Comparison of MIPI Physical Layer Protocols
-
D-PHY & C-PHY (3-phase)
-
The parallel bus uses slow edge signals at low bit rates to reduce EMI (the edge rate and EMI compliance need to be verified in ATE testing).
-
The 3-phase encoding of C-PHY requires testing for inter-symbol interference (ISI) and eye diagram symmetry.
-
The protocol specification provides aflexible, low-cost, high-speed serial interface, designed to replace traditional CMOS parallel buses.
-
Testing Focus:
M-PHY
-
Supports multiple Gear rates (multi-rate switching tests are required in ATE).
-
Current consumption testing in low power states (L1/L2).
-
Jitter tolerance verification at high bandwidth.
-
The protocol specification provides ahigh-bandwidth, low pin count serial interface technology with excellent energy efficiency.
-
Testing Focus:
-
Supports multiple Gear rates (multi-rate switching tests are required in ATE).
-
Current consumption testing in low power states (L1/L2).
-
Jitter tolerance verification at high bandwidth.
Comparison of two physical layer interfaces for different application scenarios:D-PHY (widely used in CSI-2/DSI) and C-PHY (for higher bandwidth requirements) is as follows:
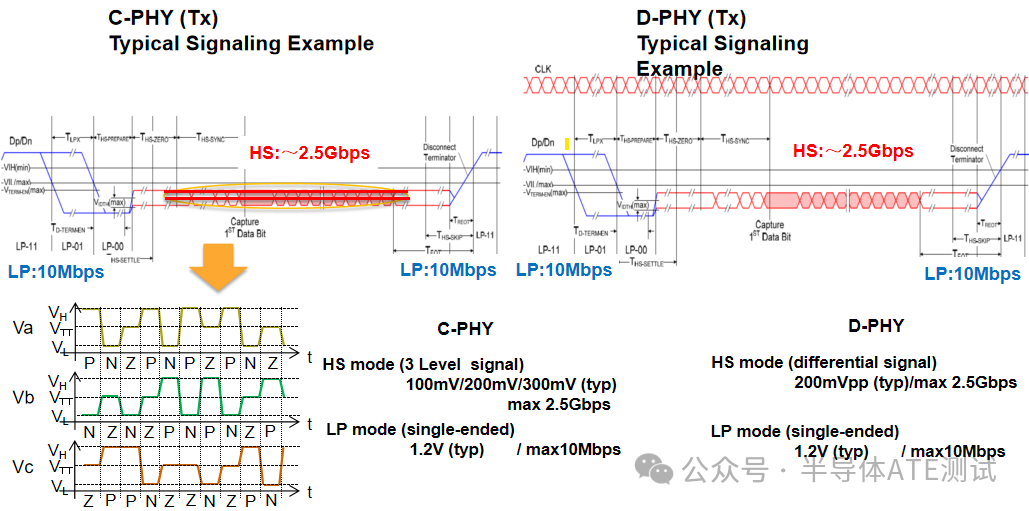
1. Electrical Characteristics and Signal Transmission
| Characteristic | D-PHY | C-PHY |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Differential signal (1 pair of Clock + 1~4 pairs of Data Lane) | Tri-State No dedicated Clock, each Lane contains 3 lines (A/B/C) |
| Modulation Method | NRZ (Non-Return-to-Zero) | 3-phase symbol encoding (1.5 bits/symbol) |
| Level Standard | Differential swing 200mV~400mV | Three levels (0/1/2), dependent on line-to-line voltage difference |
| Interference Immunity | Medium (dependent on differential pair) | Stronger (three-line redundancy, high fault tolerance) |
2. Bandwidth and Efficiency
| Characteristic | D-PHY | C-PHY |
|---|---|---|
| Single Lane Rate | 1.5Gbps ~ 4.5Gbps (HS mode) | 2.5Gsymbols/s → equivalent to 5.7Gbps (due to 1.5 bits/symbol) |
| Bandwidth Efficiency | 1bit/symbol | 1.5bits/symbol (theoretical improvement of 50%) |
| Application Scenario | 1080p@60fps camera (CSI-2) | 4K@120fps or higher resolution (e.g., multi-camera systems in smartphones) |
3. Protocol and Complexity
| Characteristic | D-PHY | C-PHY |
|---|---|---|
| Clock Requirement | Requires dedicated Clock Lane synchronization | No dedicated Clock (embedded clock into data) |
| Number of Lanes | Typically 1 Clock + 1~4 Data Lanes | Only requires 1~3 Data Lanes (saves pins) |
| Protocol Compatibility | Compatible with CSI-2/DSI standards | Requires protocol layer adaptation (e.g., CSI-2 over C-PHY) |
4. Testing Implementation
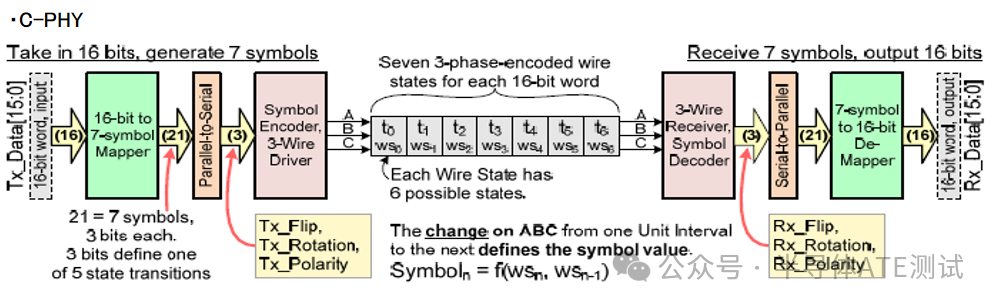
 C-PHY uses
C-PHY uses
-
3-phase symbol encoding technology (3-Phase Symbol Encoding), transmitting2.28 bits of data per symbol
-
Initial version target rate:2.5 Gsymbols/s → equivalent three-line total throughput5.7Gbps (based on existing mature protocol stack)
Advantages:Performance optimization in bandwidth-limited scenarios
-
Designed specifically for cable components and chip-on-glass (COG) display channels in bandwidth-limited environments
-
Compared to D-PHY, it can achieve a higher effective data rate under the same channel loss (ATE verification of channel tolerance is required).
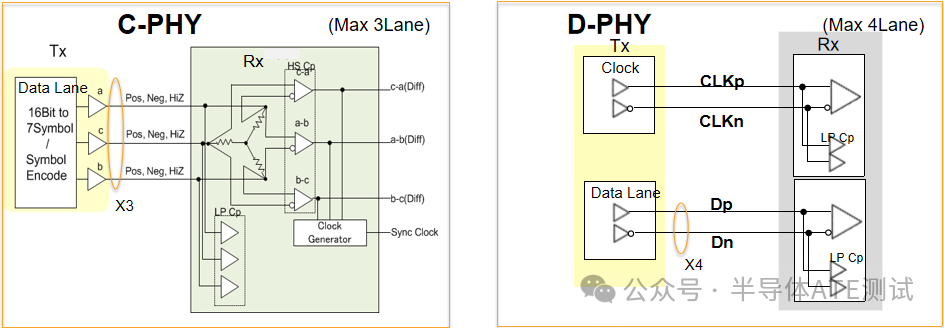
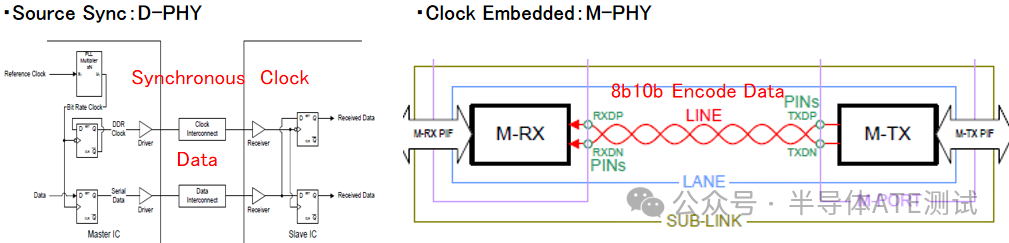
Signal Architecture Comparison
| Characteristic | C-PHY | D-PHY/M-PHY |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Signal Lines per Channel | 3 lines (A/B/C) | 2 lines (differential pair P/N) |
| Level State | Three levels (H/M/L) | Two levels (H/L) |
| Data Method | State transitions carry data (needs to compare with previous state) | Steady state levels directly carry data |
| Encoding Scheme | New 3-phase encoding | D-PHY: NRZ; M-PHY: 8b10b encoding |
How to Choose?
-
Choose D-PHY: Low complexity, cost-sensitive applications (e.g., automotive mid-low resolution cameras).
-
Choose C-PHY: High bandwidth requirements, pin-limited designs (e.g., multi-camera systems in smartphones or 8K displays).
-
Choose M-PHY: Supports multi-Gear rate switching (up to 11.6Gbps/Lane), suitable for long-distance transmission (e.g., high-speed storage/UFS interfaces, automotive SerDes).
The new generation of MIPI standards (e.g., C-PHY v3.0) is gradually replacing D-PHY, but all three may coexist for a long time.
MIPI Physical Layer and Testing ends here~