
Xinhua Finance Observation | The Balance of Smart Watches
Currently, smart watches have become the “new favorite” for health monitoring due to their portability. From simple heart rate and blood oxygen monitoring to complex sleep analysis and disease risk prediction, smart watches offer users a new experience in health management. According to analysis firm Canalys, the global wearable wrist device market is expected to achieve steady growth in 2024, with shipments reaching 193 million units, a year-on-year increase of 4%. In 2024, China will remain the largest market for wearable wrist devices, accounting for 30% of global shipments, with a year-on-year growth of 20%. Driven by the “national subsidy” policy, the sales of smart watches and wristbands have significantly increased. Research firm IDC also reported that online sales of smart wrist devices in China are expected to exceed 30 million units in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 23%.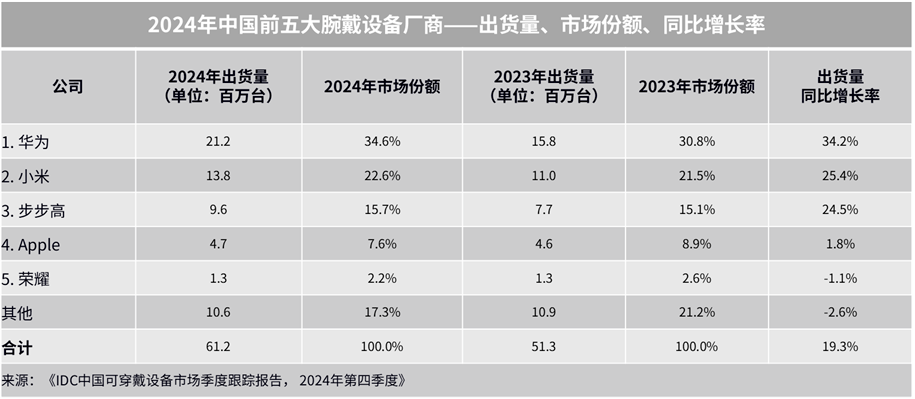 2024 China Top Five Wearable Device Manufacturers Ranking Source: “IDC China Wearable Device Market Quarterly Tracking Report, Q4 2024”However, alongside the improvement in technological convenience, the risks of “health anxiety” and data misjudgment caused by over-reliance are gradually becoming apparent. Senior analyst Anshika Jain from research consultancy Counterpoint stated that in the past year, accuracy has been the most important factor influencing consumers’ purchase of health features in smart watches. Finding a balance between technological convenience and user autonomy has become a key topic worth exploring in depth.
2024 China Top Five Wearable Device Manufacturers Ranking Source: “IDC China Wearable Device Market Quarterly Tracking Report, Q4 2024”However, alongside the improvement in technological convenience, the risks of “health anxiety” and data misjudgment caused by over-reliance are gradually becoming apparent. Senior analyst Anshika Jain from research consultancy Counterpoint stated that in the past year, accuracy has been the most important factor influencing consumers’ purchase of health features in smart watches. Finding a balance between technological convenience and user autonomy has become a key topic worth exploring in depth.
1
Technological Convenience:
Advantages of Health Monitoring in Smart Watches
The health monitoring functions of smart watches cover a wide range, such as heart rate, blood oxygen, and sleep monitoring, which have become standard features in most smart watches. Blood pressure, which once required professional equipment to measure, can now be conveniently monitored by smart watches for daily health management of hypertension patients. Moreover, smart watches are continuously exploring more advanced functions. For example, through built-in photoplethysmography sensors, smart watches can monitor users’ heart rate changes in real-time and issue warnings in case of abnormalities; or, leveraging AI technology, some smart watches can predict mental illnesses by analyzing users’ daily behavior data. The “Chinese Expert Consensus on the Application of Smart Wearable Devices in Blood Pressure Management for Young and Middle-aged People,” co-authored by the Chinese Hypertension Alliance and the Cardiovascular Metabolic Medicine Professional Committee of the Beijing Hypertension Prevention and Treatment Association, recommends “long-term monitoring through smart wearable devices to assess short-term, long-term, and seasonal blood pressure variations, and sharing data with doctors during consultations for reference in diagnosis and treatment; also considering the use of smart wearables for heart rate and arrhythmia (atrial fibrillation) monitoring, and vascular elasticity evaluation to timely detect arrhythmias, arterial stiffness, and other cardiovascular changes for early intervention and prevention of cardiovascular diseases.” The collaboration between smart watches and the medical field has yielded fruitful results. Professor Guo Yutao from the PLA General Hospital stated that exploring heart health research in collaboration with enterprises is a study aimed at proactive health management using smart wearable devices, with the initial intention based on PPG technology (photoplethysmography) to accurately screen for atrial fibrillation, creating possibilities for early diagnosis and treatment. However, for clinical doctors, the ultimate goal is to utilize trusted wearable devices for better comprehensive management of patients. IDC China Research Director Pan Xuefei noted that the elderly population has a more pronounced demand for chronic disease and medication management, and in many cases, they are not the decision-makers for purchases, but are instead chosen by their children. A user from Beijing, Mr. Zhou, said: “For health reasons, my children bought me a smart watch. After wearing it for a while, the watch showed abnormal blood pressure values. Although I was skeptical about the blood pressure readings, I went to the hospital for a check-up, and the results confirmed I indeed had high blood pressure.” During field interviews, many users like Mr. Zhou discovered health issues and sought timely medical attention through wearing smart watches.
2
Controversies and Risks:
Over-reliance and Data Misjudgment
Although smart watches excel in monitoring certain specific functions, over-reliance has also brought about negative effects. For instance, normal heart rate fluctuations may be misinterpreted as a heart attack, leading to unnecessary panic. Professor Liu Jing from Peking University People’s Hospital stated in an interview that for doctors, the greatest significance of wearable devices lies in their ability to record continuous, dynamic physiological data, especially when abnormalities occur, allowing for immediate electrocardiogram recording. The medical community generally believes that the data from smart watches should only serve as preliminary references and not as professional medical diagnoses. Smart wearable devices are rapidly evolving with technological updates, but the measurement accuracy, sensor capabilities, and algorithm levels of products remain uneven. Experts in related fields point out that a large number of unverified and uncertified smart wearables, such as wristbands and watches, flood the market, providing inaccurate parameters like blood pressure, which can lead to inappropriate medical consultations and anxiety among patients, causing certain troubles in clinical settings. Currently, on shopping platforms, smart watches range from dozens to hundreds or even thousands of yuan, all claiming to offer health monitoring functions. How should consumers choose such wrist-worn smart devices? Image showing part of the smart watch search page on e-commerce platformsAccording to Dong Guiguan, a senior engineer at the China Electronics Standardization Institute, most smart watches on the market are produced through OEM, and their quality depends on the brand’s requirements and the manufacturer’s capabilities. He stated: “When purchasing a smart watch, it is advisable to choose well-known brands. Brands that have not been certified by the market are more likely to produce inaccurate data or misjudgments, and the erroneous alerts they issue may lead users to undergo unnecessary medical interventions, wasting medical resources and potentially harming users’ physical and mental health.” Additionally, the privacy and security of users’ health data cannot be overlooked. In the digital age, data is akin to personal “digital assets”; once leaked, it may be exploited by malicious actors, causing unexpected losses to users. Dong Guiguan stated that China’s Data Security Law and Personal Information Protection Law clearly stipulate requirements for the collection, storage, processing, and transmission of personal health data. This requires manufacturers to consider not only the product’s functions and performance but also to establish necessary security mechanisms to enhance privacy protection, data security, and user control, ensuring product compliance and increasing user trust.
Image showing part of the smart watch search page on e-commerce platformsAccording to Dong Guiguan, a senior engineer at the China Electronics Standardization Institute, most smart watches on the market are produced through OEM, and their quality depends on the brand’s requirements and the manufacturer’s capabilities. He stated: “When purchasing a smart watch, it is advisable to choose well-known brands. Brands that have not been certified by the market are more likely to produce inaccurate data or misjudgments, and the erroneous alerts they issue may lead users to undergo unnecessary medical interventions, wasting medical resources and potentially harming users’ physical and mental health.” Additionally, the privacy and security of users’ health data cannot be overlooked. In the digital age, data is akin to personal “digital assets”; once leaked, it may be exploited by malicious actors, causing unexpected losses to users. Dong Guiguan stated that China’s Data Security Law and Personal Information Protection Law clearly stipulate requirements for the collection, storage, processing, and transmission of personal health data. This requires manufacturers to consider not only the product’s functions and performance but also to establish necessary security mechanisms to enhance privacy protection, data security, and user control, ensuring product compliance and increasing user trust.
3
The Path to Balance:
Mutual Pursuit of Technological Rationality and Humanistic Care
In response to the aforementioned issues, enterprises and medical institutions are actively participating in actions to explore solutions together.
It is reported that multiple brands are increasing R&D investment, continuously overcoming technical challenges, promoting the development of medical-grade functions, and applying for numerous patents related to health monitoring.
Recently, the Huawei WATCH D2 received a Class II medical device registration certificate, which can be purchased using personal accounts under the policy regulations. The national subsidy policy for electronic consumer products has also benefited more consumers; when purchasing any smart watch on the JD shopping platform, consumers can enjoy a 15% discount by claiming a smart watch subsidy. A smart watch that previously cost 2499 yuan can now be purchased for 2124.15 yuan after the national subsidy. Currently, the smart watch market still has regulatory gaps and lacks unified industry standards, leading to some unverified devices exaggerating their claims and misleading consumers. The lack of unified standards and interfaces between wearable devices of different brands and operating systems also troubles application developers. Dong Guiguan stated that strengthening standardization in the wearable electronics field is essential. On one hand, unified standards can improve the reliability and credibility of data, providing consumers with a better user experience while enhancing privacy protection and compliance; on the other hand, standardized data formats facilitate data interoperability among medical institutions, health platforms, and the insurance industry, promoting the development of the health management ecosystem. Additionally, unified standards can lower technical barriers, promote product interconnectivity, and foster cooperation and competition among manufacturers, preventing bad products from driving out good ones and supporting healthy industry development. Establishing and improving industry norms is also urgent. Dong Guiguan stated that the China Electronics Standardization Institute is currently working on the formulation of a standard system for wearable electronics and drafting national standards. To achieve a balance between technological convenience and user autonomy, users must clearly understand the positioning of smart watches in health management; they are merely auxiliary tools and cannot replace professional medical diagnoses. To help users rationally view monitoring data and avoid falling into health anxiety, psychological intervention mechanisms can also be introduced. For example, adding an “anxiety prompt” function in smart watches can provide timely reminders to users who frequently check data or show excessive concern about abnormal data, guiding them to remain calm and rational in dealing with data fluctuations. Smart watches represent an innovation in the field of health monitoring, making health management more convenient and efficient, allowing people to grasp their physical conditions in real-time, and promoting the popularization of health management concepts. However, it is also crucial to recognize that while technology is powerful, it should not be blindly relied upon.
Enterprises, users, and medical institutions need to work together to build a health management model of “technology assistance + professional guidance.” Dong Guiguan stated that enterprises should enhance their technical capabilities to ensure data accuracy and security; users should rationally view the monitoring data from smart watches; and medical institutions should fully explore the value of smart watch data to provide users with more precise and considerate health services. Only in this way can users enjoy the convenience brought by technology while firmly grasping their health autonomy, allowing smart watches to truly become effective assistants in safeguarding health rather than sources of anxiety.
Source: Xinhua Net
Reporters:Zhou Jingjie Zheng Wei

Follow!