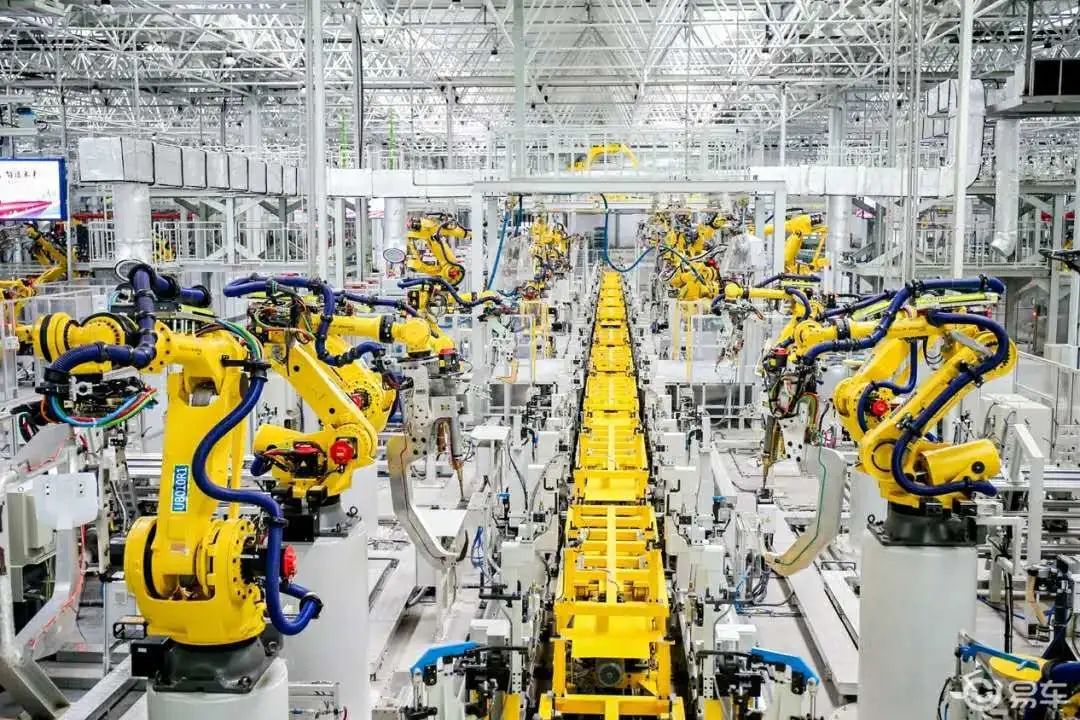


-
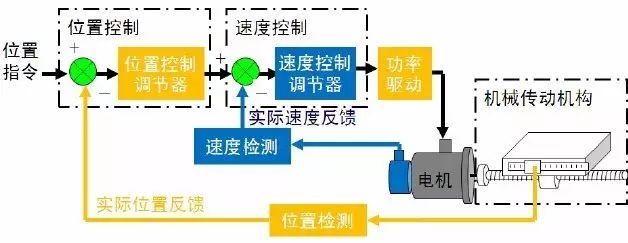
Must have high-precision sensors that can accurately provide electrical signals for the output. -
The power amplifier and control system must be reversible. -
Must have a sufficiently large speed regulation range and strong low-speed load performance. -
Fast response capability and strong anti-interference ability.
-
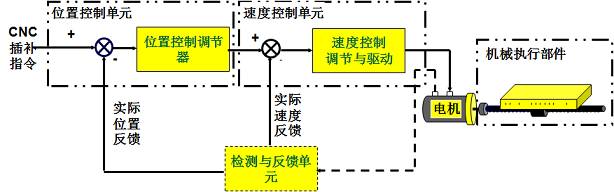
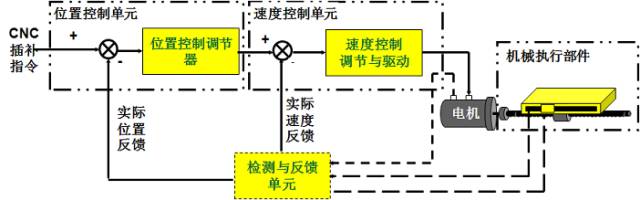
By control principle: There are three forms: open loop, closed loop, and semi-closed loop -
By the nature of the controlled quantity: there are displacement, speed, force, and torque servo system forms -
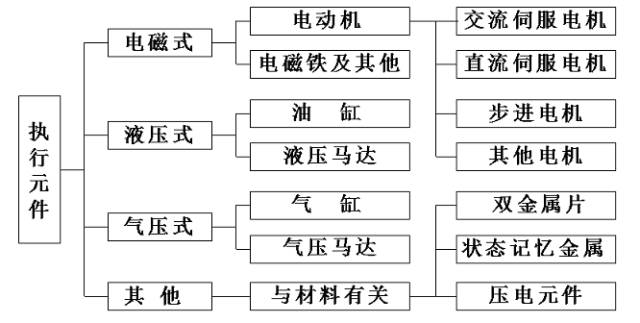
By driving method: there are electrical, hydraulic, and pneumatic servo drive forms -
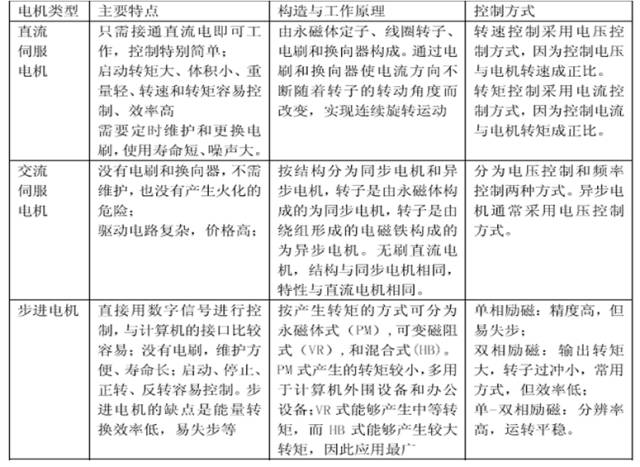
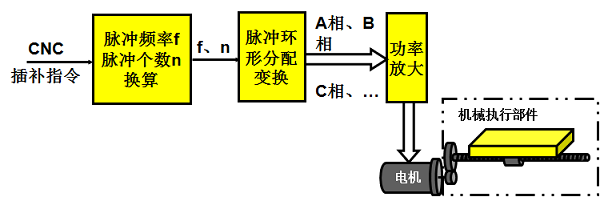
By actuating components: there are stepper motor servo, DC motor servo, and AC motor servo forms
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
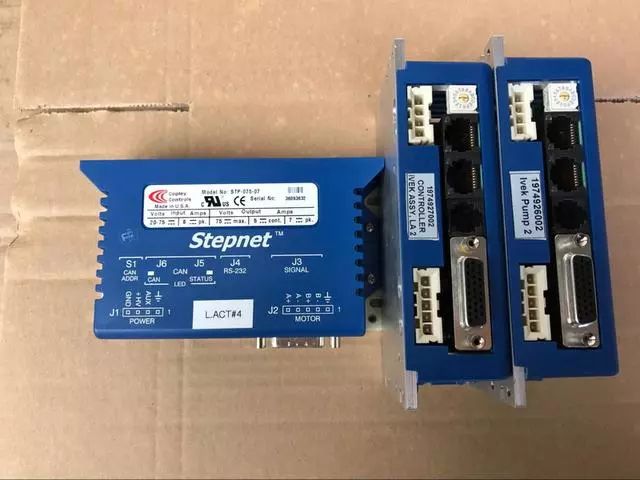
Famous Foreign Servo Motor/System Manufacturers

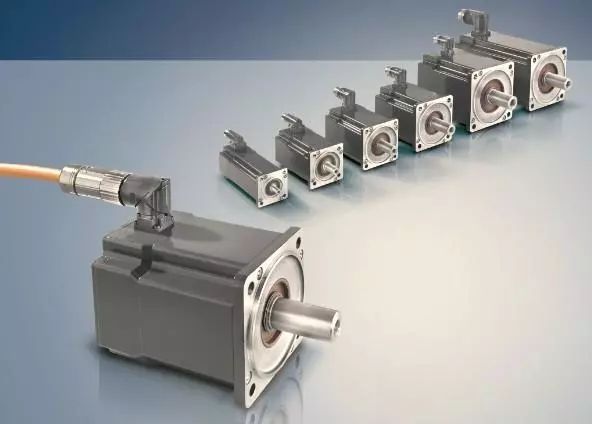
Bosch Rexroth (Germany)












Famous Domestic Servo Motor/System Manufacturers
First, their shapes are generally longer and appear rough, making it difficult to apply them to high-end robots. Especially in desktop robots with light loads around 6kg, the installation space for the robot’s arm is very limited, requiring strict length specifications for the servo motor. Second, the reliability of signal connectors needs improvement, and there is a need for miniaturization, high density, and integrated design with the servo motor body for easier installation, debugging, and replacement. Third, another core technology is high-precision encoders, especially multi-turn absolute encoders used in robots, which heavily rely on imports, posing a significant bottleneck for the development of high-end robots in China. The miniaturization of encoders is also a core technology that cannot be bypassed when miniaturizing servo motors. Fourth, there is a lack of fundamental research, including absolute encoder technology, industrialization manufacturing technology for high-end motors, breakthroughs in production processes, practical verification of performance indicators, and the establishment of assessment standards. Fifth, there is insufficient collaboration between various parts of the servo system industry, leading to difficulties in achieving overall performance for servo motors and drive systems.
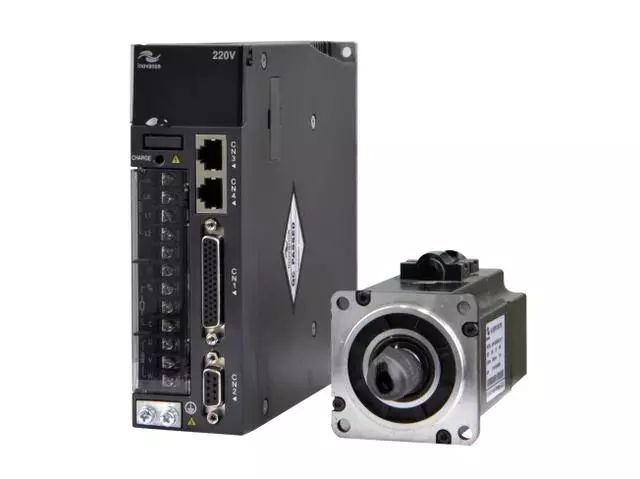
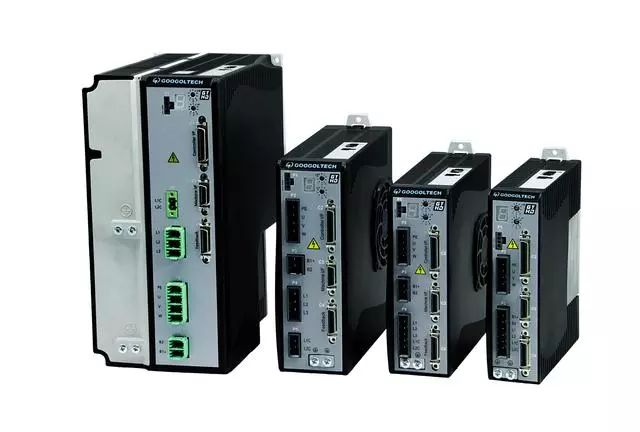
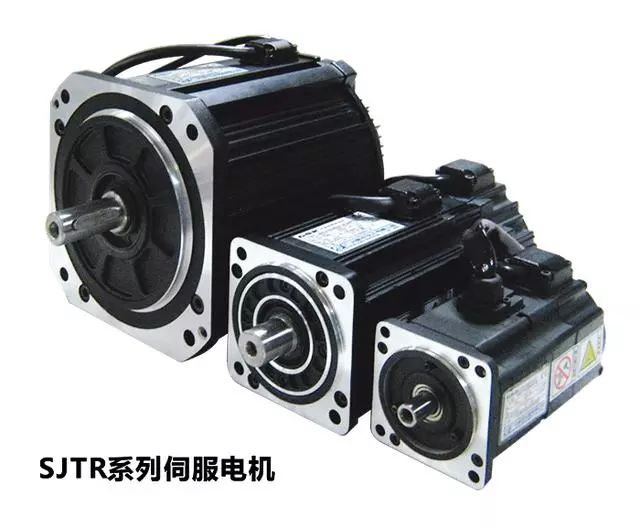








Transcribed from: Industrial Robots
Disclaimer: The reposted article does not represent the views of this public account or its authenticity. Due to numerous reposts, it is impossible to confirm the true original author. Therefore, only the source of the repost is indicated. If there are copyright issues regarding the works, please contact us in a timely manner, and we will delete the content to ensure your rights!
Scan to follow
Micro
Special
Electric
Motor
Official Website: www.wdj21.com
Phone: 021-64821783
Email: [email protected]
Address: 30 Hongcao Road, Xuhui District, Shanghai