In bus systems, both RS-485 and CAN-bus are commonly used buses, each with unique characteristics and application scenarios, widely applied. Today, let’s discuss their differences.
1. What is RS-485?
RS-485 is a serial communication protocol that has been around since the mid-1980s, originally defined for industrial market applications.
It uses differential signaling with negative logic, providing good noise immunity, suitable for environments with strong interference.
The RS-485 interface is a combination of balanced drivers and differential receivers, with a maximum transmission distance of up to 1200 meters in ideal conditions, but actual usage may be shorter due to various factors.
It supports multipoint data communication and operates in half-duplex mode, meaning only one device can transmit data at a time while others must listen.
The network topology generally adopts a terminal-matched bus structure and does not support ring or star networks.
2. What is CAN-bus?
CAN-bus, or Controller Area Network bus technology, was originally developed by Bosch in Germany for automotive applications.
It is an open, digital, multipoint communication control network that effectively supports distributed control and real-time control.
The CAN bus uses a multi-master competitive bus structure, where each node can actively send information to other nodes on the network without a master-slave distinction.
It has high flexibility and real-time capability, supporting lossless bus arbitration technology to ensure high-priority nodes communicate without delay.
The CAN bus also features automatic detection of successful message transmission and automatic retransmission, providing extremely high transmission reliability.
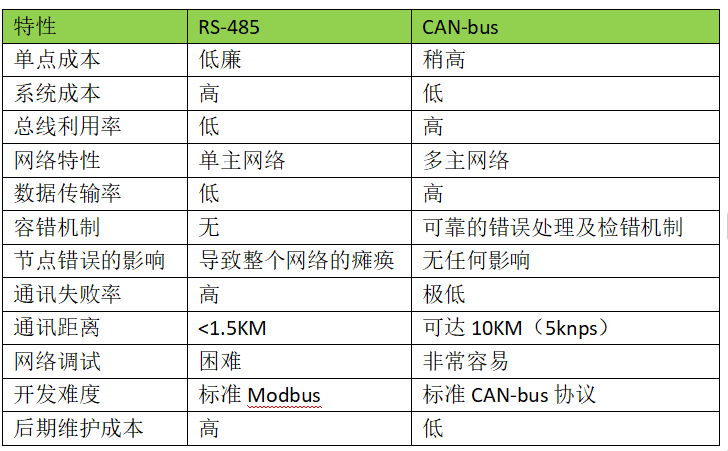
3. Differences Between RS-485 and CAN-bus
This article is an original piece by Fan Yi Education. Please indicate the source when reprinting!