
Semiconductor
Chip
What is a semiconductor chip?
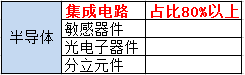
Internal Structure of Semiconductor Chips


(1) System Level




(2) Module Level


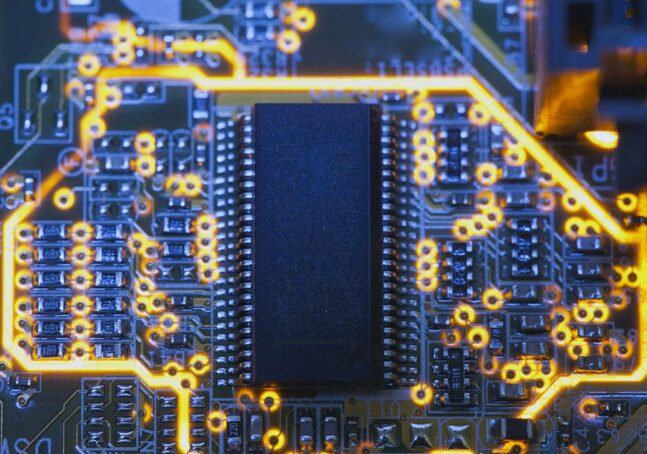


(3) Register Transfer Level (RTL)




(4) Gate Level




(5) Transistor Level


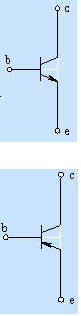
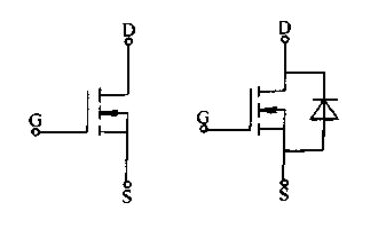
-
Method 1: Scan the QR code below to enter the page

-
Method 2: 18510898133 (WeChat) Li Jingli
Welcome to share



