On February 12, a piece of news from the Yingtan Daily shook the communications industry.
As of January 22 at 12:00, China Mobile Yingtan Branch successfully completed the construction and launch of the NB-IoT network covering the entire Yingtan city, marking the successful establishment of the first city-level NB-IoT network fully covering a city in the country.

Exciting! The era of the Internet of Things has begun in 2017! However, as communication professionals, everyone must want to know how an NB-IoT network is built, right?
Don’t rush, take a little stool and let’s discuss…
1 Overall Network Architecture
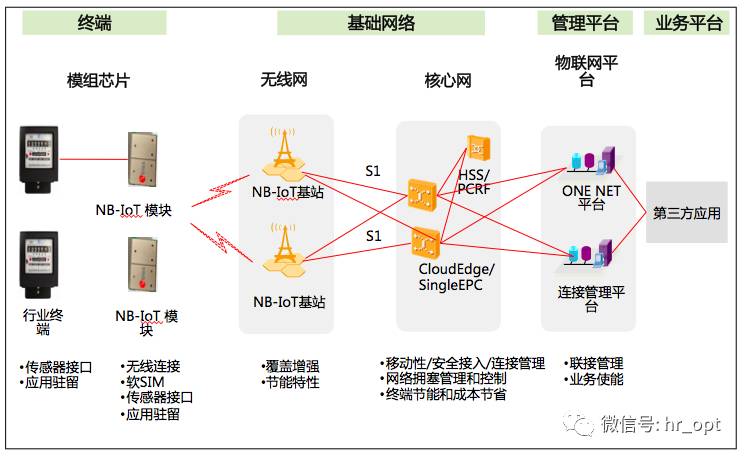
2 Core Network Construction
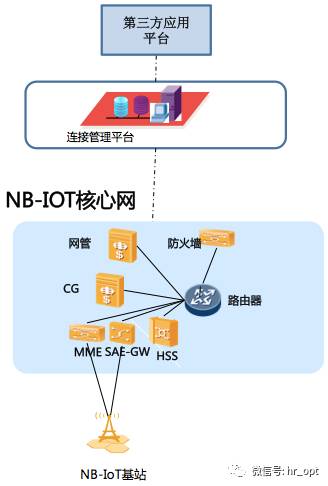
If built independently, it will add network elements and devices like SAEGW, MME, CG, HSS, routers, isolation firewalls, and network management.
Note:
Supplementary Knowledge on NB-IoT Core Network
To send IoT data to applications, Cellular IoT (CIoT) defines two optimization schemes in EPS:
• CIoT EPS User Plane Function Optimization
• CIoT EPS Control Plane Function Optimization
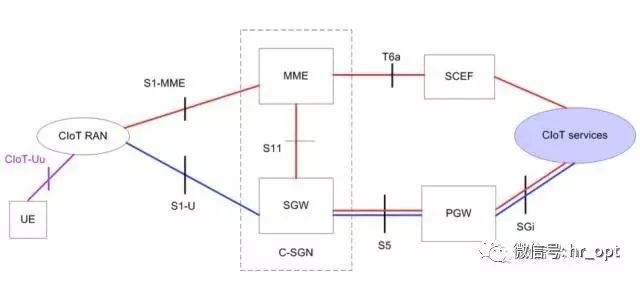
As shown in the figure above, the red line indicates the CIoT EPS Control Plane Function Optimization scheme, while the blue line indicates the CIoT EPS User Plane Function Optimization scheme.
CIoT EPS Control Plane Function Optimization: Uplink data is sent from eNB (CIoT RAN) to MME, where the transmission path splits into two branches: either sent via SGW to PGW and then to the application server, or connected to the application server (CIoT Services) through SCEF (Service Capability Exposure Function), the latter only supports non-IP data transmission. The downlink data transmission path is the same, just in the opposite direction. This scheme does not require establishing a data radio bearer; data packets are sent directly on the signaling radio bearer. Therefore, this scheme is very suitable for infrequent small data packet transmission. SCEF is newly introduced specifically for NB-IoT, used to transmit non-IP packets in the control plane and provide an abstract interface for network services such as authentication.
CIoT EPS User Plane Function Optimization: The transmission method for IoT data is the same as traditional data traffic, sending data over the radio bearer, transmitted from SGW to PGW and then to the application server. Therefore, this scheme incurs additional overhead when establishing connections; however, its advantage is that data packet sequence transmission is faster. This scheme supports both IP and non-IP data transmission.
3 Wireless Network Construction
Base station construction method: If adopting an independent new construction scheme co-located with existing sites, additional RRU, main control board, baseband board, etc., are required.
Antenna construction method: In principle, all multi-port independently adjustable antennas replace the original existing network antennas, integrated and shared with existing sites.
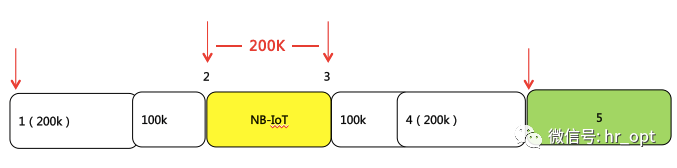
Capacity configuration: Each cell is configured according to a single carrier frequency. Theoretically, NB-IoT 200K cells can support 50,000 users.
Frequency configuration: Deploy using 200K frequency bandwidth for both uplink and downlink, with 300K used as a guard band on both sides.
Note:
Supplementary Knowledge on NB-IoT Wireless Network
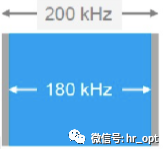
NB-IoT occupies 180KHz bandwidth, which is the same as the bandwidth of one resource block in the LTE frame structure. Therefore, the following three deployment methods are possible:
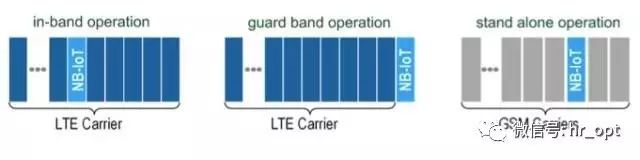
1) Standalone Operation: Suitable for redeployment in the GSM frequency band, where the GSM channel bandwidth is 200KHz, leaving space for NB-IoT 180KHz bandwidth, with a 10KHz guard interval on both sides.
2) Guard Band Operation: Utilizing unused 180KHz bandwidth resource blocks in the LTE edge guard band.
3) In-band Operation: Utilizing any resource block in the middle of the LTE carrier.
4 Transmission Construction
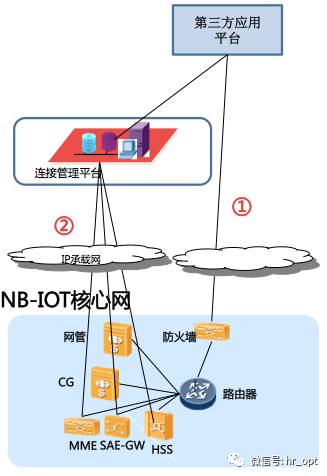
① Business Platform: Router connects through a firewall directly to the third-party application platform.
② Connection Management Platform: NB-IoT core network devices (MME, SAEGW, HSS) access the connection management platform through the IP bearer network, enabling card data management, connection information querying, and other functions.
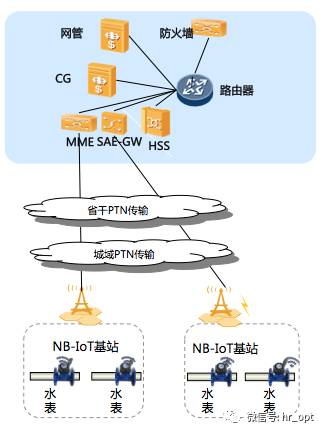
Base station and core network connection: NB-IoT base stations access the city transmission PTN, then through the provincial PTN, connecting to the core network MME and SAEGW devices via GE optical ports.
5 Project Construction
Similar to 4G network construction, the entire construction process includes: equipment room and site survey, design, equipment procurement, installation and debugging, optimization, and end-to-end joint debugging.
Additionally, network optimization engineers, like 4G construction, NB-IoT also requires single-site testing, including ATTACH verification, PING latency testing, upload rate testing, and RSRP, RS-SINR testing.
Other theoretical knowledge about NB-IoT can be read in detail (click the blue title below):
The most comprehensive NB-IoT knowledge that every communication professional should understand…
According to Yingtan Daily, as of January 22, 2017, 135 NB-IoT base stations have been launched, basically achieving full network coverage in Yingtan city. This project started on December 1, 2016, lasted 33 days, with a total investment of approximately 44.65 million yuan, and currently, 135 IoT base stations and a complete core network and related network management have been constructed.
It is worth mentioning that, as the Internet of Things needs to provide end-to-end solutions, this NB-IoT network not only completed network construction but also achieved bidirectional transmission between terminals and business platforms, truly representing an end-to-end Internet of Things, laying a solid foundation for building an end-to-end industrial chain.

▲On January 13, 2017, end-to-end testing was completed with the SanChuan Water Meter Factory server, allowing SanChuan Water Meter to receive instructions from the SanChuan Water Service platform.
The next step is for the government and industry to join forces, leveraging the advantages of NB-IoT full coverage, to attract enterprises in the IoT industry chain to incubate startups in the Yingtan Smart Entrepreneurship Park, building an IoT industry development alliance and actively cultivating new momentum and new business formats for Yingtan’s economic development.
At the same time, pilot applications for NB-IoT services will be developed in areas such as smart city management, smart street lighting, smart parking, smart logistics, and smart agriculture, constructing a “new smart city” with NB-IoT characteristics to promote information benefits for the public, striving to make Yingtan a national benchmark city for narrowband IoT applications.
Network Optimization Freelance Submission Email: [email protected]
Long press the QR code to follow

On the road of communication, let’s walk together!