing the development, deployment, and maintenance costs of industrial robots.
Smart Homes
In current smart homes, smart appliances are mainly composed of smart individual products, such as password locks, smart lighting, smart air conditioning, security monitoring, smart bathrooms, indoor environment monitoring, and home theater multimedia systems. These smart appliances rely on cloud platforms for remote control via mobile devices. Smart homes based on cloud platforms cannot be controlled when the network fails, especially in scenarios where multiple smart products need to coordinate. Smart appliances connect to the cloud/data center via Wi-Fi modules, and users also worry about the leakage of household data stored in the cloud/data center. Additionally, large amounts of monitoring video data consume the communication bandwidth between smart home devices and the cloud/data center. By adopting edge computing technology, household video data can be stored on local edge computing gateway devices, ensuring that users’ privacy is not leaked; coordination between multiple smart products can also be achieved through local edge computing in near real-time; edge computing nodes can also periodically synchronize updates with the cloud computing to control and update device status information.
References:
[1] Li Linzhe, Zhou Peilei, Cheng Peng, Shi Zhiguo. The Architecture, Challenges, and Applications of Edge Computing [J]. Big Data, 2019, 5(02): 3-16.
[2] Shi Weisong, Zhang Xingzhou, Wang Yifan, Zhang Qingyang. Edge Computing: Current Status and Prospects [J]. Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(01): 69-89.
[3] Zhao Ziming, Liu Fang, Cai Zhiping, Xiao Nong. Edge Computing: Platforms, Applications, and Challenges [J]. Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55(02): 327-337.
[4] Shi Weisong, Sun Hui, Cao Jie, Zhang Quan, Liu Wei. Edge Computing: A New Computing Model in the Era of the Internet of Everything [J]. Computer Research and Development, 2017, 54(05): 907-924.
[5] Chu Junsheng, Zhang Bosheng, Lin Zhaoji. Applications and Prospects of Edge Computing in the IoT Field [J]. Information and Communication Technology, 2018, 12(05): 31-39.
Event Recommendation:CNCC2019
From October 17-19, 2019, the 2019 China Computer Conference (CNCC 2019) will be held at the Suzhou Jinji Lake International Conference Center, hosted by the China Computer Society (CCF) and organized by the Suzhou Industrial Park Management Committee. This year’s conference theme is “Intelligent + Leading the Development of Society”, and it includes: keynote speeches from fifteen renowned experts and entrepreneurs in the field of computer science, three thematic forums, over seventy cutting-edge technology forums, twenty special events, and a hundred technology achievement exhibitions.
The three main forums will focus on the 50th anniversary of the Internet, industrial Internet, and deep learning. The more than seventy technology forums will consist of a variety of hot topics across multiple computing fields, such as artificial intelligence, big data, blockchain, quantum computing, neuromorphic computing, industrial Internet, information security, health care, and education. Professor Guo Dekai from the National University of Defense Technology will chair the “CNCC 2019 5G and Edge Intelligence” sub-forum, sharing more cutting-edge information about edge computing with all sectors of society.
Strategic Media Partners


Click Read Original to view the conference details↓