Imagine you have two devices in front of you.
One is a laptop with a brand new 8-core computer processor chip, 64GB of RAM, a dedicated graphics card, priced at 14,999 RMB.
The other is a smartphone with a brand new 8-core mobile chip, 8GB of RAM, priced at only 4,999 RMB.
Excluding portability, if you want to buy a device for online gaming, watching 4K movies, editing photos, or cutting Vlog videos, which one do you think would be more suitable for you?
Five years ago, you might have thought that only a laptop had enough performance for high-intensity tasks like photo editing, video cutting, and playing large games.
But today, five years later, you suddenly realize: all of the above tasks can be done by a smartphone. The reason is that the performance of mobile chips has become very strong, and smartphones can fully handle tasks that laptops can do.
However, why do we still have to use a laptop that is four times heavier and twice as expensive to do things that a computer can do? This is because, although mobile chips have become powerful, smartphones have not evolved alongside them. The root cause is that mobile chips do not fully match the functionalities of smartphones.
This has led many manufacturers to wish they could create a 100% customized chip to meet user needs. Earlier, Apple switched to using its own mobile chip in its laptops, achieving remarkable efficiency, prompting many smartphone companies to decide to design their own chips.
As one of the most influential smartphone manufacturers globally, vivo also wants to have such mobile chips, but the path they have chosen is completely different from other smartphone manufacturers.
Why Are Apple Chips So Powerful?
Why did Apple’s shift to “in-house chips” shake the entire smartphone industry? The reason is that the new Apple M1 chip they use is frighteningly strong in both performance and battery life.
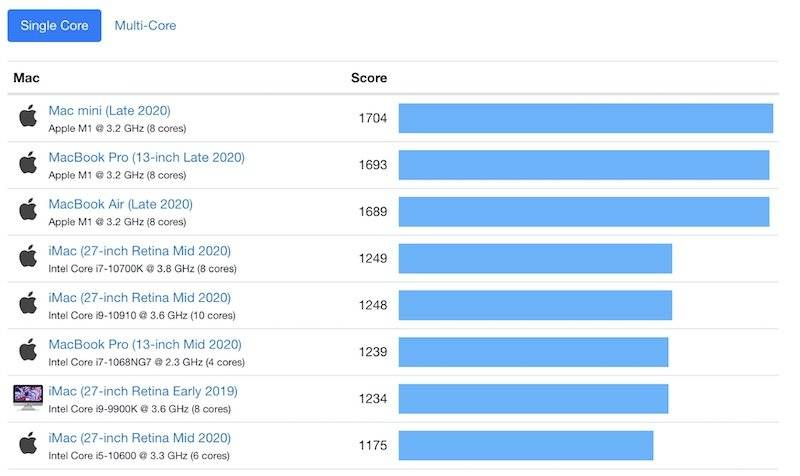
The new Apple M1 chip has the best single-core performance among currently available chips (as shown in the image above), and even its multi-core performance can be compared to top Intel server chips. At the same time, this Apple M1 chip, which performs on par with top desktop chips, has a battery life and heat generation that are far lower than those of these high-end computer chips.
For many years, people have felt that the performance of mobile chips cannot compare with that of desktop processors. However, the Apple M1 chip, based on a mobile chip architecture and designed specifically for Macs, manages to achieve such powerful performance. Thus, it is evident that mobile chips actually possess enormous potential, but mobile terminals and chip manufacturers have been unable to fully realize this potential.
Therefore, we must first discuss why Apple chips can achieve such powerful performance.
According to current mainstream analysis, the advantages of Apple chips lie in three main aspects:
· Apple chips are produced using the most advanced 5nm process, which is at least three years ahead of Intel’s 10nm process technology.
· Apple chips use what is known as a System-on-the-Chip (SoC), which integrates various computational assistance modules (such as memory and image processing) onto the chip, resulting in higher integration and greater computational efficiency.
· Apple can deeply optimize and adapt the chip for its own system.
Unfortunately, these analyses do not provide any new insights for chip manufacturers. After all, today’s top mobile chips have long adopted the most advanced process technology and highly integrated SoC designs. However, what they find most difficult to achieve is precisely what Apple excels at: deep optimization and adaptation of chips to meet the specific needs of their mobile systems.
Apple can design chips to create the strongest systems tailored for its phones and computers, as well as its own systems (as shown in the image above). However, most mobile chips used in many smartphones are purchased from pre-designed third-party companies.These chips, bought from third-party companies, have fixed performance curves and functional interfaces, making it impossible for smartphone companies to make deeper adaptations based on their specific phone conditions.
In this regard, what smartphone manufacturers currently want to achieve is to customize mobile chips for their own smartphones.
Why Do Smartphones Also Need to Change Chips?
In fact, smartphone manufacturers not only want to customize chips for their own phones, but they also have to consider the necessity of doing so. This is not only to maximize chip performance but also because many functions that off-the-shelf chips can achieve are not what smartphone manufacturers want. The functions that smartphone manufacturers desire are often not provided by these off-the-shelf chips.
Chip companies like Qualcomm or MediaTek only design chips and do not produce terminal devices. Therefore, they cannot directly interact with users and lack efficient communication channels with end users, making it difficult to accurately understand many usage scenarios and user pain points. As a result, they find it challenging to know the true needs of users and provide corresponding functions; they also cannot customize or adjust chip performance according to user habits.

For example, the Deep Fusion feature on the iPhone 11 in 2019 allowed the phone to capture very detailed images, garnering widespread attention from users. At that time, Apple’s Phil Schiller stated (as shown in the image above) that this feature was the first in smartphone history to use the Neural Engine instead of the Image Signal Processor (ISP) to output images.
However, a year later, most mobile chips on the market still did not support deep integration of the Neural Engine into ISP image processing, failing to meet user demand for this feature. As a result, many Android users could only admire the photos taken with the iPhone Deep Fusion.
However, most smartphone manufacturers have not developed their own chips like Apple; they can only continue to select suitable chips from a limited number of chip companies and try to optimize their systems to adapt to off-the-shelf chips, even at the cost of sacrificing some hardware performance.
As a result, under the limitations of mobile chips, smartphone manufacturers can only use the same few chips and the same few system interfaces to achieve the same few functions, leading to a serious degree of homogenization, making it difficult for smartphone manufacturers to achieve true innovation.
Users May Not Wait for Self-Developed Chips
Smartphone manufacturers are well aware of the problem, which is why they are all learning from Apple and embarking on the path of self-developed chips, hoping to break free from the limitations of chip manufacturers. Undoubtedly, they are on the right path, but the correct path is often the most difficult one. Huawei, which also has the capability to develop its own chips, understands this difficulty best.
Huawei has been developing its own chips for 11 years. They began developing mobile chips in 2009, but the initial chips they launched were far from expectations (as shown in the image above). It wasn’t until around 2016 that Huawei’s self-developed chips began to gain more recognition.
Although today’s Huawei mobile chips have gained recognition from many, many people forget how difficult their initial journey was.
In fact, just because a mobile company decides to develop its own chips does not mean that the chips they develop will necessarily be good. Developing self-made chips is incredibly difficult; without investing billions and spending 5 to 10 years, it is impossible to achieve significant results.
After all, during the arduous process of self-development, mobile companies either sell their still rough initial self-developed products or sell phones limited by off-the-shelf chips that cannot meet users’ true needs. As a result, these manufacturers spend a lot of money, but their competitiveness actually decreases.
But while manufacturers are repeatedly failing and trying again, will users accept your failed products? Are they willing to wait for your eventual success in self-development? We do not know if users have the patience to wait, but the leaders of mobile companies must endure for a long time.
In 2014, Xiaomi’s Lei Jun understood that “the chip industry starts at 1 billion and results in 10 years,” but resolutely embarked on the path of self-developed chips, and in 2017 finally launched the Surge S1 chip (as shown in the image above). However, during the development of the Surge S2 chip, it was reported that there were five failed trial productions, leading to significant delays. When Qualcomm launched a new generation of Snapdragon mobile chips with better performance, Lei Jun could only return to compete for the launch of the new generation of Snapdragon phones.
This time, Xiaomi’s chip trial production failure is estimated to have burned about 130 million RMB, and this does not even account for the billions in upfront R&D costs. However, if Xiaomi had initially invested this wasted tens of millions in R&D for camera algorithms and communication technology, they might have produced a higher quality, more attractive Xiaomi phone and would not have lost significant market share to Huawei and Honor during the 2016-2019 period.
But even if you are willing to spend money and wait, it is still not easy. OPPO is another example. Earlier, it was rumored that they launched a self-developed chip plan called “Mariana,” choosing to step into the world’s deepest “trench”.
However, chip design is currently one of the most technically advanced fields globally, and excellent engineers with relevant skills are extremely scarce. Even when Apple had strong technology, they still had to acquire chip companies to find enough excellent engineers for their self-developed chips.
Therefore, regardless of OPPO’s strong R&D capabilities, mobile engineers still do not understand chip design; they can only slowly poach talent from chip companies like Spreadtrum and MediaTek.
The true expertise of mobile companies lies in their years of experience in developing terminal devices and understanding the needs of end users.
But now, abandoning their existing expertise and rushing into the world’s most specialized industry, can they really bring sufficient benefits to users?
The True Expertise of Smartphone Manufacturers
In fact, the goal of smartphone manufacturers is simply to have chips that naturally fit consumer needs; “self-development” is just one method, not the only method.
Therefore, vivo has chosen to collaborate with Samsung, bringing their years of understanding of consumer usage scenarios and real needs to the chip definition stage, helping Samsung create mobile chips that are more suitable for users.
After all, projects as highly specialized as chips need to be handled by specialized industries. And like vivo, a terminal smartphone manufacturer, is responsible for its own expertise, which is “the user.”
Since terminal manufacturers are directly facing users, they certainly know better than chip companies what users need and what their usage habits are. They know in what situations users feel that performance is insufficient and when they feel that the device overheats.
Therefore, as long as vivo exchanges information sufficiently with Samsung, they cancreate the functions that users need and adjust the chip’s performance curve according to user habits, further optimizing the system to achieve both strong performance and long-lasting battery life under limited conditions.
Indeed, no matter how powerful a mobile chip is, it ultimately requires smartphone manufacturers to exercise their imagination, flexibly allocate functional interfaces, integrate various new hardware, and adjust various algorithms and parameters to bring applications to fruition, allowing users to experience the related benefits. It is evident that mobile terminal products also require sufficient R&D capabilities to unleash the powerful performance of chips.
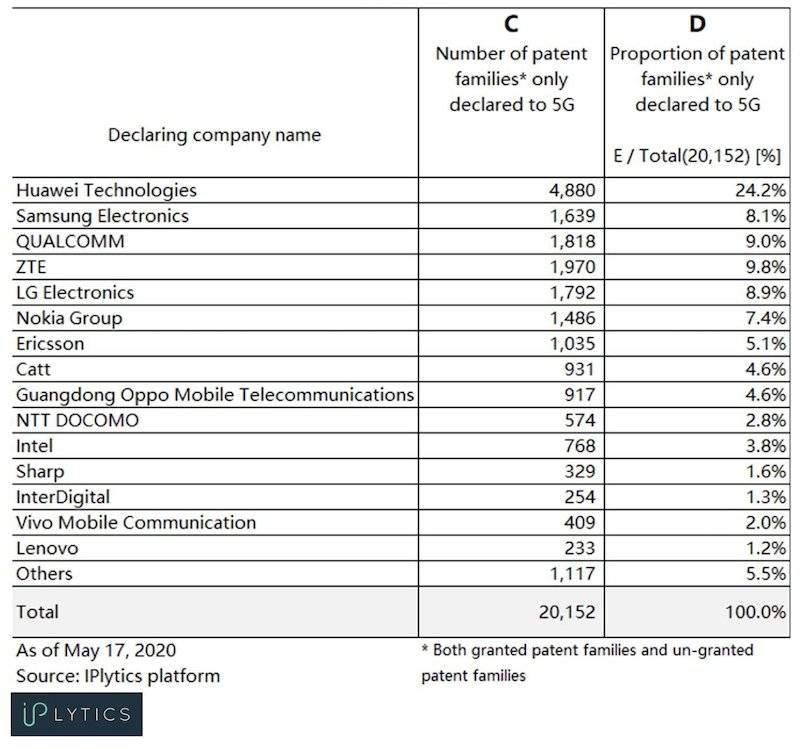
vivo’s years of experience in mobile terminals have allowed them to accumulate a wealth of technology at the application level. For example, in the 5G field, they have quietly climbed to the top 15 in the global 5G patent rankings (as shown in the image above) and developed technologies such as multi-antenna side distribution and antenna decoupling.
Additionally, vivo has repeatedly launched phones using new technologies such as micro-gimbals, in-screen fingerprint recognition, and RAW domain noise reduction. As long as vivo integrates these technologies into chip design, they can optimize at the chip level and further improve user experience.
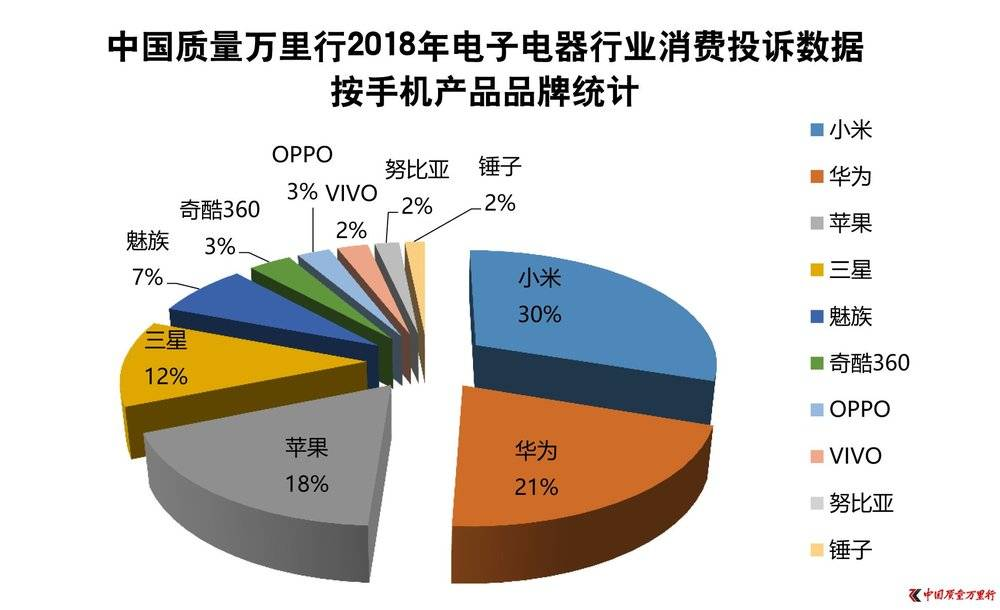
How well does vivo understand its users? The image above shows the proportion of mobile complaints received by the China Quality 10,000 Miles Consumer Complaint Platform in 2018, where vivo accounted for only 2% of the 4,378 mobile complaints. Considering that at that time, vivo held a 19% share of the Chinese smartphone market, higher than Apple, Xiaomi, and Samsung, but received very few complaints, it is evident that manufacturers like vivo, which focus on the mobile business, have a deeper understanding of Chinese users.
Collaborative Innovation Upgrades User Experience
Last year, vivo, which understands users better, attempted to collaborate with Samsung, launching the first batch of dual-mode 5G Exynos 980 mobile chips.
This year, vivo collaborated with Samsung again, not only helping Samsung bring consumer needs to the forefront of chip design definition but also launching the flagship-level powerful chip—Exynos 1080—in the X60 series.

In addition, vivo addressed the power consumption issues caused by 5G large data traffic and scattered background application transmissions by incorporating a CP-engine and multi-transmission mode architecture into the chip, optimizing power consumption. As a result, terminals equipped with the Exynos 1080 can achieve 20% less power consumption compared to the vivo X30.
Moreover, vivo discovered that the refresh rate of high-refresh screens does not completely match the actual refresh rate of games, leading to “frame mismatch” issues that cause users to feel stuttering and broken images. In response, vivo introduced dynamic frame rate adaptive technology on the Exynos 1080 for the first time, allowing the frame rate of game content to better match the screen refresh rate, avoiding stuttering caused by frame mismatch and providing users with a smoother gaming and video experience.
vivo also exclusively customized a new AISP architecture for the Exynos 1080, integrating the neural processing unit and artificial intelligence deeply into the ISP, allowing for intelligent adjustment of various parameters to optimal values through machine learning on the original RAW domain, enabling the ISP to better adjust white balance, exposure, color, saturation, and clarity, allowing users to easily take professional-grade photos.

There are many other performance improvements that I will not list here. However, the improvements mentioned above are almost all aimed at addressing the power consumption and stuttering issues brought about by the previous rush of manufacturers to launch 5G and high-refresh-rate phones, as well as finally achieving the deep collaboration between the neural processing unit and ISP that was not realized before.
All of this can only be achieved through the deep understanding of users by vivo and the years of experience in semiconductors by Samsung, working together to solve these long-standing pain points at the chip level.
More importantly, since the 5nm process technology is the most advanced yet also the most challenging chip technology, current production capacity is very limited. The vivo X60 series, which will be equipped with the Exynos 1080 chip, has obtained the first launch priority for Samsung’s 5nm process technology, ensuring access to the scarce advanced process capacity, allowing users to experience the powerful performance brought by 5nm chip technology earlier.
Not the Best Solution, But the Best Solution for Users
Every terminal manufacturer wants to have a mobile chip that is 100% compatible with their phones and can unleash 100% of the phone’s potential. Therefore, every terminal manufacturer also wants to emulate Apple by developing powerful mobile chips on their own.
However, since mobile chips involve highly specialized technology, manufacturers must invest significant funds and R&D personnel, but it is impossible to achieve good results in a short time. Therefore, they have to reduce R&D funding that could improve user experience and let users use immature self-developed products.
This is a huge gamble for smartphone manufacturers.
Undoubtedly, the collaboration plan between vivo and Samsung may not be the most ideal solution, but it is currently the most efficient and maximizes user benefits.
By leveraging each other’s strengths, they can significantly improve user experience without sacrificing users’ short-term interests, making it a solution that is best for users.
Special Planning