Polarized components require special attention throughout the PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) processing, as incorrect orientation of polarized components can lead to mass failures and the complete failure of the PCBA board. Therefore, it is crucial for engineering and production personnel to understand SMT polarized components.
1. Definition of Polarity
Polarity refers to the positive and negative terminals of a component or the first pin being aligned with the positive and negative terminals on the PCB. If the orientation of the component does not match that on the PCB, it is referred to as reverse polarity.
2. Methods for Identifying Polarity
1. Chip Resistors (Resistor) are non-polarized

2. Capacitors (Capacitor)
2.1 Ceramic capacitors are non-polarized

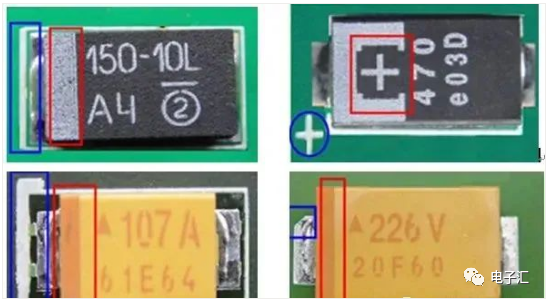
2.2 Tantalum capacitors are polarized. The positive terminal on the PCB and component is indicated by: 1) color band; 2) ‘+’ sign; 3) angled marking.
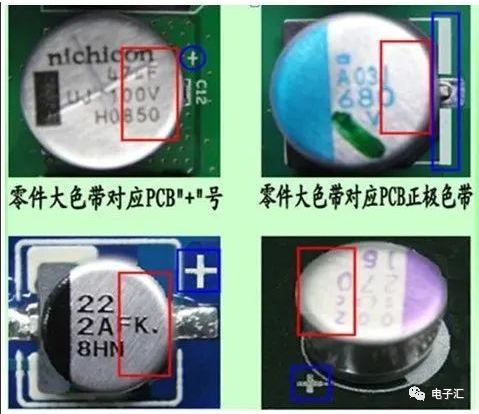
2.3 Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are polarized. The component marking indicates: color band represents negative; PCB marking: color band or ‘+’ sign represents positive terminal.
3. Inductors (Inductor)
3.1 Chip coils and similar two-terminal packages have no polarity requirements
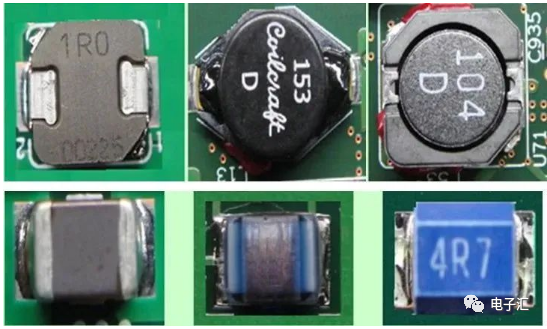
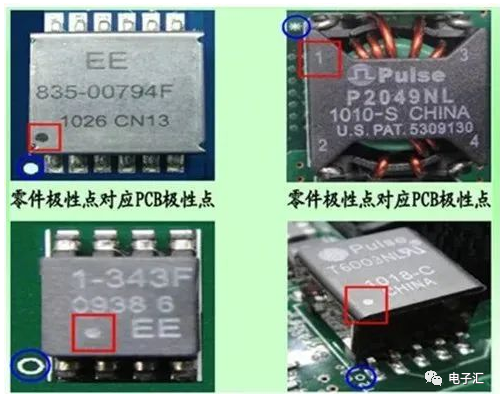
3.2 Multi-pin inductors have polarity requirements. Component marking: dot/’1′ indicates polarity point; PCB marking: dot/circle/’*’ indicates polarity point.
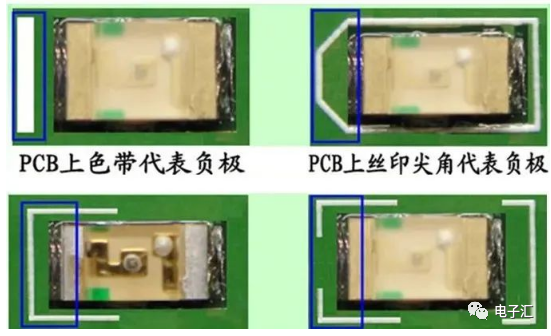
4. Light Emitting Diodes (LED)
4.1 SMT surface mount LEDs are polarized. The negative terminal of the component is indicated by: green for negative; PCB negative terminal indicated by: 1) vertical bar; 2) color band; 3) pointed silk screen; 4) ‘匚’ frame in silk screen.
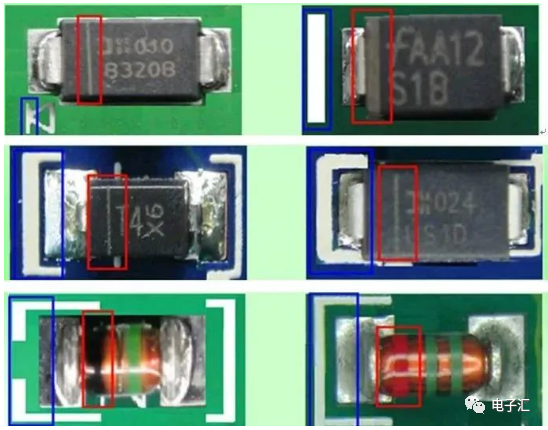
5. Diodes (Diode)
5.1 SMT surface mount two-terminal diodes are polarized. The negative terminal of the component is indicated by: 1) color band; 2) groove; 3) color marking (glass body); PCB negative terminal indicated by: 1) vertical bar; 2) color band; 3) pointed silk screen; 4) ‘匚’ frame marking.
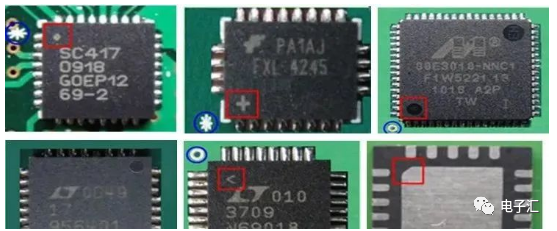
6. Integrated Circuits (Integrated Circuit)
6.1 SOIC type packages are polarized. Polarity marking: 1) color band; 2) symbol; 3) indentation/groove; 4) slanted edge.

6.2 SOP or QFP type packages are polarized. Polarity marking: 1) indentation/groove marking; 2) one point differs in size/shape from the other two/three points.

6.3 QFN type packages are polarized. Polarity marking: 1) one point differs in size/shape from the other two points; 2) slanted edge marking; 3) symbol marking (horizontal bar/’+’ sign/dot).
7. Ball Grid Array (BGA)
7.1 Component polarity: indentation/groove marking/circle marking; PCB polarity: circle/dot/letter ‘1 or A’/slanted marking. The component polarity point corresponds to the polarity point on the PCB.
 |
Sharing technical articles, news, and communication meetings related to electronics Subtle progress every day Gathering electronic technology |