
Click here to download the materials (3rd update)

We are giving away materials, copy and reply with the following keyword to receive them
Material Collection



About Today’s Post
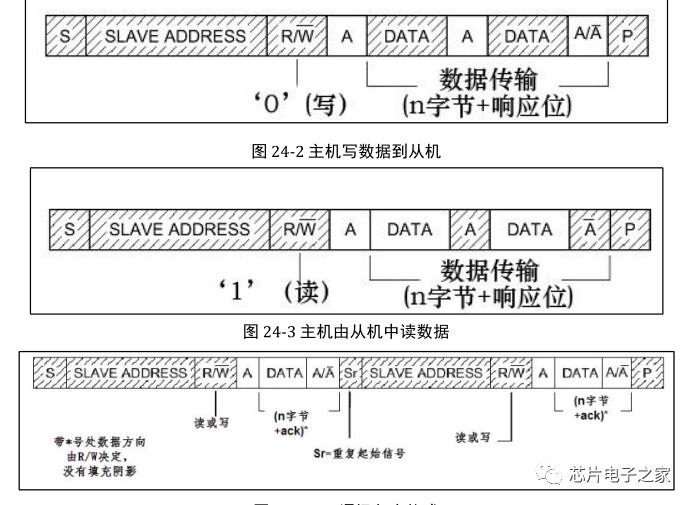


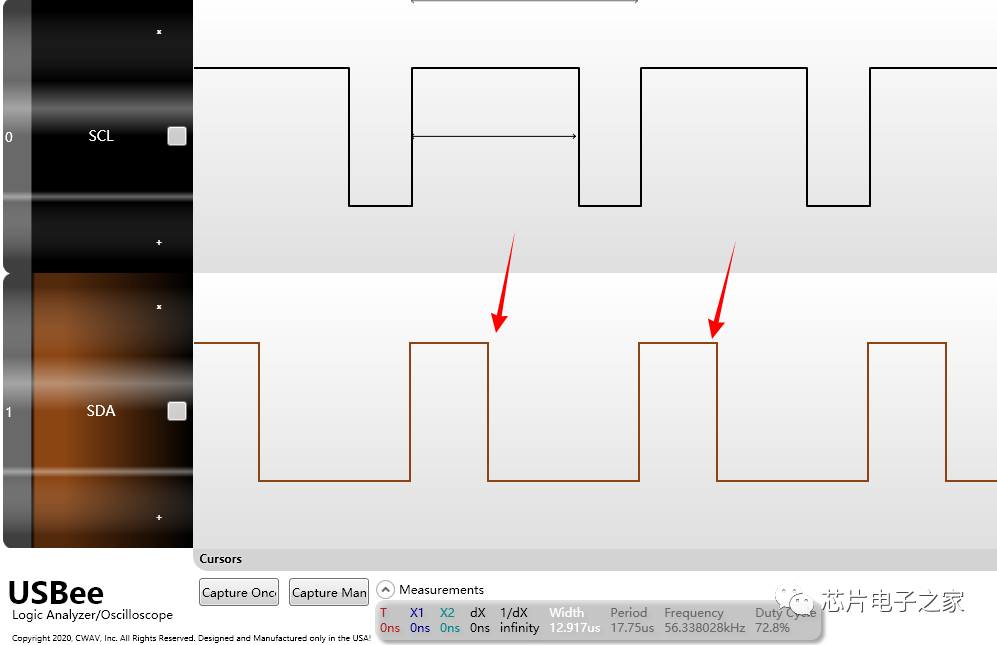
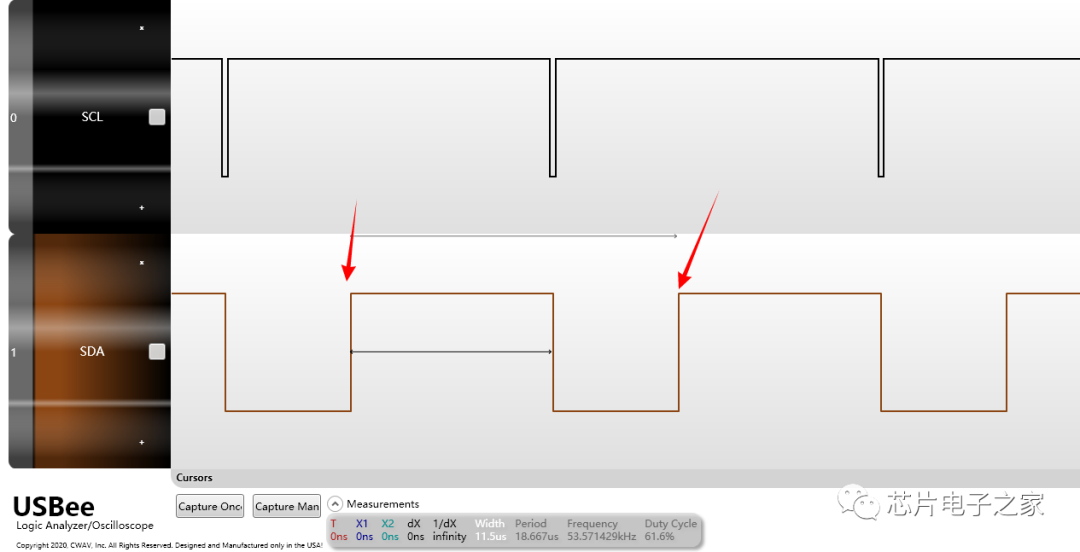
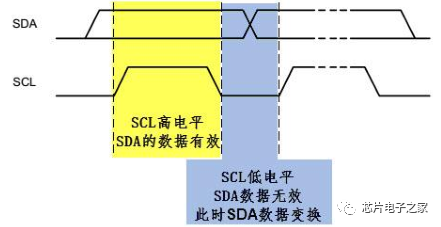
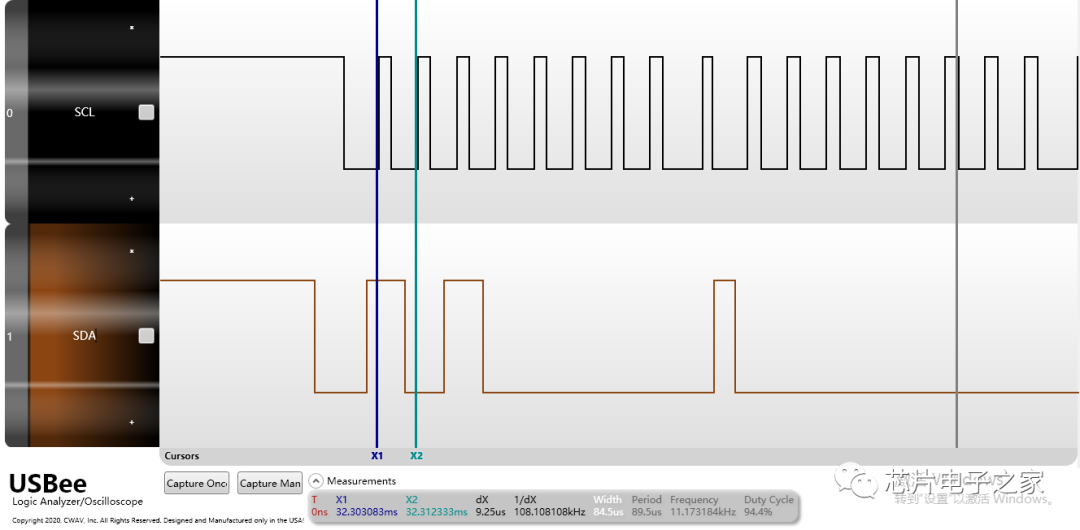
Each device on the I2C bus has its own unique address. When the master initiates communication, it sends the device address (SLAVE_ADDRESS) via the SDA signal line to locate the slave.
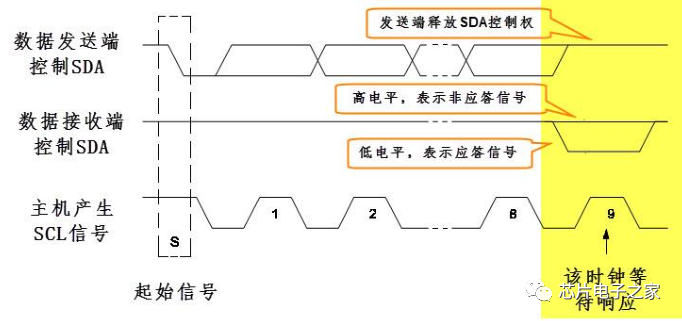
During transmission, the master generates the clock, and at the 9th clock cycle, the data sender releases control of the SDA, which is then controlled by the data receiver. If SDA is high, it indicates a not acknowledge signal (NACK); if low, it indicates an acknowledge signal (ACK).
—Click below for keyword search—
(Disclaimer: This article is compiled for the purpose of disseminating relevant technical knowledge, and some collected materials are copyrighted by the original authors)



Previous Highlights
▲Multisim Simulation Example Materials
▲Electronic Circuit Videos | Analog and Digital Electronics Learning Improvement
▲300 Sets of Electronic Circuit Analysis | Video Animated Tutorials
▲Switching Power Supply Video Repair Tutorial | 164 Series
▲Mini Program Development Technical Tutorial
▲Electronic Circuit Hardware Design Switching Power Supply Analog and Digital Design Video DIY Hard Tutorial
▲PCB Design Routing Details Explained (Text and Image Combined | Highly Recommended)
▲PCB&&||USB Differential Routing Experience and Lessons Learned
▲0 Ohm Resistor Usage Finally Summarized
▲PCB—The Role of Serpentine Lines, Explained
▲Should Power Inductors Have Copper Coverage?
▲Teaching You How to Design Schematics
▲Introduction to the Principles and Applications of Varistors, Discharge Tubes, Zener Diodes, and TVS
▲The Principles and Differences of DC-DC and LDO
▲Question: Why Does This Circuit Burn Out the MOSFET?
▲Reading Datasheets for Components, It Took Me a Long Time to Understand How to Read Them
▲Common Tips for Circuit Board Repair
▲MATLAB Made a Love Declaration Tool with Code
▲Introduction to the Principles of Lithium Battery Protection Boards
▲Essentials to Consider When Designing LDOs
▲Usage of Transistor and MOSFET Driver Circuits
▲How to Consider Analog Ground and Digital Ground in Circuit Design
▲Layout Considerations for Power Supply Boards
▲100 Knowledge Points on PCB Layout and Routing | Video Included
▲60 Essential Skills for Circuit Design
▲Detailed Explanation of Voltage Followers
▲MOSFET, Just Discussing How to Apply It
▲Design of Pyroelectric Infrared Sensor Amplifier Circuits
▲Deep Learning Switching Power Supply
▲Common Circuits for Voltage Comparators
▲12th Freescale | Remembrance
▲C Language | Unions, Structures
▲Design of a Pyroelectric Detection Circuit
▲Some Thoughts on Switching Power Supply Layout
▲STM32 Driving 16-bit ADC
▲Disassembly of Huawei Mobile Phone Power Supply #Process
▲Selection of Power Supply Chips
▲Precise Current Direction Analysis Starting from Capacitor and Inductor Formulas
▲Starting and Automatic Shutdown of LDO
▲Large Current Analysis Starting from Capacitor and Inductor Formulas
▲Microcontroller Driving MOSFET Circuit Applications
▲Differences Between Transistors and MOSFETs in Circuit Design
▲How to Make the 7805 Output Voltage Reach 10V
▲Switching Circuit to Achieve Crystal Oscillator Shutdown Function
▲How to Understand Input and Output Capacitors in LDOs
▲These Two Capacitors and Resistors in Switching Power Supplies
▲All Buffer Absorption Circuits in Switching Power Supplies
▲Tips for Using 10uF and 0.1uF Capacitors in Parallel