Source: Electric Control Knowledge Transporter
MOST is a data bus technology specifically developed for in-vehicle use, serving multimedia applications. MOST stands for “Media Oriented Systems Transport”.
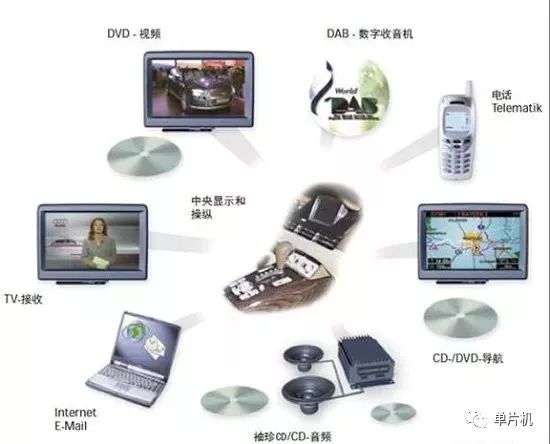
Since BMW’s 7 Series first adopted MOST (Media Oriented Systems Transport) technology, the popularity of this technology has increased rapidly in recent years, enabling real-time transmission of audio and video to meet the demands of high-end automotive entertainment systems; it can be used in driving systems such as onboard cameras.
Characteristics of the MOST Bus:
(1) Achieves a data transmission speed of 24.8 Mbit/s under low-cost conditions.
(2) Can operate regardless of whether there is a master control computer.
(3) Supports real-time processing of audio and compressed images.
(4) Supports synchronous and asynchronous data transmission.
(5) Transmitters/receivers are embedded with a virtual network management system.
(6) Supports various network connection methods, providing a standard for MOST devices, facilitating a simple and convenient application system interface.
(7) By adopting MOST, not only can the quality of the wiring harness connecting various components be reduced, lowering noise, but it can also lessen the burden on system development technicians, ultimately achieving centralized control of various devices at the user end.
(8) The optical fiber network is not affected by electromagnetic radiation interference and grounding loops.
Most bus networks connect multimedia control units through a ring data bus that transmits data in only one direction, meaning each control unit always has two optical fibers, one for the transmitter and the other for the receiver.
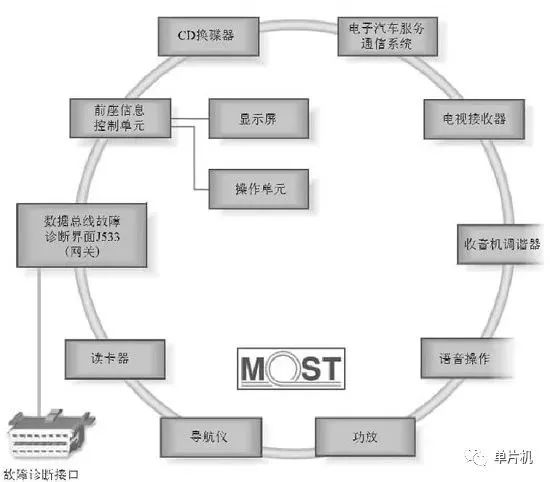
The MOST bus adopts a ring network structure.
Optical fiber connectors: The optical fiber connects to the control unit using specialized optical connectors. An arrow on the connector indicates the signal direction (to the receiver), and the connector housing forms the connection with the control unit. The optical signal enters the control unit or is transmitted to the next bus user through the optical fiber wire and connector.
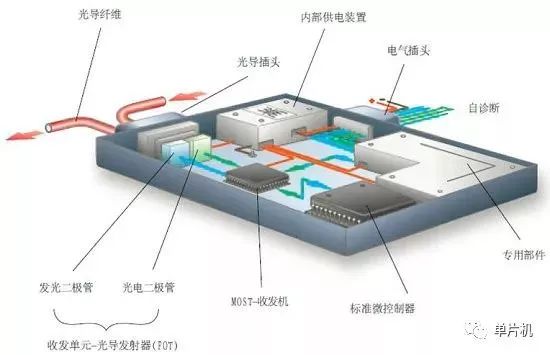
Diagram of the MOST bus control unit structure
Control unit power module: Electricity delivered by electrical connectors is distributed to various components by an internal power supply device, allowing for the individual shutdown of certain components within the control unit, thus reducing static current.
Transceiver – Optical Transmitter (FOT): This device consists of a photodiode and a light-emitting diode. Incoming optical signals are converted into voltage signals by the photodiode and sent to the MOST transceiver.
MOST transceiver: The MOST transceiver consists of two components: the transmitter and the receiver.
Control Unit (ECU): The internal structure of the Control Unit (ECU) contains a microprocessor that operates all basic functions of the control unit.
Specialized components: These components are used to control specific functions, such as CD players and radio tuners.
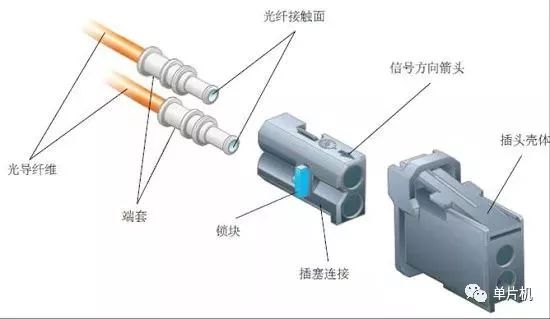
MOST bus optical fiber pull line diagram
The MOST bus uses optical pulses to transmit data. The MOST bus has a ring structure. Data can only be transmitted in one direction within the ring bus.
The transmission technology of MOST is similar to that of the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), with defined designations for data channels and control channels, where the control channel is used to set how to use and receive data channels. Once set, data will continuously flow from the sender to the receiver without further packet processing during the process, making this operational mechanism ideal for real-time audio and video streaming transmission.
MOST fully complies with the ISO/OSI 7-layer data communication protocol reference model, and in network connections, MOST adopts a ring topology. However, for more stringent control applications, MOST also allows for star (also known as radial) or dual-ring connection configurations. Furthermore, each MOST control network allows for a maximum of 64 devices (nodes) to connect.
(Images and text sourced from the internet)
Click the mini-program below to see more repair cases









