On the grand stage of modern industrial production, various automation devices resemble precision instruments, collectively playing a symphony of efficiency, accuracy, and safety. Core devices such as PLCs, sensors, encoders, inverters, and relays not only perform unique roles but also collaborate closely to ensure the smooth operation of the entire production process. Next, let us delve into the mysteries and charms behind these key devices through a series of vivid practical cases.First: Physical Wiring of PLC and Temperature Sensor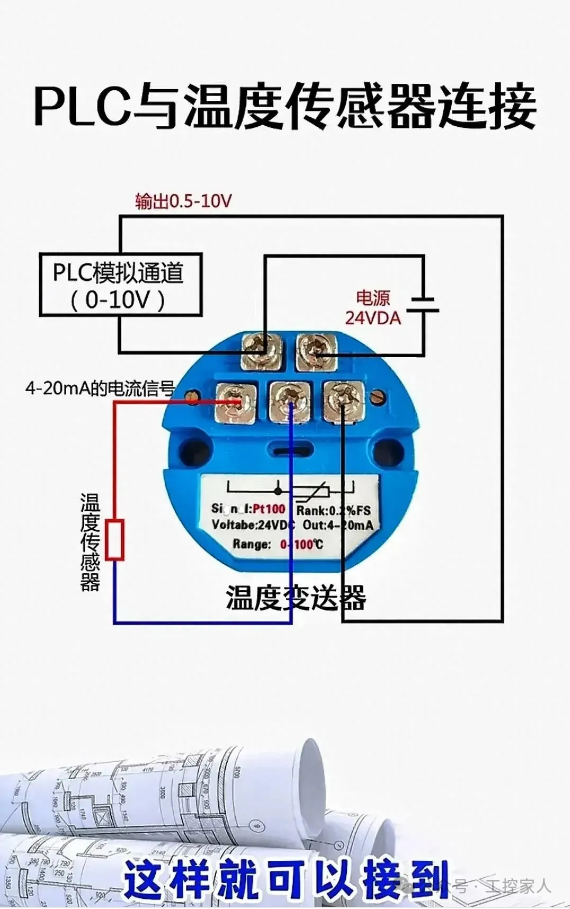 Second: Understanding the Basic Parameters of Encoders
Second: Understanding the Basic Parameters of Encoders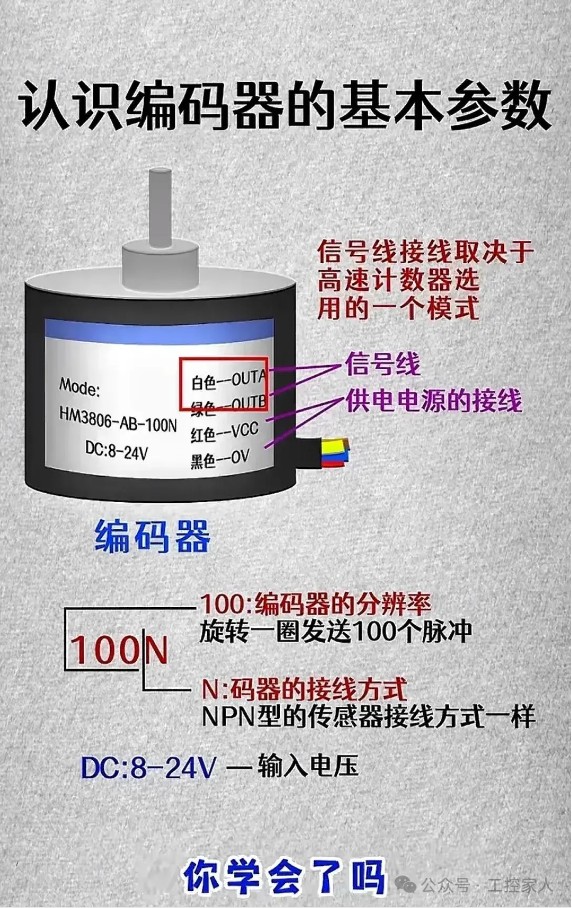 Third: Meaning of Terminal Letter Symbols on Inverter Control
Third: Meaning of Terminal Letter Symbols on Inverter Control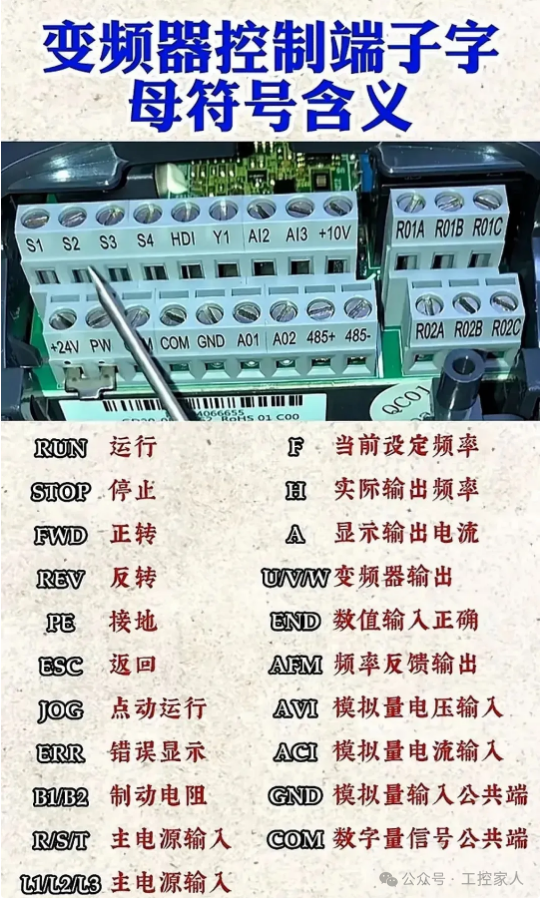 Fourth: Wiring of PLC and Servo Drive
Fourth: Wiring of PLC and Servo Drive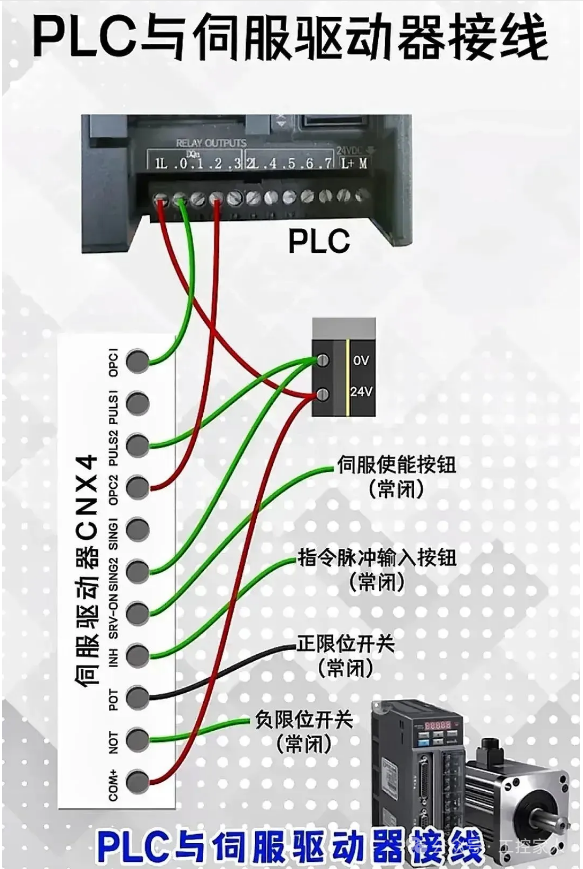 Fifth: Wiring Diagram of Relay Type PLC Operation
Fifth: Wiring Diagram of Relay Type PLC Operation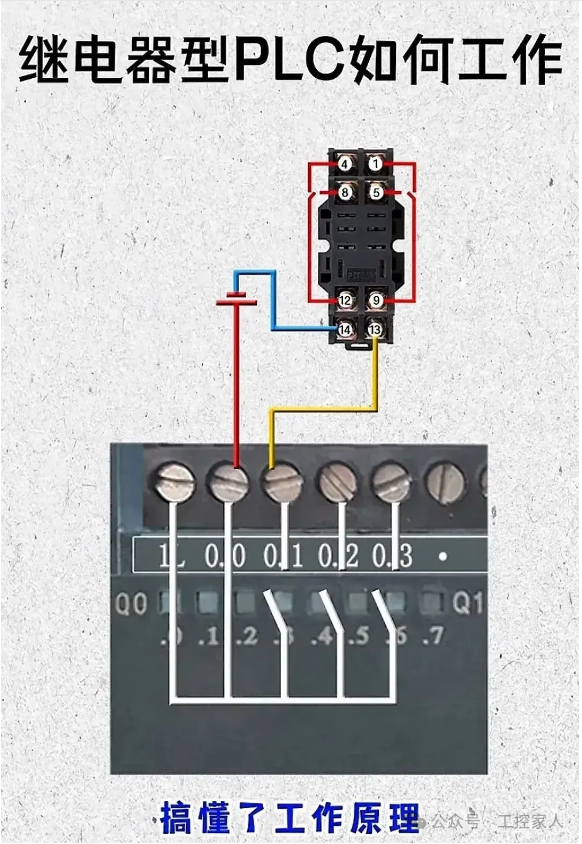 Sixth: Common Special Auxiliary Relays in Siemens PLC Programming
Sixth: Common Special Auxiliary Relays in Siemens PLC Programming Seventh: Differences Between RS232 and RS485
Seventh: Differences Between RS232 and RS485 Eighth: Wiring of NPN Proximity Switch and 200SMART PLV
Eighth: Wiring of NPN Proximity Switch and 200SMART PLV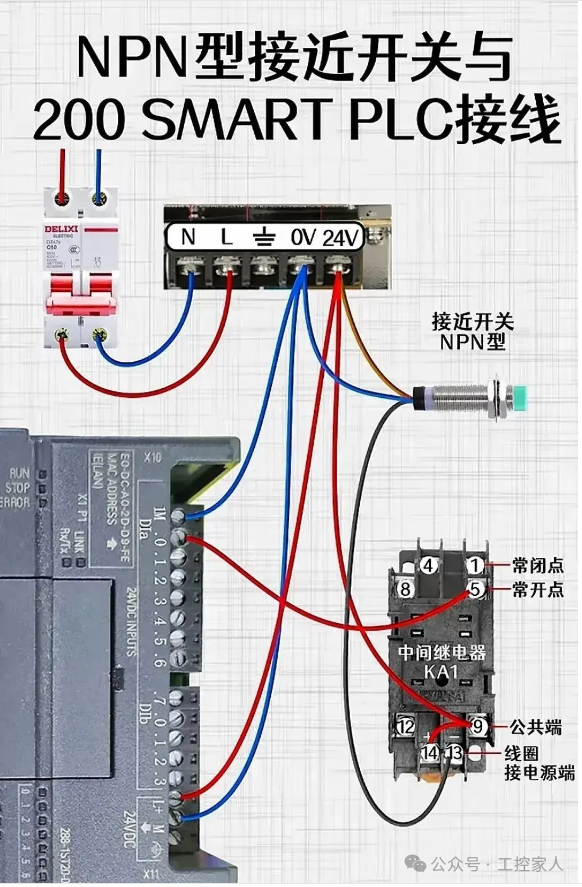 Ninth: Differences Between Servo Motors and Stepper Motors
Ninth: Differences Between Servo Motors and Stepper Motors Tenth: One-Button Start-Stop Circuit Diagram and PLC Program
Tenth: One-Button Start-Stop Circuit Diagram and PLC Program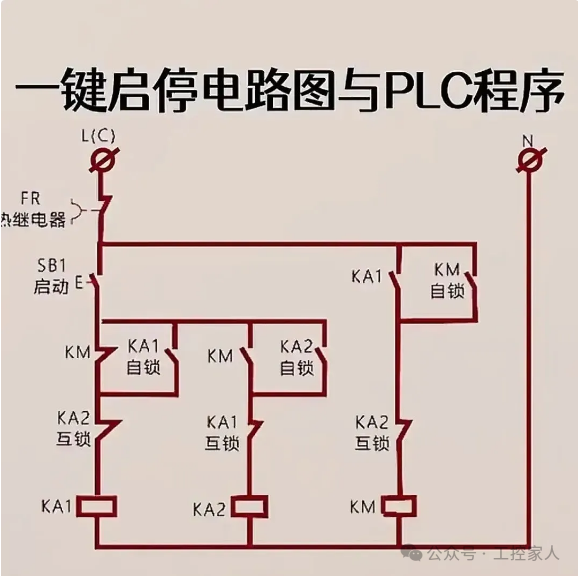
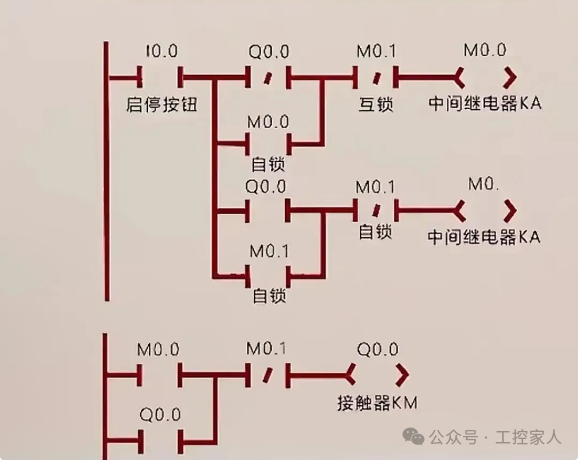 Eleventh: Framework Structure of PLC Programs
Eleventh: Framework Structure of PLC Programs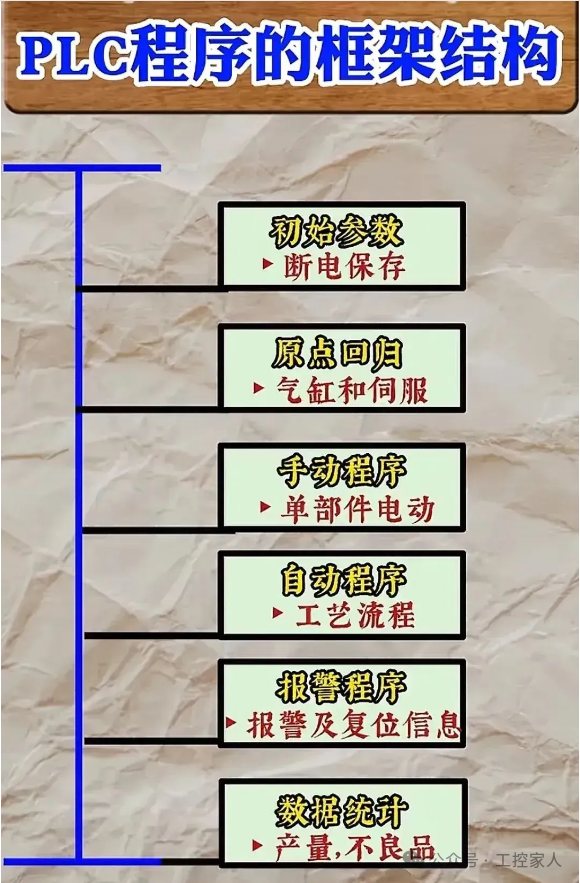 Twelfth: What is a PLC Pulse Signal
Twelfth: What is a PLC Pulse Signal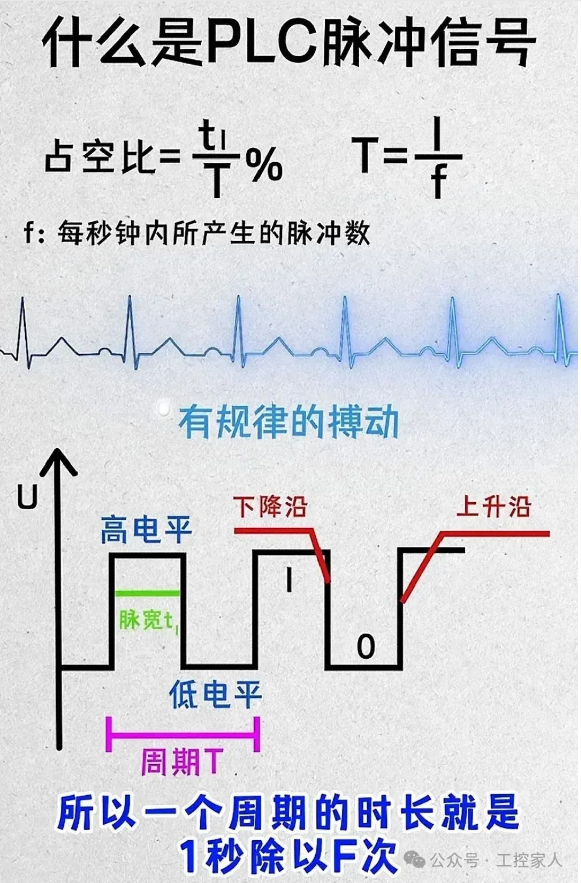 Thirteenth: Differences Between RS232, RS422, and RS485
Thirteenth: Differences Between RS232, RS422, and RS485 Fourteenth: Function Description of Common Letter Symbols for Servo Motors
Fourteenth: Function Description of Common Letter Symbols for Servo Motors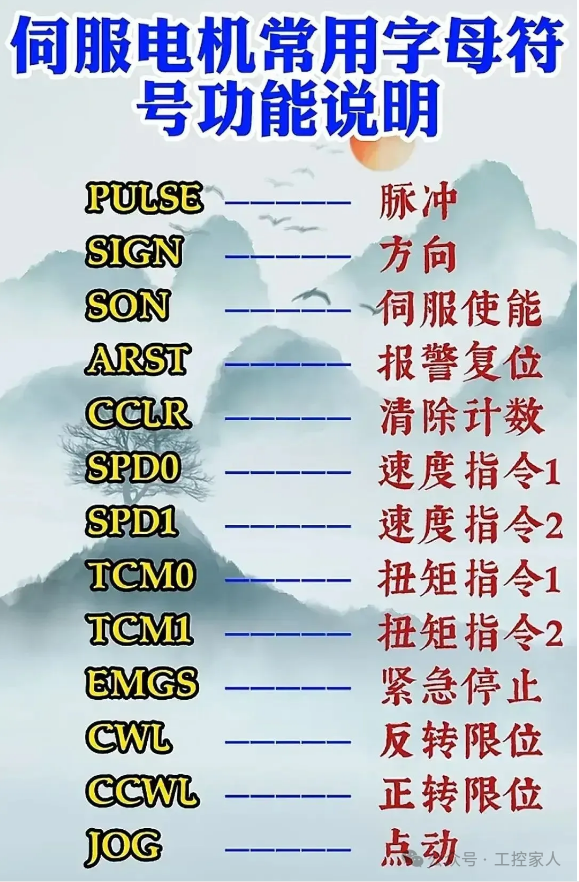 Fifteenth: Differences Between NPN and PNP
Fifteenth: Differences Between NPN and PNP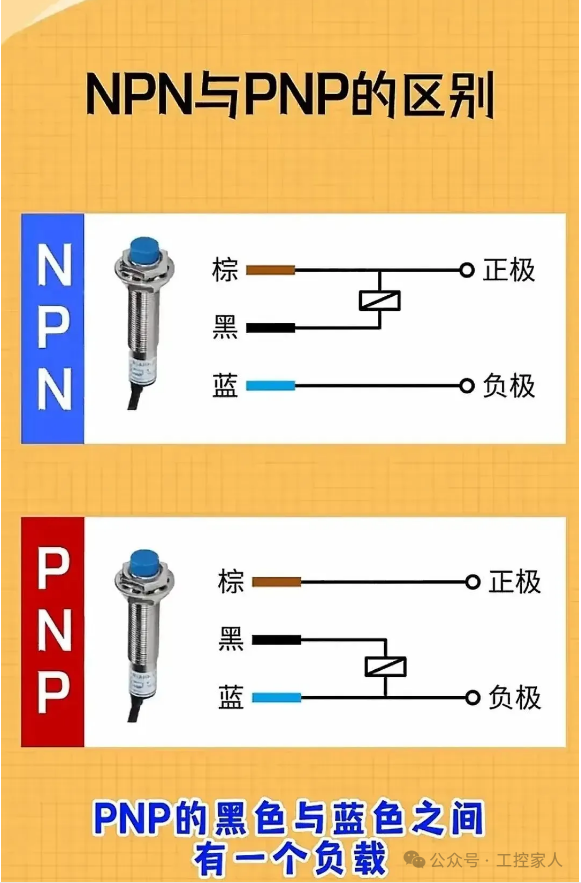 Sixteenth: How to Wire Encoder A Phase and B Phase
Sixteenth: How to Wire Encoder A Phase and B Phase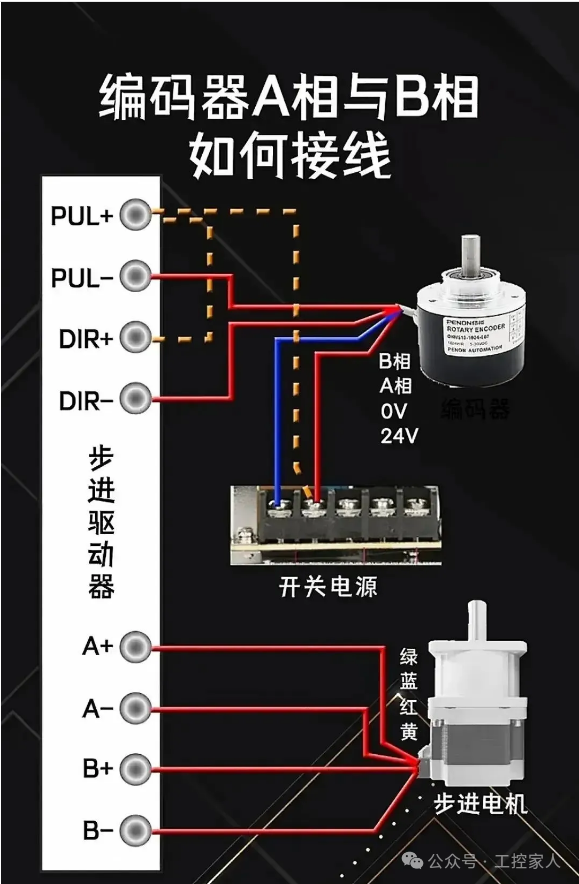 Seventeenth: Modbus RTU Communication Commands
Seventeenth: Modbus RTU Communication Commands Eighteenth: External Potentiometer and Braking Resistor Parameter Settings for Inverters
Eighteenth: External Potentiometer and Braking Resistor Parameter Settings for Inverters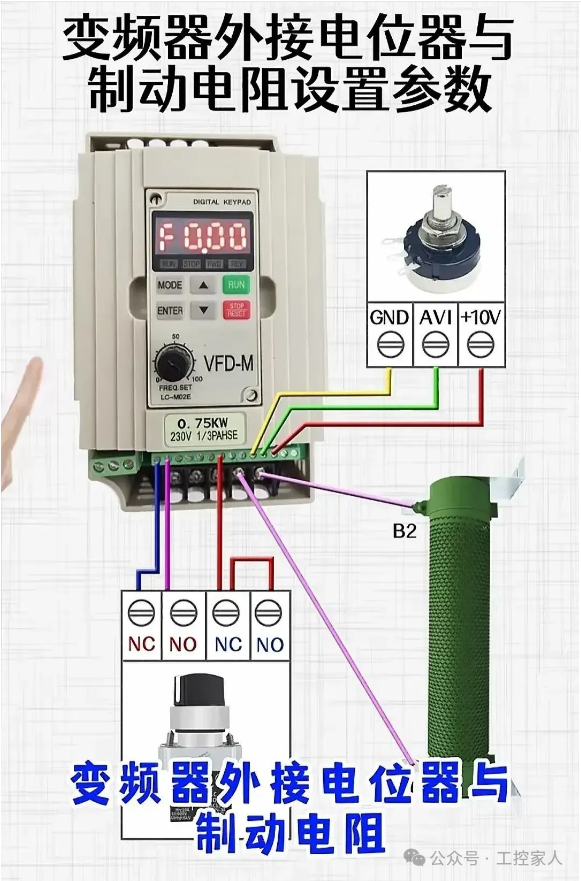 Nineteenth: Understand PLC Wiring and Working Principles in 1 Minute
Nineteenth: Understand PLC Wiring and Working Principles in 1 Minute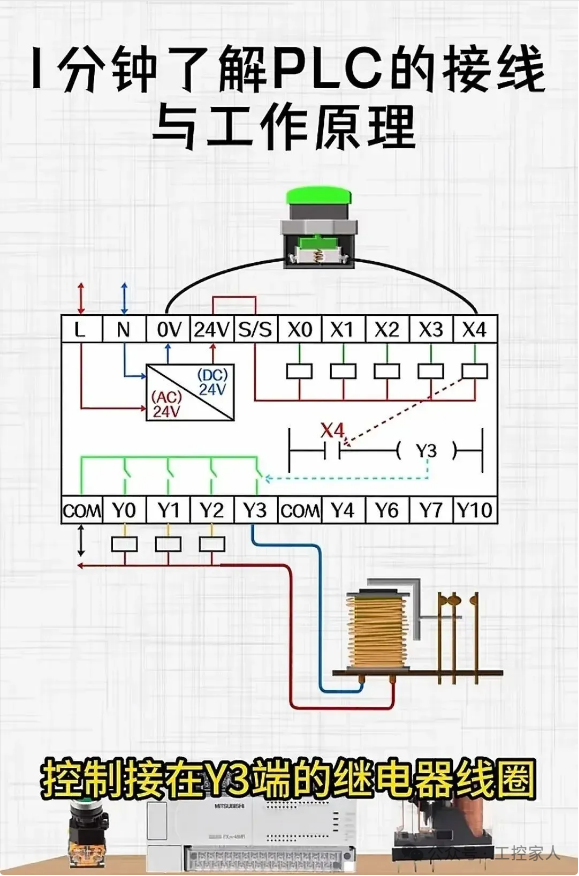 Twentieth: Reading Surface-Mounted Resistors
Twentieth: Reading Surface-Mounted Resistors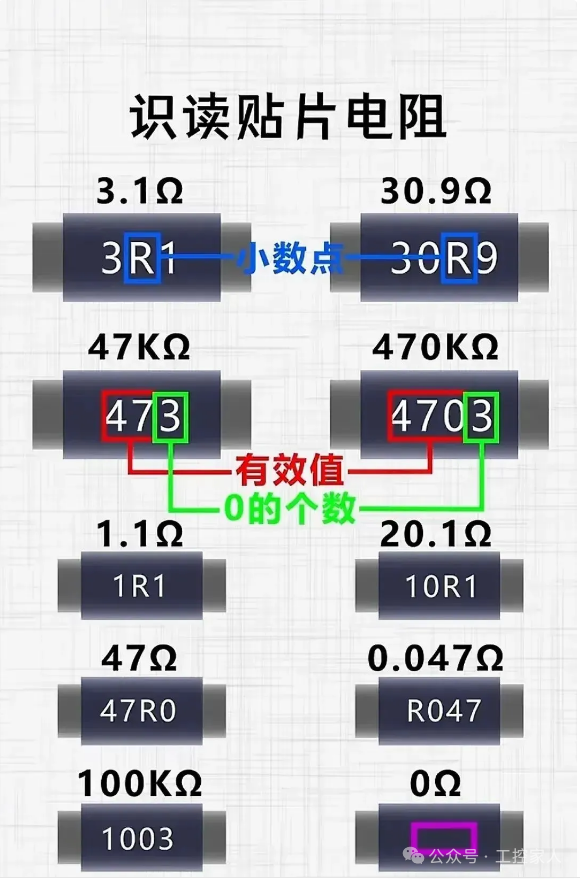 Everyone, please like and share!
Everyone, please like and share!