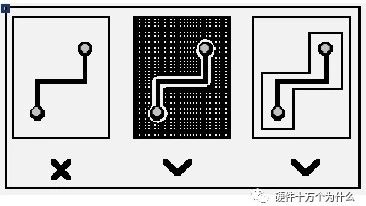
Considerations for MIPI Signal PCB Design
MIPI (Mobile Industry Processor Interface) is a core transmission standard for devices such as smartphones, tablets, and automotive systems, which includesD-PHY (used for CSI cameras/DSI displays) andC-PHY (higher bandwidth, no independent clock) physical layer protocols. Its characteristics include: Differential Signals: D-PHY includes 1 pair of clock + 1~4 pairs of data lines; C-PHY transmits embedded … Read more