1. Introduction
In the field of game development, Unity has always been a favorite among many developers. With the continuous advancement of technology, developers are beginning to explore how to combine Unity with cutting-edge computing technologies to further tap into the potential of game performance. The emergence of the Unity ECS (Entity Component System) architecture provides a new approach to game performance optimization. This article will delve into the Unity ECS architecture and combine it with Ascend NPU heterogeneous computing, sharing insights on performance optimization.
2. Overview of Unity ECS Architecture
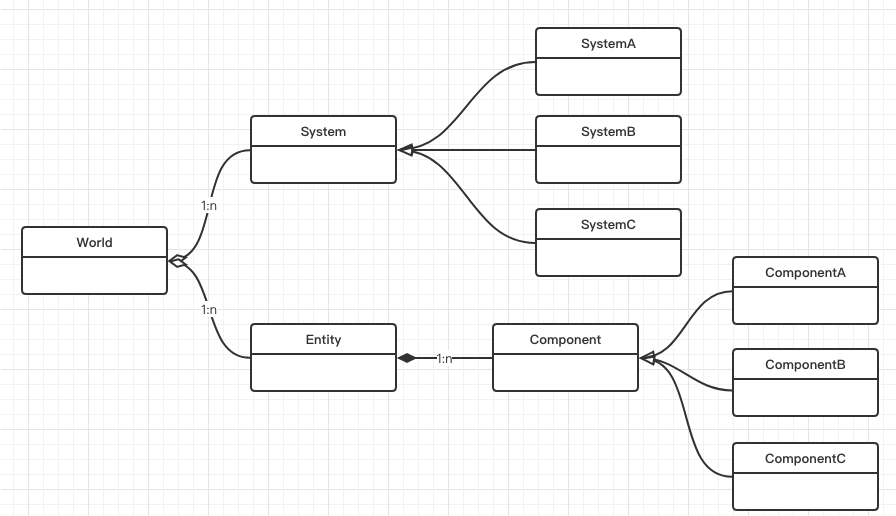
Figure 1: ECS Architecture Diagram
2.1 Entity
An entity is a unique identifier for a game object, containing no data or behavior, and serves only as a container for components. In Unity, entities are typically represented by integer or long integer IDs. Simply put, an entity is like an empty container waiting for us to add various attributes and behaviors.
Code example:
public struct Entity { public int id; }2.2 Component
A component is a pure data structure used to describe specific attributes of an entity, such as position, velocity, etc. The design of components follows the single responsibility principle, meaning each component is responsible for a specific aspect. For example, the Position component contains only the position information of the entity.
Code example:
public struct Position { public float3 Value; }2.3 System
A system is responsible for processing logic by operating on entity components and implementing functionality. Systems typically filter entities based on the combination of components. For example, a movement system entity can update its position based on the Position and Velocity components.
Code example:
public class MovementSystem : SystemBase { protected override void OnUpdate() { Entities.ForEach((ref Position pos, in Velocity vel) => pos.Value += vel.Value * Time.DeltaTime).Schedule(); }}3. Job System and Parallel Processing
The ECS architecture uses the Job System to process game entities, and its parallelization feature lays a solid foundation for enhancing game performance.
- Declare a struct that implements the IJob interface
- Add blittable types or NativeContainer type member variables
- Implement the Execute method
When a Job executes, Execute runs once on a core
public struct MyJob : IJob { public float a; public float b; public NativeArray<float> result; public void Execute(){ result[0] = a + b; }}3.1 JobSystem Working Principle
The JobSystem manages work threads in a multi-core environment, typically assigning one work thread per logical core to avoid context switching. The JobSystem holds a Job queue, from which work threads fetch Jobs to execute. A Job is a small unit of work that performs a specific task and can have dependencies.
Creating a Job requires implementing the Execute method, while scheduling a Job is done by calling the Schedule method. The Schedule method can only be called on the main thread, placing the Job in the queue for execution. Once a Job is scheduled into the queue, it cannot be interrupted.
3.2 IJobParallelFor Optimization
IJobParallelFor is a method in the JobSystem used to handle batch tasks. When scheduling a ParallelFor Job, the total length of the scheduled task and the batch length must be specified. The C Job# System divides the total length of tasks into batches based on the batch length and places them into the Unity Job queue, executing each batch synchronously, with only one Job executed within each batch.
When a Native Job completes first, it can “steal” half of the batch tasks from other Jobs, optimizing performance while ensuring memory access locality. The lower the number of batches, the more evenly tasks are distributed among threads, but this also incurs additional overhead, so the optimal batch size needs to be tested individually.
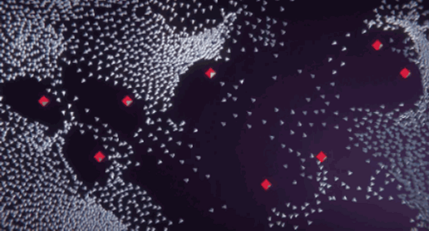
Figure 2: IJob Parallel Example
4. Performance Optimization Insights Based on Ascend NPU Heterogeneous Computing
4.1 Advantages of Heterogeneous Computing
The Ascend chip is a heterogeneous computing architecture that integrates CPU, GPU, and NPU, where the NPU is specifically designed for deep learning and parallel computing tasks, particularly excelling in vector and matrix operations. This architecture allows the Ascend chip to provide performance far exceeding traditional CPUs when handling large-scale parallel computing tasks while accommodating different computational loads.
4.2 Integration of Unity ECS and Ascend NPU
In the Unity ECS architecture, the parallel computing of the JobSystem inspires us: in scenarios with many game objects, compute-intensive tasks (such as physics simulation, AI computation, etc.) can be offloaded to the Ascend NPU for processing. This not only alleviates the burden on the CPU but also fully utilizes the NPU’s parallel computing capabilities, achieving significant performance improvements.
For example, we can adapt the computation logic of the Flocking algorithm to the Ascend NPU by developing custom NPU operators to accelerate calculations. The following image shows the real-time display of a Unity project using the NPU heterogeneous algorithm for flocking.

Figure 3: Real-time display of Flocking algorithm Demo
4.3 Performance Optimization Strategies
- Reasonable Task Allocation: Assign tasks suitable for NPU processing (such as large-scale parallel computations) to the NPU, while keeping some lightweight logical tasks on the CPU, achieving collaborative work between CPU and NPU to fully leverage the advantages of both.
- Optimize Data Transfer: Reduce the frequency and volume of data transfer between CPU and NPU, completing continuous computation tasks on the NPU whenever possible to avoid performance loss caused by frequent data movement. For example, by designing data structures and computation processes reasonably, multiple related computation tasks can be integrated and completed at once on the NPU, reducing the number of data transfers.
- Utilize NPU Features: Deeply study the architectural features and optimization techniques of the Ascend NPU, such as utilizing its vectorized instructions and memory access optimizations to further enhance the execution efficiency of operators. Additionally, keep an eye on NPU version updates and optimization tools to timely apply the latest technologies to improve performance.
5. Conclusion
The Unity ECS architecture provides an efficient and flexible development model for game development, while the integration of Ascend NPU heterogeneous computing offers us more powerful performance optimization means. By reasonably utilizing the component-based design and parallel processing capabilities of Unity ECS, and fully leveraging the computational advantages of the Ascend NPU, we can achieve higher performance and better user experience in game development. In the future of game development, we can further explore and tap into the potential of combining Unity ECS with Ascend NPU to bring players a more spectacular gaming world.
6. References
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/59879279
- https://docs.unity3d.com/Manual/JobSystem.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/komorebi_wq/article/details/139848091
Compiler SIG focuses on technical exchanges and sharing in the field of compilers, including GCC/LLVM/OpenJDK and other program optimization technologies, gathering scholars, experts, and peers in the field of compilation technology to jointly promote the development of compiler-related technologies.
Scan to add the SIG assistant on WeChat, inviting you to join the Compiler SIG WeChat group.

Click Read the original text to start using the Biheng compiler