
Author: Zhao Xiaofei
IoT Think Tank Original
Reprint must indicate the source and origin
—— [Introduction] ——
The “complementarity” of NB-IoT/eMTC/LoRa and local area networks is reflected in the vertical expansion of existing solutions, more choices in complex scenarios, and the new capability for product lifecycle management, which may lead to new production and operation models in the existing industry.

In last Saturday’s article “Is NB-IoT/eMTC/LoRa Competing Fiercely with WiFi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee Technologies?”, I questioned ABI Research’s latest viewpoint that “wireless local area network solutions are facing fierce competition and threats from low-power wide area network technologies”. I believe that the commercial use of low-power wide area network technologies such as NB-IoT/eMTC/LoRa forms a “complementary effect” in many scenarios dominated by short-range technologies like WiFi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee. In many technical discussion articles, researchers have discussed the non-exclusive relationship between LPWAN and LAN based on a comparison of their main parameters in various scenarios. However, in practical applications, we often face complex wireless environments, and in many cases, the combination of LPWAN and LAN achieves the best application effect. Let’s summarize some typical cases under these “complementary effects”.
In IoT commercialization, many companies have brought better IoT use cases through the complementary practices between low-power wide area networks and local area networks. In summary, this “complementary effect” is reflected in the vertical expansion of existing solutions, more choices in complex scenarios, and the new capability for product lifecycle management, which may lead to new production and operation models in the existing industry.
1. Vertical Expansion of Existing Solutions
Undoubtedly, in many fixed locations, the IoT applications of local area networks have advantages. For instance, in scenarios with frequent, real-time, and large data interactions in smart homes, WiFi plays an irreplaceable role; in indoor lighting and switch scenarios, low-power Bluetooth and Zigbee’s Mesh function are effective; indoor positioning often relies on Bluetooth Beacons, and the ultra-low cost of traditional 433 wireless and other local connection methods also becomes a choice in many indoor scenarios. However, when these fixed-location applications often require personalized design and management for each project, some replicable and vertically integrated management methods cannot be formed.
For example, a domestic startup named Sensoro initially deployed hundreds of thousands of low-power Beacon sensors in indoor scenes such as shopping malls, sports venues, and tourist sites to achieve services like indoor positioning, crowd analysis, environmental monitoring, and digital experiences. However, managing these widely deployed sensors uniformly often requires local gateway devices, and the limited transmission distance of Beacons necessitates a large number of gateways, leading to high construction and management costs. After introducing LoRa technology, Sensoro developed wireless communication chips embedded with near-field and far-field communication protocols. Near-field communication is achieved through low-power Bluetooth, while far-field communication is realized through enhanced LoRa protocols. After embedding this chip into their sensors, they achieved vertical expansion of the original indoor positioning solution. At this point, only a few LoRa base stations need to be deployed in densely populated sensor areas to manage all sensors remotely.

Coincidentally, Xunxi Electronics also launched a Bluetooth + LPWAN positioning service system, collecting various perception data through iBeacon and transmitting the collected data via LoRaWAN.
The indoor positioning case is a typical example of a Bluetooth solution achieving vertical expansion through low-power wide area networks, where LPWAN and LAN have a complementary relationship, not a substitution relationship.
2. More Choices in Complex Scenarios
Many IoT applications face complex network environments, and to enhance user experience, it is often necessary to have multiple wireless methods as backups and supplements, especially for IoT terminals and applications directly facing consumers. In fact, the smartphones we use daily are a typical example of devices coexisting with multiple wireless methods: 2G/3G/4G cellular networks and WiFi, Bluetooth, NFC, and other near-field network functions are all present, allowing users to switch to the appropriate wireless method in different scenarios for the best experience.
Do you remember the launch of China’s first eMTC/NB-IoT/GSM multi-mode outdoor test on May 23 by Mobike, Qualcomm, and China Mobile? Shared bicycles use low-power wide area network technology for data transmission, and in the face of complex urban environments, bike lock communication adopts a multi-mode approach of eMTC/NB-IoT/GSM, selecting communication methods based on network conditions, vehicle speed, and vehicle status to ensure seamless communication in urban environments. In addition to these wide-area communication technologies, Bluetooth, as a local communication technology, complements them. The Qualcomm MDM9206 modem and Mobike’s low-power Bluetooth solution will be used in Mobike’s “smart recommended parking points”, achieving “sub-meter” positioning comprehensively. Moreover, most of the time, users unlock the bike primarily through wide-area networks, and when the wide-area network cannot support quick unlocking, users can unlock quickly through Bluetooth point-to-point, making Bluetooth an important backup method to enhance user experience. This is undoubtedly a typical manifestation of the complementarity between low-power wide area networks and local area networks in the shared bicycle application scenario.

3. New Product Lifecycle Management Capabilities
In the past, IoT scenarios using local area network technologies like WiFi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee often had manufacturers focusing more on creating suitable user scenarios, lacking better ways to manage their product lifecycle. After the commercial use of low-power wide area networks in various products, manufacturers can remotely manage the lifecycle of products they have sold, which may lead to better business models.
For instance, in the past, smart home manufacturers focused more on usage scenarios and experiences brought by local area network technologies, especially for electrical appliances and home devices, enhancing interaction between users and devices through technologies like WiFi and Bluetooth, or creating scenario-based experiences. Manufacturers managed these devices by collecting information from the wireless modules of devices through home gateways. However, most devices in homes do not operate with power 24 hours a day, and users only power on washing machines, air conditioners, rice cookers, and other terminals when needed. Moreover, a considerable number of users do not necessarily connect these home appliances to gateways, and some have never used connected features. At this point, these smart home manufacturers cannot understand the usage situation of devices, and the information source between manufacturers and devices is cut off after the products are sold, making product lifecycle management impossible.
Previously, some manufacturers considered using cellular networks for product lifecycle management, but 2G/3G/4G modules consume more power, making it impossible for battery-powered devices to support this when not powered. However, low-power wide area networks, especially the deployment of operator-level networks, provide unprecedented opportunities for these manufacturers. Taking air conditioners as an example, embedding NB-IoT modules powered by batteries allows for regular collection of the status of core components such as filters and motors, as well as location information. Over the 5-10 year replacement cycle of air conditioners, whether the air conditioner is powered on or not, it can remain online continuously, and information can be obtained timely during various lifecycle stages, including production, sales, usage, resale, recycling, and disposal, providing appropriate services to achieve full lifecycle management.
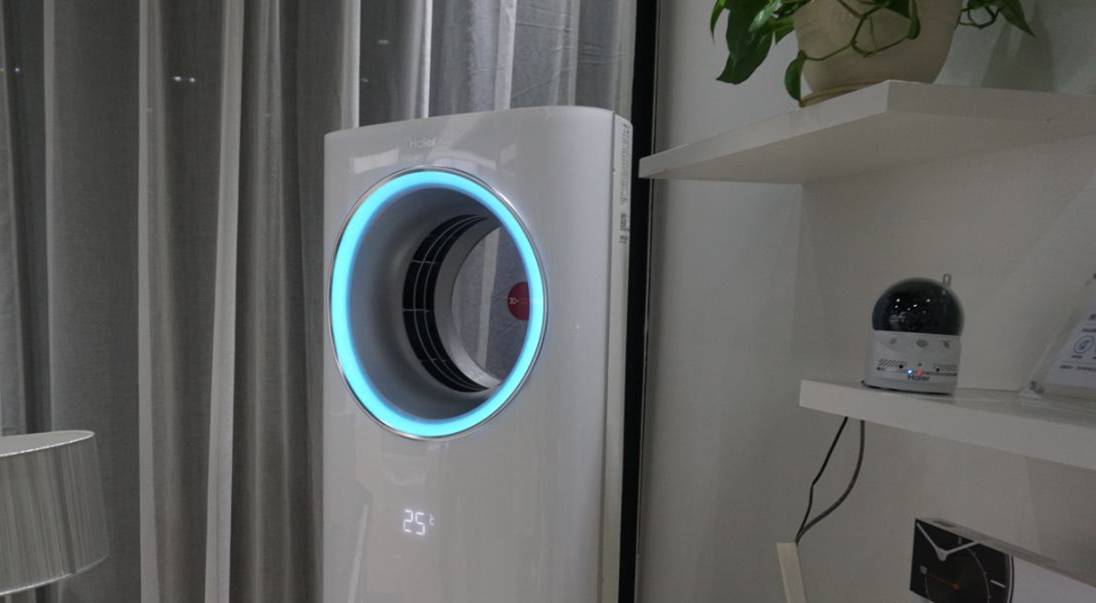

Recently, home appliance manufacturers such as Haier, Midea, and Hisense have collaborated with communication equipment and operators to develop and test appliances based on NB-IoT, and the ability to achieve product lifecycle management is undoubtedly one of the important reasons for their active embrace of NB-IoT. Just like many heavy machinery, printers, and floor cleaning machines have already transformed from providing products to providing services through IoT means, for devices that can achieve product lifecycle management through low-power wide area networks, they can also explore transitioning to service providers, and the entire production and operation model of the industry may undergo fundamental changes in the future. It must be said that low-power wide area networks have given manufacturers of smart devices that originally only used WiFi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee better product lifecycle management capabilities, which can be seen as an industrial transformation brought about by the “complementary effect” of both.
As a diversified market, no single technology can solve all the problems of IoT applications. While low-power wide area network technologies like NB-IoT/LoRa/eMTC have not yet been widely commercialized, we need to consider the complementary and substitutive relationships between various technologies from a holistic perspective, rather than merely emphasizing the “omnipotence” of emerging technologies.
Previous Hot Articles (Click on the article title for direct reading):
-
[Cognitive Computing, Blockchain IoT, IoT Security… Those Who Understand Will Control the Future]
-
[KUKA, ABB, Fanuc, Yaskawa, Four Industrial Robot Giants Have Already Garrisoned in the IoT Field]
-
[[Heavyweight] IoT Industry Panorama Report, The First Domestic IoT Industry Two-Dimensional Perspective Panorama]
-
[A Cartoon Explains: Besides WiFi and Bluetooth, What Can the Recently Popular NB-IoT Do?]
-
[A Cartoon Explains: Behind NB-IoT, What Is LoRa That Everyone Is Talking About?]
