
Abstract—The evolution from 5G to 6G networks highlights the strong demand for Machine Learning (ML), particularly for Deep Learning (DL) models, which have been widely applied in mobile networks and communications to support advanced services in emerging wireless environments such as smart healthcare, smart grids, autonomous driving, aerial platforms, digital twins, and the metaverse.
With the rapid growth of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, many of which have limited computational capabilities, there is an accelerated development of TinyML and resource-efficient ML methods to achieve cost-sensitive services. However, deploying Large-scale Machine Learning (LargeML) solutions typically requires substantial computational resources and complex management strategies to support large-scale IoT services and ML-based content applications. Therefore, the integration of TinyML and LargeML is seen as a promising direction for achieving seamless connectivity and efficient resource management in the future.
Despite the enormous potential for integrating TinyML and LargeML, several challenges remain, including performance optimization, deployment strategies, resource management efficiency, and security considerations. In this review, we revisit and analyze the latest research progress aimed at promoting the integration of TinyML and LargeML models to enable intelligent services and applications in future 6G networks and beyond. Finally, this paper summarizes the current key challenges and points out future research directions for achieving deep integration of TinyML and LargeML in next-generation wireless networks.
Keywords—6G, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Deep Learning (DL), Distributed Learning, Federated Learning (FL), Internet of Things (IoT), Large-scale Machine Learning (LargeML), Machine Learning (ML), Tiny Machine Learning (TinyML).
1. Introduction
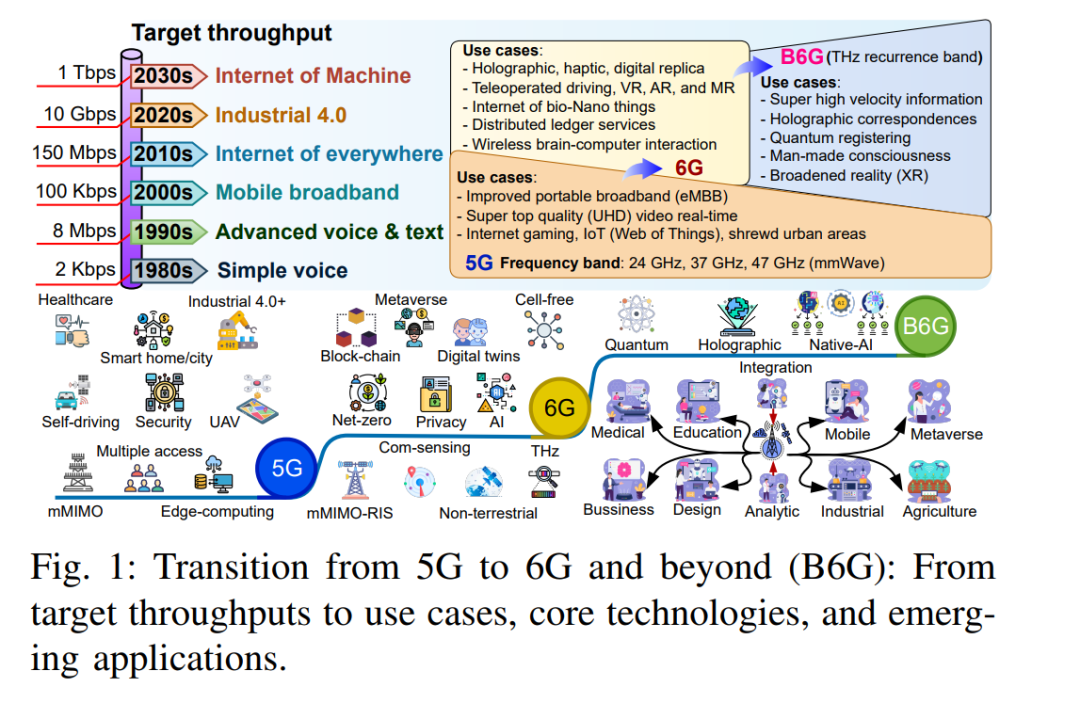
The evolution of communication technology has shown significant leaps every decade. From the first generation (1G) analog systems that introduced mobile voice communication to the fifth generation (5G) networks that revolutionize industries with ultra-high speeds and low latency, each generation of technology has had a profound impact [1]. Looking ahead, the sixth generation (6G) networks are expected to further break technological boundaries, providing unprecedented capabilities and driving a wave of global innovation. The core characteristics of 6G will significantly distinguish it from previous generations of communication systems (see Figure 1) and empower diverse application scenarios. These characteristics focus on meeting the growing demand for data rates, higher reliability, more efficient spectrum management capabilities, and “super-intelligent” communication services. Additionally, 6G will achieve a deep integration of advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies, significantly expanding the capabilities of wireless networks and enhancing the quality of delivery for high-end applications and services.
The introduction of AI and ML will bring unprecedented levels of automation and intelligence to 6G, opening up a range of emerging high-end application scenarios [2]. Currently, AI operates at multiple levels of the network to enhance dynamic resource management, predictive maintenance, and personalized user experiences. ML, particularly the breakthroughs of Deep Learning (DL) architectures in tasks such as image recognition and natural language processing (NLP) [3], will support high-fidelity holographic communication. This will enable users to interact in immersive three-dimensional environments, potentially transforming remote collaboration methods. In a future society where everything is interconnected, 6G will fully unleash the potential of the Internet of Things (IoT) and mobile big data, advancing the arrival of a deeply interconnected era.
A. Background and Motivation
Over the past decade, the field of AI has gradually focused on two distinct yet complementary paradigms: TinyML and LargeML. TinyML focuses on building efficient models for resource-constrained edge devices to achieve real-time analysis of near-source data [4]; whereas LargeML relies on powerful cloud computing resources to handle complex data-intensive tasks, with typical representatives including large language models such as GPT-4 and BERT, widely used in sentiment analysis, text generation, and other scenarios [5] (e.g., large language models LLM, generative AI, Agentic AI, etc.).
However, the high dependence of LargeML on computational resources limits its real-time deployment capabilities on resource-constrained devices and also brings privacy risks. TinyML effectively mitigates these issues by preprocessing data on the edge; moreover, through Knowledge Distillation technology, LargeML can deploy compressed models on edge devices to achieve collaborative learning [6]. This collaborative strategy enhances the flexibility and efficiency of IoT service deployment. TinyML can leverage the complex learning capabilities of LargeML to improve prediction accuracy, while LargeML benefits from the real-time responsiveness and privacy protection capabilities of TinyML. Table 1 compares the main characteristics of TinyML and LargeML.
The integration of TinyML and LargeML is expected to combine the advantages of both, breaking through their respective limitations and enhancing the overall capabilities of AI in 6G networks. For example, wearable health monitoring devices can use TinyML to analyze vital signs in real-time [7], while LargeML can identify health risks based on historical data. In virtual environments, TinyML can process electroencephalogram (EEG) signals to assess emotional states [8], while LargeML can drive interactive behaviors in the metaverse based on this information [9].
Despite the promising outlook, this integration still faces challenges such as security risks, AI explainability, and data privacy. In summary, combining the lightweight deployment capabilities of TinyML with the powerful learning capabilities of LargeML will enable seamless interaction from devices to servers, promoting intelligent living and data-driven innovation.
B. Current Status Review and Contributions of This Paper
The current AI ecosystem is driven by the complementary paradigms of TinyML and LargeML. TinyML supports resource-constrained devices to perform machine learning tasks locally, while LargeML trains large models in the cloud to handle massive data. With the continuous development of the IoT and the approach of 6G, the collaborative integration of these two learning methods shows great potential, especially in enhancing network performance and service quality under complex conditions.
In recent years, review studies on TinyML have covered its foundational knowledge, development tools, application scenarios, and future directions [10]–[15]. These literatures highlight the wide applications of TinyML in industrial IoT, smart healthcare, autonomous driving, environmental monitoring, public safety, human-computer interaction, agriculture, and emergency response. Among them, [10] emphasizes the key role of hardware-software co-design in achieving efficient TinyML, while [12] systematically summarizes the current mainstream development toolchains, including hardware platforms, software frameworks, and supporting libraries.
However, in the context of 6G, existing reviews on TinyML still have some shortcomings. For instance, most literature fails to delve into the integration challenges and collaborative strategies with LargeML [11], and there is little focus on key issues such as communication protocol optimization and power consumption control [14][15].
Meanwhile, research on LargeML has focused on model architectures, application paradigms, and deployment challenges [16]–[20], such as performance analysis of large models based on Transformers, pre-trained language models (PLMs), and parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) technologies [18]. Although these studies are systematic, most do not consider the deployment adaptability of LargeML in 6G scenarios and its interoperability with TinyML.
Therefore, there is still a lack of systematic reviews discussing the application potential and implementation pathways of the integration of TinyML and LargeML in 6G networks. This review aims to fill this gap by providing a systematic analysis of the application of TinyML-LargeML integration in 6G and future network paradigms. Its main contributions are as follows:
-
Background Review: Systematically outline the development trajectory of TinyML and LargeML, analyzing their respective advantages and collaborative possibilities;
-
Motivation and Demand for Integration: Summarize the technical motivations, design requirements, and their key roles in the 6G architecture;
-
Efficient Integration Strategies: Propose and evaluate a series of bidirectional integration mechanisms to enhance model performance and system intelligence;
-
Application Analysis: In-depth exploration of the practical applications of integrated systems in smart healthcare, autonomous driving, industrial IoT, and more;
-
Challenges and Future Research Directions: Summarize existing challenges and propose future research directions, such as resource scheduling, communication efficiency, standardization, and security.
C. Structure of the Paper
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 introduces the basic concepts and recent developments of TinyML and LargeML; Section 3 analyzes the motivations and technical requirements for promoting the integration of the two in 6G networks; Section 4 reviews efficient bidirectional integration strategies, including transfer learning (TL), federated transfer learning (FTL), split learning (SL), and federated split learning (FSL); Section 5 discusses the applications of integrated systems in data privacy, network security, contactless networks, brain-like metaverse, and more; Section 6 summarizes research insights and proposes future research directions; Section 7 concludes the paper.


For convenient viewing, visit the following website or click the “Read Original” link at the bottom
https://www.zhuanzhi.ai/vip/e8c65d0b40b0fa19d653dbcde333571d

Click “Read Original” to view and download this article