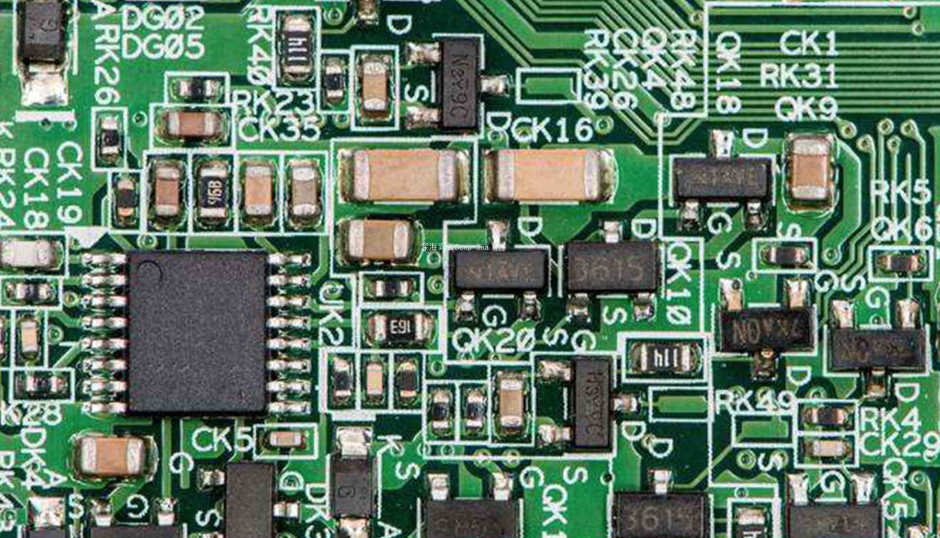
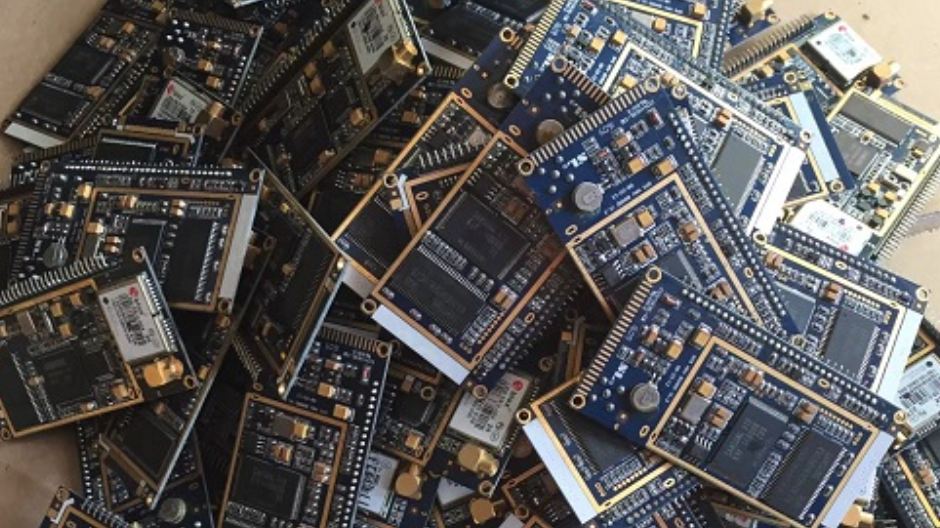
The price of waste circuit boards mainly depends on the content of precious metals inside. For example, the price of a ton of waste circuit boards from TV circuit boards is around 30,000 to 40,000 yuan. A ton of computer boards typically contains about: 300-500g of gold, 130kg of copper, 10kg of iron, 60kg of lead, 40kg of tin, 36kg of nickel, and 40kg of antimony, as well as small amounts of palladium and platinum. Copper can account for more than 90% of the mixed metals.
The price of common mixed boards with average metal content is around 6,000 to 8,000 yuan per ton. The price of waste circuit boards may vary depending on the region.
Circuit boards contain chips and electronic components, so the condition of these components also matters. Chips can be removed and sold separately; a ton of circuit boards with removed chips will be much cheaper than those without. Therefore, it is recommended to remove the chips for separate sale after recycling old circuit boards.
The current basic market recycling price for waste circuit boards is about 3.8 yuan per jin. One ton equals 2000 jin, so 3.8 multiplied by 2000 gives about 7600 yuan per ton. Generally, the price for waste circuit boards ranges from 3 to 20 yuan per jin, with TV circuit boards around 3.5 yuan, while better quality boards like DVD, CD, and computer mainframes range from 18 to 20 yuan. The power supply box for computer mainframes is about 6 yuan, and the motherboard is around 22 yuan.
Classification of Waste Circuit Boards
Waste circuit boards include waste copper-clad laminates (CCL), waste printed circuit boards (PCB), and printed circuit board cards with integrated circuits and electronic components (commonly known as waste circuit boards).
1. Waste Copper-Clad Laminate
Copper-clad laminate is the raw material for producing printed circuit boards, mainly composed of substrates, copper foil, and adhesives. The main materials for the substrate are synthetic resin and reinforcing materials, with common synthetic resins being phenolic resin, epoxy resin, and polytetrafluoroethylene, while reinforcing materials are generally paper-based or cloth-based.
The surface of the substrate is copper foil, which is produced through mechanical processing and electroplating, with electroplating being the main method used currently. The thickness of copper foil generally ranges from 18µm, 25µm, 35µm, 70µm, to 105µm. The copper foil is firmly bonded to the substrate with adhesive, forming a copper-clad laminate.
Currently, the copper-clad laminates widely used in China include phenolic paper-based copper-clad laminate, epoxy paper-based copper-clad laminate, epoxy glass cloth copper-clad laminate, polytetrafluoroethylene copper-clad laminate, and polyimide flexible copper-clad laminate. Mid-range and higher-grade civil appliances and instruments mainly use epoxy (paper or glass cloth) copper-clad laminates in large quantities. Low to mid-range civil appliances mostly use phenolic paper-based copper-clad laminates.
Waste copper-clad laminate consists of defective products and trimmings generated during production, appearing yellow due to the pressed copper foil on the surface, commonly referred to as yellow boards. The copper content in waste copper-clad laminate varies, with low content around 15% and high content exceeding 70%, making it an important resource for copper recycling.
2. Waste Printed Circuit Board
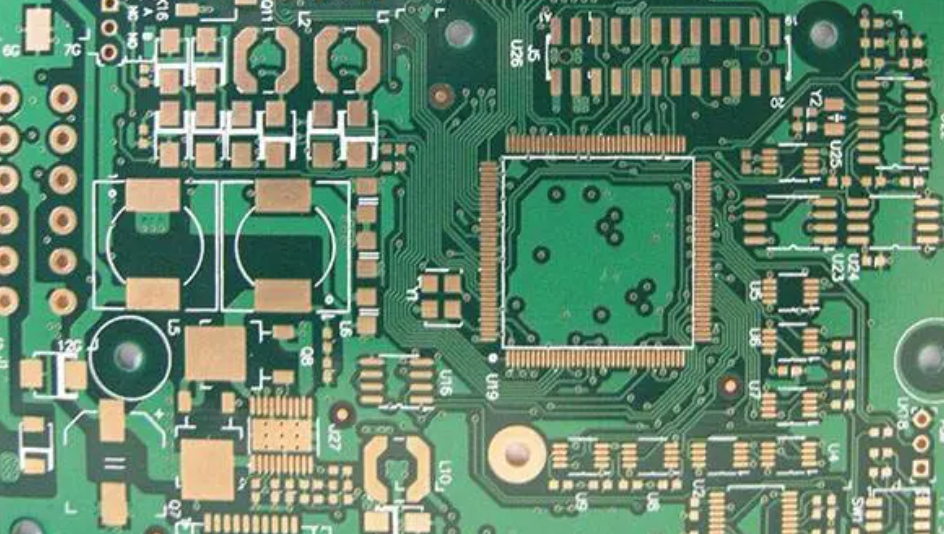
A printed circuit board is abbreviated as PCB. It refers to the conductive pattern made on insulating materials according to a predetermined design, which may consist of printed circuits, printed components, or a combination of both. The finished board of printed circuits or printed lines is referred to as a printed circuit board.
Printed circuit boards are mainly used to provide support for the fixed assembly of various electronic components like integrated circuits, realize wiring and electrical connections between these components, and provide solder mask patterns for automatic soldering, as well as identification characters and patterns for component insertion, inspection, and maintenance.
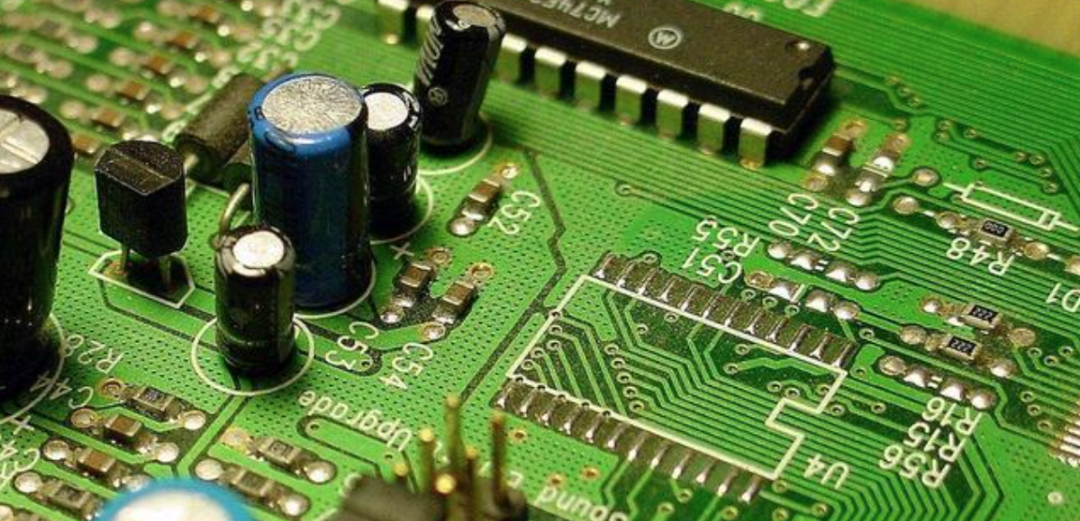
Almost all electronic devices we encounter have PCBs, such as calculators, computers, communication electronics, military weapon systems, etc. As long as there are integrated circuits and other electronic components, electrical interconnections between them will utilize PCBs. Common computer boards are generally double-sided printed circuit boards based on epoxy resin glass cloth, with one side for component insertion and the other for soldering component leads, with solder points typically arranged in a regular pattern.
Defective products generated during the production of printed circuit boards are what we commonly refer to as waste printed circuit boards. They mainly appear green, hence also known as green boards. Although some copper has been corroded during the production of printed circuit boards, resulting in a lower copper content compared to copper-clad laminates, printed circuit boards are still one of the resources for copper recycling.
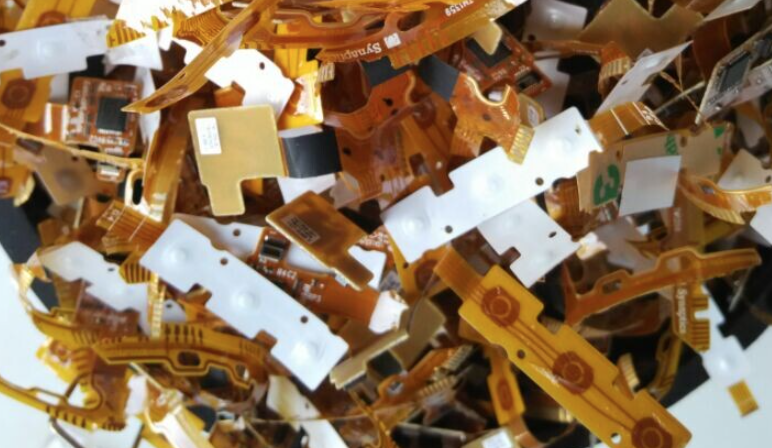
3. Waste Circuit Board Cards
Waste circuit board cards mainly come from various discarded electrical appliances, with many types, commonly including green boards and yellow boards. Green boards are mainly dismantled from waste televisions, computers, and communication devices, with a higher value; yellow boards are mainly dismantled from tape recorders, audio equipment, washing machines, and air conditioners, with a lower value.
The composition of waste circuit board cards is quite complex; in addition to printed circuit boards, they also contain integrated circuits and various electronic components. The main components include silica, copper foil, lead, tin, iron, trace precious metals, and organic substances such as plastics, resins, and paints, making their processing more challenging than that of waste copper-clad laminates and waste printed circuit boards.
Hazards of Waste Circuit Boards
The hazards of waste circuit boards: In daily life, billions of tons of discarded circuit boards accumulate together. Once circuit boards pile up, they will gradually pose threats to our ecological environment and human health.
The electronic components on circuit boards can also cause pollution. The main pollution is metal pollution, especially heavy metals like tin, lead, and cadmium, which directly endanger human health. If not handled and disposed of properly, they not only cause a significant loss of valuable resources but also contain a large number of teratogenic, mutagenic, and carcinogenic substances, such as cadmium and brominated flame retardants, which will severely harm the environment and human health.
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author and does not represent the views of the association. Articles promoted by the “Jiangxi Province Electronic Circuit Industry Association” are for sharing purposes only and do not represent the position of this account. If there are copyright issues, please contact us for removal.