PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is an important component of electronic devices.
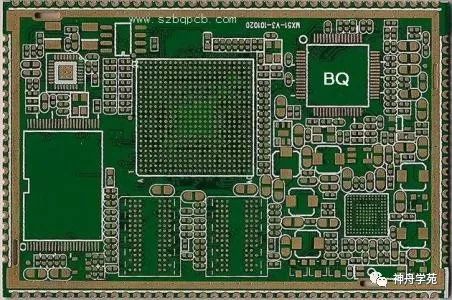
The main function is to provide mechanical support and electrical connections for components.

01 The Inventor of PCB
The creator of the printed circuit board is Austrian Paul Eisler. In 1936, he first used printed circuit boards in radios. (Baidu Encyclopedia)

(From Wikipedia)
Before the advent of PCB, interconnections between electronic components were directly done using wires.

After the emergence of PCB, the connections between electronic components look like this.

02 PCB in the Eyes of Designers
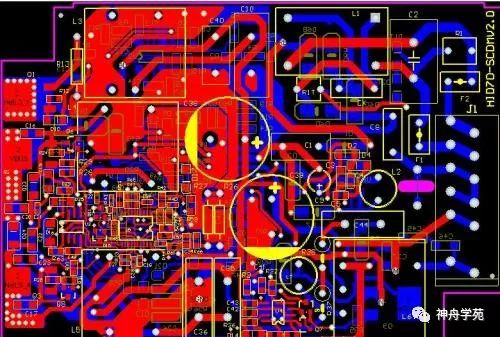
First, this is how PCB looks in the hands of designers. It is drawn using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software.
However, in reality, the PCB in the minds of designers looks like this, as shown in the PCB cross-section diagram. This PCB includes 6 layers, which are the outer component side (top layer) and solder side (bottom layer), generally arranged with copper wires; the middle power layer and ground layer, which are large copper areas; and the inner layers one and two, which are similar to the component side and solder side, generally arranged with copper wires; and the light yellow insulating material sandwiched between these layers.
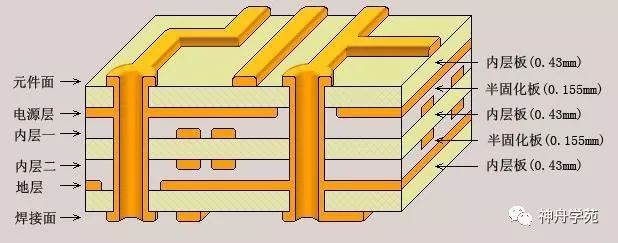
The continuous structure on the left side of the diagram is a via, which connects the signal lines of the component side to the power layer.
03 Who Produces PCBs?
Due to the complex production process and high material standards, PCBs are produced by specialized manufacturers. Remember to communicate more with manufacturers about the technical issues in production; you will surely gain something!

04 Classification of PCBs
1. Classification by Purpose
Military PCBs: PCBs for military computers, communication devices, instruments, aerospace, etc.

Civil PCBs: PCBs for mobile phones, televisions, audio equipment, electronic toys, etc.

2. Classification by Structure
Rigid PCBs

Flexible PCBs
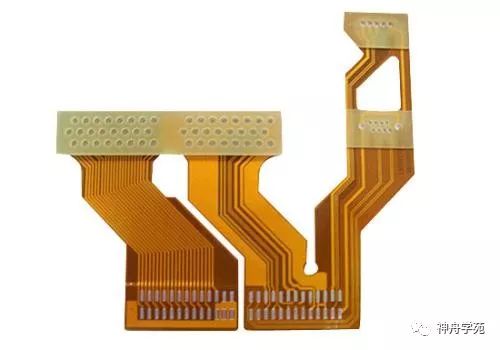
Rigid-Flexible Combined PCBs

3. Classification by Substrate Material
The so-called substrate is not simply one type of material.
The insulating materials between the PCB layers mentioned earlier are only part of the substrate. The substrate is only referred to as the copper-clad laminate when a copper plate used for etching circuit wires is thermally pressed onto it.

Substrate Effect Diagram
The classification of PCBs by substrate includes the following common types:
Paper-based PCB: Paper-based PCBs come in several types, among which FR-1 paper-based PCB is representative, commonly known as bakelite. Look at the picture below; it will be easy for you to have a perceptual understanding!
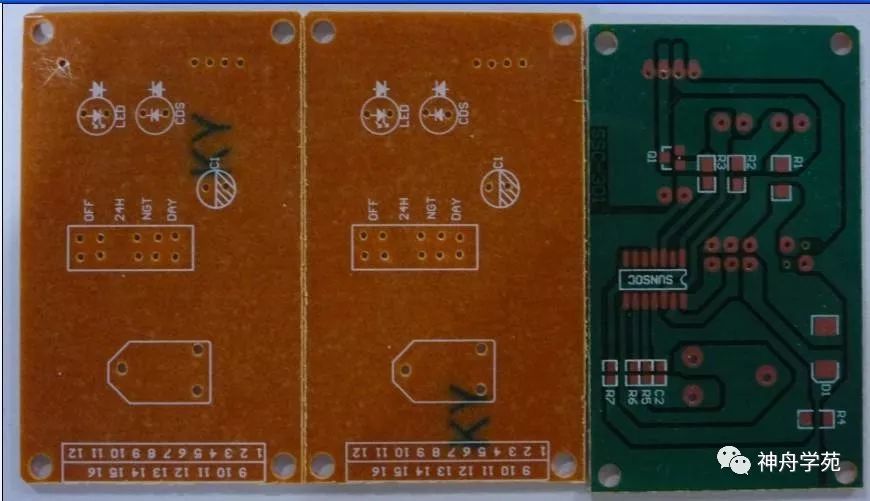
Glass-fiber-based PCB: FR-4 is made from glass fiber impregnated with epoxy phenolic resin and is hot-pressed at high temperature and pressure.
Characteristics: It has high mechanical properties and dielectric properties, good heat resistance and moisture resistance, and good machinability.

(From Baidu Encyclopedia)
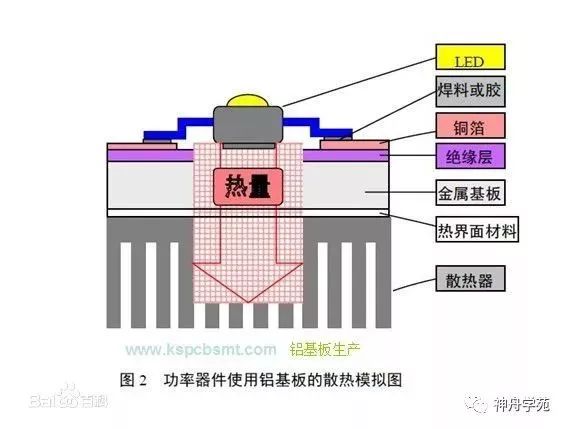
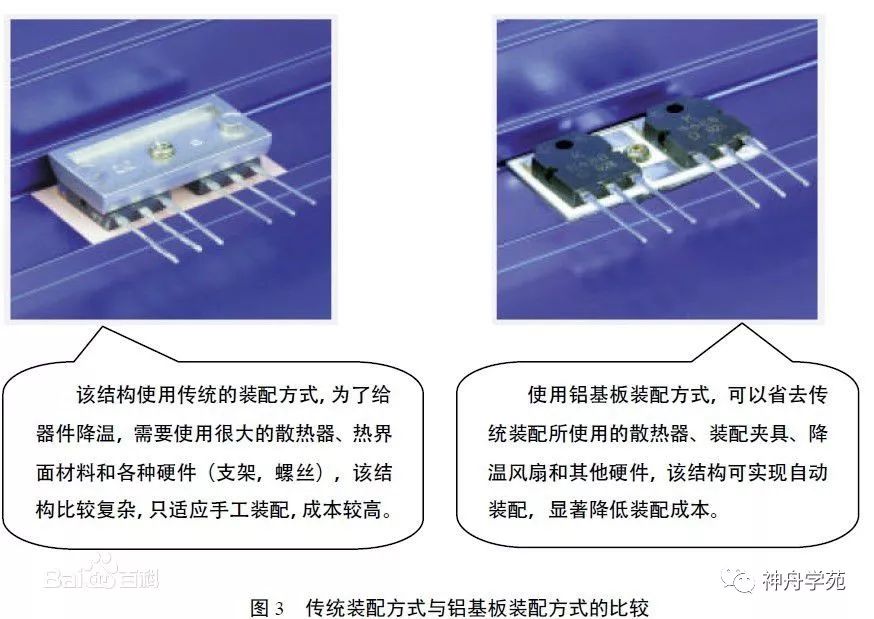
Metal-based PCB: Represented by electronic aluminum substrates, which are a unique type of aluminum-based copper-clad laminate.
Characteristics: It has good thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and machinability. The biggest difference between aluminum-based copper-clad laminate and conventional FR-4 copper-clad laminate is its heat dissipation. Compared to a 1.5mm thick FR-4 copper-clad laminate, which has a thermal resistance of 20 to 22 °C/W, the aluminum-based copper-clad laminate has a thermal resistance of 1.0 to 2.0 °C/W, which is significantly lower, resulting in better heat dissipation. (Baidu Encyclopedia)
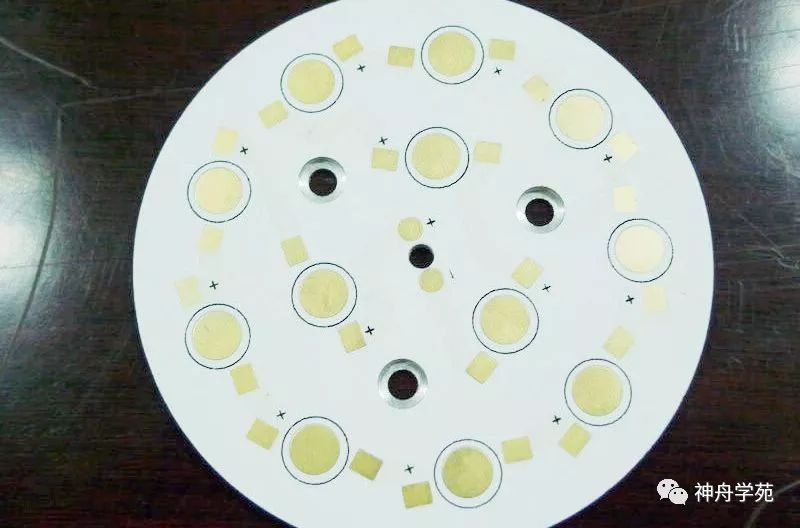

(From Baidu Encyclopedia)
(From Baidu Encyclopedia)
(From Baidu Encyclopedia)
Ceramic substrate: Ceramic substrates refer to special process boards where copper foil is directly bonded to alumina (Al2O3) or aluminum nitride (AlN) ceramic substrates at high temperatures (single-sided or double-sided).
Characteristics: Strong mechanical stress, stable shape; high strength, high thermal conductivity, high insulation; strong bonding force, corrosion resistance. Therefore, ceramic substrates have become the basic materials for high-power power electronic circuit structure technology and interconnection technology. (Baidu Encyclopedia)
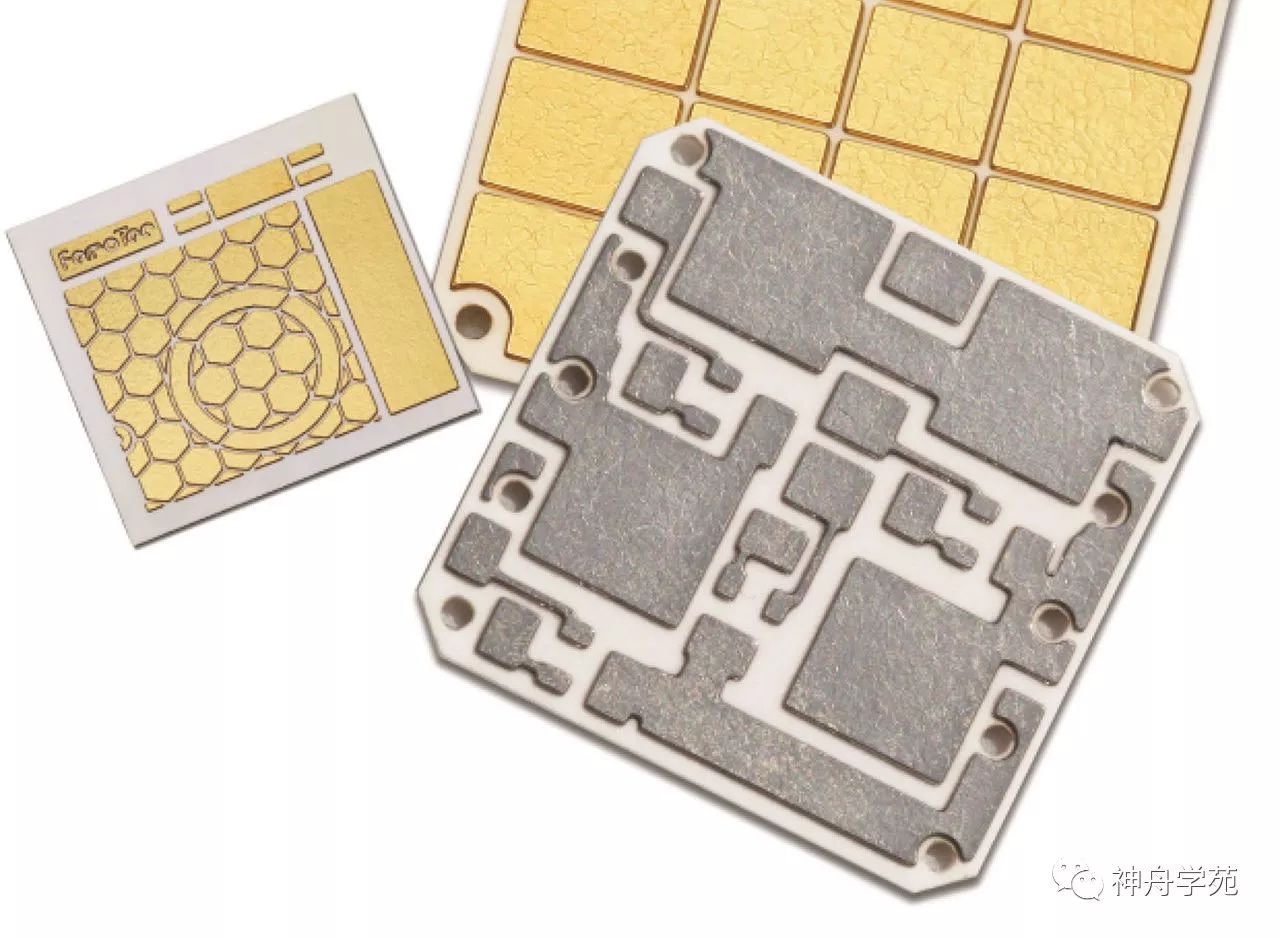

Of course, there are many types of PCBs classified by substrate, and I have only introduced a few representative ones.
Reprint Statement: Unauthorized reprinting of articles, images, and videos from [Shenzhou Academy] is prohibited. For reprints, please contact customer service: [email protected]
01
—
Postscript
Long press to identify the QR code to follow the [Shenzhou Academy] subscription number and start our learning journey together.

02
—
About Shenzhou Academy
[Shenzhou Academy] is the WeChat subscription number of the Yantai Branch of the Shenzhou Academy of the China Academy of Space Technology, affiliated with the Shandong Aerospace Electronic Technology Research Institute. It is an information exchange platform for internal training applications within enterprises. In [Shenzhou Academy], managers can share management stories, engineers can hold technical salons, and operators can compete in skills. The academy also welcomes you to actively participate by writing articles, filming videos, or sending pictures. Remember the editor’s email: [email protected], and the editor will carefully help you publish.
Come on, let’s showcase your sense of achievement!

Disclaimer: This account is non-profit. The text, images, and audio-visual materials in this article are reprinted from the internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author. If the relevant rights holder has any objections, please contact: [email protected] for deletion.
The leader said, if you like it, the editor’s salary will increase by 0.5 yuan!