Smooth Muscle Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a as a Therapeutic Target to Reverse Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension
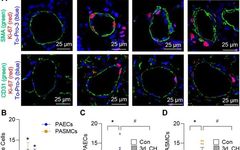
Acid-sensing ion channel 1a (ASIC1a) is a voltage-independent, non-selective cation channel that simultaneously conducts Na+ and Ca2+. The activation of ASIC1a causes depolarization of the plasma membrane, stimulating Ca2+-dependent signaling pathways in various cell types, including vascular smooth muscle (SM) and endothelial cells (ECs). Previous studies have indicated that the increase in pulmonary vascular resistance … Read more