

This article is a popular science introduction to LoRaWAN. You have probably seen countless superficial articles about LoRaWAN in your social circles, and it’s time to get some real technical insights. This article first provides a horizontal introduction to the forces behind LoRaWAN and its network deployment situation, and then offers a vertical explanation of the network architecture and specific protocol content, helping practitioners understand the LoRaWAN protocol systematically.
1. What Is LoRaWAN
According to the official white paper from the LoRa Alliance titled “What is LoRaWAN,” LoRaWAN is a communication protocol and system architecture designed for LoRa long-range communication networks.
LoRaWAN defines the communication protocol and system architecture for the network while the LoRa physical layer enables the long-range communication link.
Additionally, the official document provides a slightly technical diagram of the protocol layers for your reference.
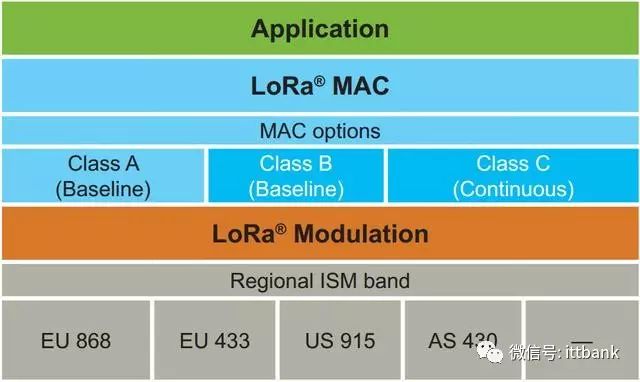
In the design of the protocol and network architecture, LoRaWAN fully considers several factors such as node power consumption, network capacity, QoS, security, and the diversity of network applications. The following sections will provide a deeper understanding of this introduction.
2. Interest Groups Behind – LoRa Alliance
In contrast to the well-established NB-IoT, which comes from the global standardization organization 3GPP, and is supported by the renowned ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute), ARIB (Association of Radio Industries and Businesses) in Japan, TTC (Telecommunication Technology Committee), CCSA (China Communications Standards Association), TTA (Telecommunications Technology Association) in Korea, and ATIS (Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions) in North America, the LoRa Alliance is somewhat weaker.
From the cover of the protocol, we can see that the authors come from three board member companies: N. Sornin (Semtech), M. Luis (Semtech), T. Eirich (IBM), T. Kramp (IBM), O. Hersent (Actility).
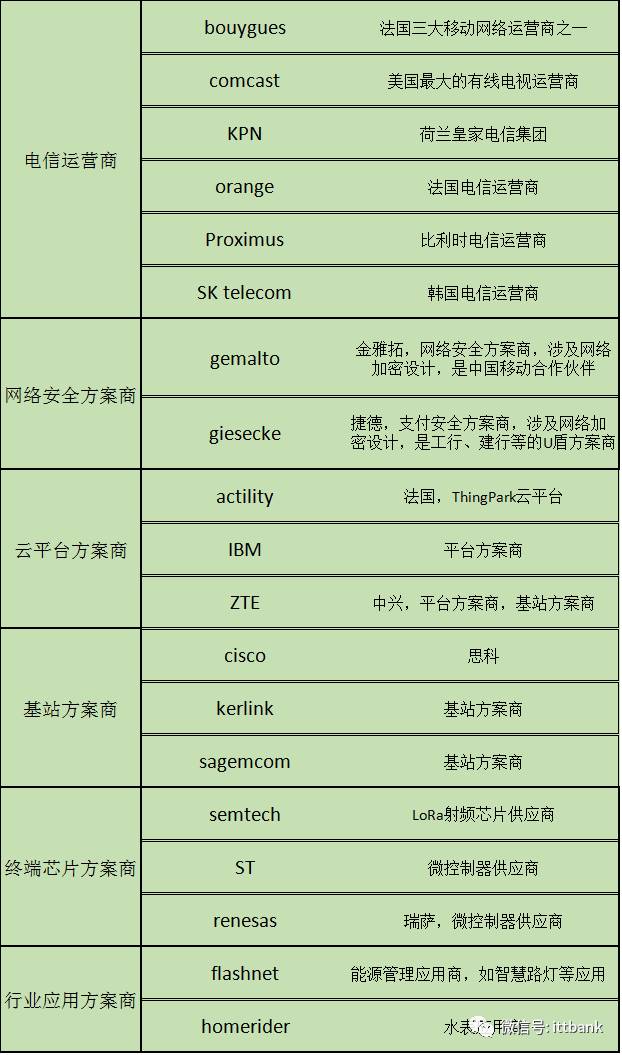
We know that the promotion of any technology is accompanied by the push of interests. Although organizations and alliances are non-profit organizations, the member companies are not entirely focused on public welfare. From a business perspective, spending $50,000 to invest in something is destined to be aimed at leveraging at least $500,000 in returns.
The LoRa Alliance was jointly initiated by several manufacturers, including Cisco, IBM, and Semtech, in the first half of 2015. As of now (April 2017), it has over 400 members, and many large enterprises are also board members, all working together to carve up the future low-power wide-area network cake. I created a table that collects 19 board members who are willing to pay a $50,000 membership fee, which shows the visions of these companies.
3. LoRaWAN Network Deployment Status
After binding with several major telecom operators, the network deployment situation has become quite promising. According to the official statement as of now (April 2017), the network deployment status is as follows:
34 publicly declared deployed networks, with at least 150 ongoing city pilot deployments.
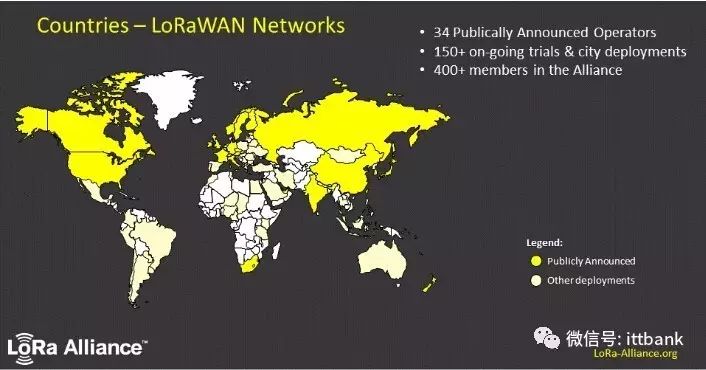
Have you noticed that there’s a bit of white on the chicken neck? Perhaps it’s the brilliance of subjectivism that shines too brightly.
4. LoRaWAN Network Architecture
Having understood how popular LoRaWAN is, let’s delve into the technical aspects. Below is the network architecture diagram from the official white paper of the LoRa Alliance.
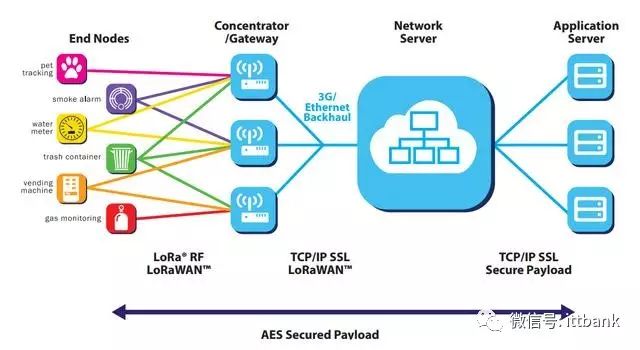
A LoRaWAN network architecture includes four parts: terminal, base station, NS (network server), and application server. The base station and terminal use a star network topology, and due to the long-range characteristics of LoRa, they can use single-hop transmission. In the terminal section, the official document lists six typical applications, and you will notice that terminal nodes can send data to multiple base stations simultaneously. The base station processes the LoRaWAN protocol data between the NS and terminal, carrying the LoRaWAN data on both LoRa RF transmission and TCP/IP.
Now, let’s look at this network architecture in conjunction with the industry ecosystem for a deeper understanding.
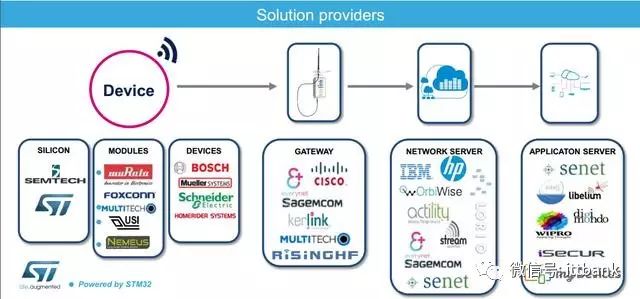
The image is from ST’s LoRa white paper “IoT connectivity made easier STM32 MCUs & LoRa.”
5. Protocol Overview
5.1 Classification of Terminal Nodes
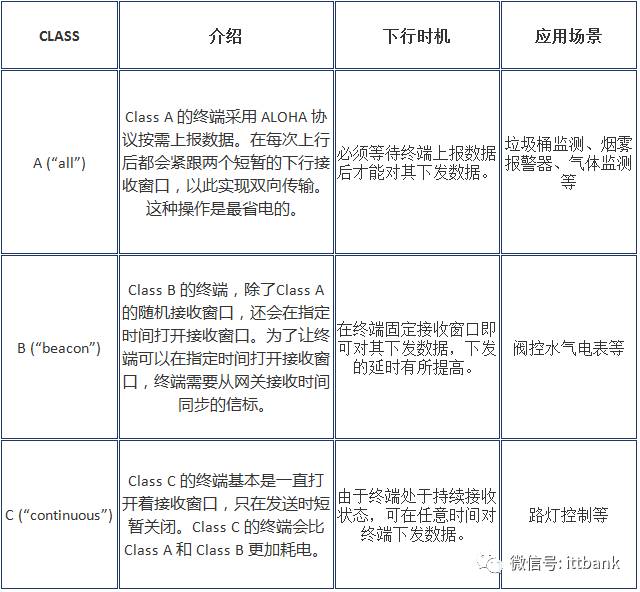
In the introduction, we saw that the protocol specifies three classes of terminal devices: Class A/B/C, which cover almost all application scenarios in the Internet of Things.
To make it easier for everyone, I created another table.
5.2 Upstream and Downstream Transmission of Terminal Nodes
Now let’s look at some timing diagrams for a deeper understanding.
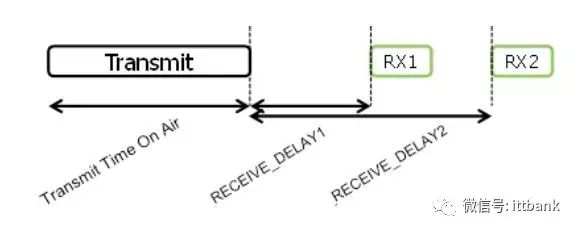
This is the timing diagram for Class A upstream and downstream. Currently, the receiving window RX1 generally starts 1 second after the upstream transmission, and the receiving window RX2 starts 2 seconds after.
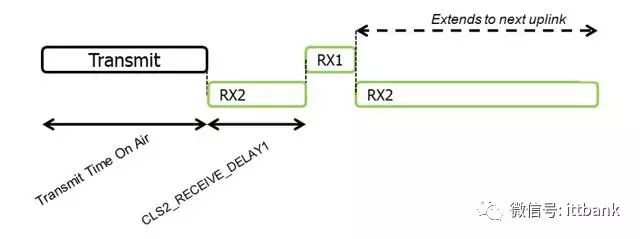
Class C is basically the same as A, except that during Class A’s sleep period, it opens the receiving window RX2.
Class B’s timing is a bit more complex; it has a synchronization time slot beacon and a fixed-period receiving window ping time slot. For example, in this case, the beacon period is 128 seconds, and the ping period is 32 seconds.
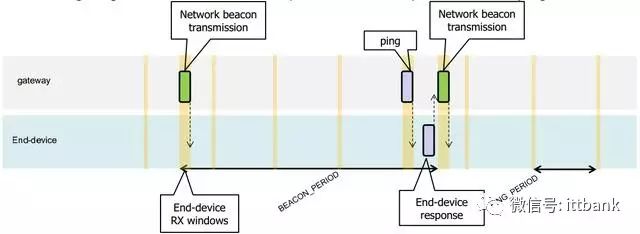
5.3 Network Joining of Terminal Nodes
Once you understand the basic concepts, you can learn how nodes operate. Before officially sending and receiving data, the terminal must first join the network.
There are two ways to join the network: Over-the-Air Activation (OTAA) and Activation by Personalization (ABP).
Commercial LoRaWAN networks generally follow the OTAA activation process to ensure security. This method requires three parameters: DevEUI, AppEUI, and AppKey.
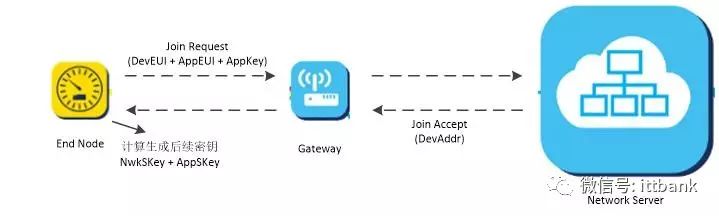
DevEUI is a globally unique ID similar to IEEE EUI64, identifying a unique terminal device. It’s like the device’s MAC address.
AppEUI is a globally unique ID similar to IEEE EUI64, identifying a unique application provider. For instance, various applications for monitoring trash bins, smoke alarms, etc., each have their unique ID.
AppKey is assigned to the terminal by the application owner.
After the terminal initiates the join process, it sends a join command. If the NS (network server) confirms it is correct, it will respond to the terminal, assigning a network address DevAddr (32-bit ID). Both parties use the relevant information in the join response and AppKey to generate session keys NwkSKey and AppSKey for data encryption and verification.
If the second joining method, ABP activation, is used, it’s relatively straightforward; you directly configure the three LoRaWAN communication parameters: DevAddr, NwkSKey, and AppSKey, without needing the join process. In this case, the device can directly send application data.
5.4 Data Transmission and Reception
After joining the network, application data is encrypted.
LoRaWAN specifies two types of data frames: Confirmed or Unconfirmed, meaning whether a response is needed or not. Manufacturers can choose the appropriate type based on application needs.
Moreover, as mentioned, one major consideration in the initial design of LoRaWAN was to support application diversity. Besides using AppEUI to categorize applications, data can also be handled separately using the FPort application port during transmission. The FPort value range is (1~223), specified by the application layer.
5.5 ADR Mechanism
We know that there is a concept of spreading factor in LoRa modulation, where different spreading factors result in different transmission distances and rates, and they do not affect data transmission.
To expand the capacity of the LoRaWAN network, a LoRa Adaptive Data Rate (ADR) mechanism has been designed in the protocol. Devices at different transmission distances will use the fastest data rate possible based on transmission conditions. This also makes overall data transmission more efficient.
5.6 MAC Commands
For network management needs, a series of MAC commands have been designed in the protocol to modify network-related parameters, such as receiving window delays, device rates, etc. In practical applications, these are generally rarely involved, so we will not discuss them for now.
6. Regional Parameters
The LoRa Alliance has also released a supplementary document titled “LoRaWAN Regional Parameters” in addition to the protocol, which describes the specific parameters of LoRaWAN in different regions worldwide. To avoid changes to the document due to the addition of new regions, the regional parameters section has been separated from the protocol specifications.
This document mainly discusses the specific physical layer parameters of LoRaWAN in various regions, which differ not only in frequency bands but also in channel divisions, data rates, transmission power, maximum data lengths, etc.
To make it easier for everyone to understand the overall situation, I created another table.
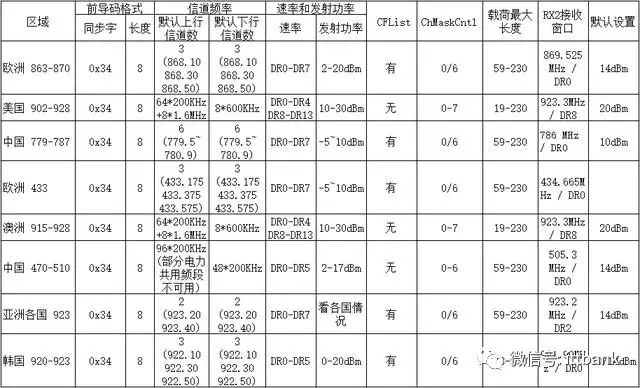
In fact, this table also reveals an interesting fact: why the parameters in Korea are not much different from those in other Asian countries, yet are singled out. If you remember the record of board members mentioned earlier, you should know the position of Korea’s SK Telecom in the LoRa Alliance. With such a high status, is it too much to have a little special treatment?
Author: twowinter, thanks to the original author for their hard work. If there are any copyright or inappropriate issues with the article, please contact us, and we will delete it as soon as possible. Thank you! Phone: 4000933666 or 15818560804, Email: [email protected]

