Click Above↑ “Old Wang Talks to You”ElectricalI
The bus short-circuit isolator is mainly used to isolate components on the bus, isolating fire detectors, combustible gas detectors, manual alarm buttons, and sound and light alarms in a specific area or segment, to avoid affecting the reliable operation of the system in areas that are not isolated. This is key to ensuring the overall functionality of the system is maximally protected from the impact of faulty components.

1. Setting of Short-Circuit Isolators
The fire protection standard “Design Specification for Automatic Fire Alarm Systems” states:
Short-circuit isolators should be installed on the system bus. The total number of fire detectors, manual fire alarm buttons, and modules protected by each short-circuit isolator should not exceed 32 points. When the bus crosses fire compartments, short-circuit isolators should be installed at the crossing points.
This regulation requires that short-circuit isolators be installed on the bus, and the number of field components protected by each short-circuit isolator should not exceed 32 points. This is to ensure that when a field component fails, the short-circuit isolator can isolate the faulty component, maximizing the protection of the overall system functionality from the impacts of faulty components.
Note:
1. The 32 points in the regulation refer to the number of fire protection devices, not considering device addresses. Standardized modules (such as input/output modules or multi-input/output modules) are counted as one device. For module boxes, the count is based on the number of modules within the box.
a. One input module connects to one device
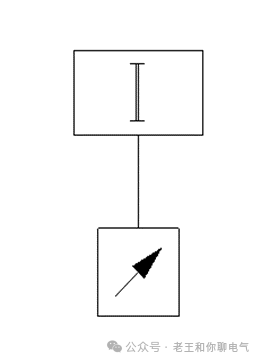
1 device count
b. One input/output module connects to one device
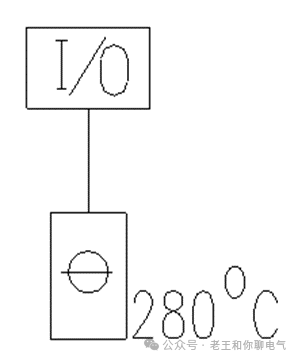
1 device count
Standardized multi-input/output modules (regardless of how many addresses they occupy) are counted as 1 point. For example, the GST-LD-8303 dual input/dual output module counts as 1 device when calculating device count, even though it has 2 encoding addresses when calculating addresses.
The GST-LD-8303 dual input/dual output module is a bus control interface that can be used to control dual-action devices such as two-step fire shutter doors, water pumps, and smoke exhaust fans. It is mainly used for controlling the position of the fire shutter door, allowing it to be controlled from the upper position to the middle position, and from the middle position to the lower position, while also confirming the current position of the fire shutter door. This module can also be used as two independent GST-LD-8301 single input/output modules. The GST-LD-8303 dual input/output module has two encoding addresses, which are continuous.
2. The bus in the regulation includes alarm buses and power lines; short-circuit isolators should be able to isolate faulty alarm buses and power lines.
3. The term “crossing” in the regulation includes entering another fire compartment from one fire compartment.
2. The setting of bus short-circuit isolators is divided into tree structure and ring structure.
Tree Structure:
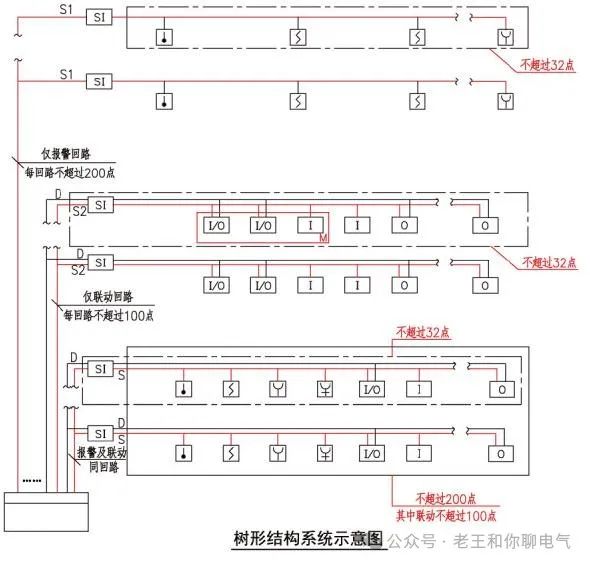 Tree Structure System Diagram
Tree Structure System Diagram
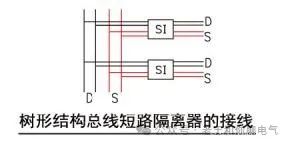 Wiring of Tree Structure Short-Circuit Isolators
Wiring of Tree Structure Short-Circuit Isolators
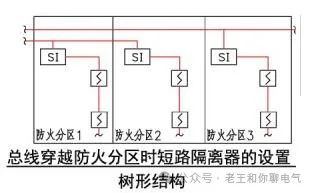 Setting When Tree Structure Crosses Fire Compartments
Setting When Tree Structure Crosses Fire Compartments
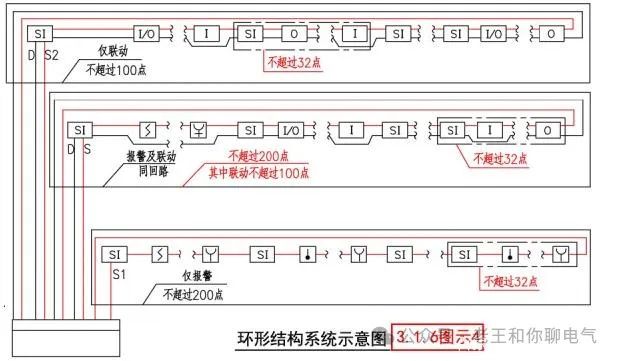 Ring Structure Diagram
Ring Structure Diagram
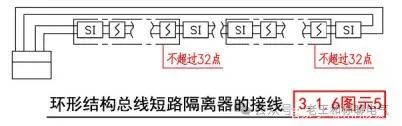 Wiring of Ring Structure Short-Circuit Isolators
Wiring of Ring Structure Short-Circuit Isolators
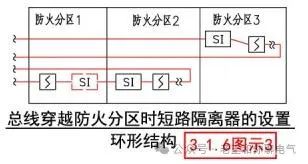 Setting When Ring Structure Crosses Fire Compartments
Setting When Ring Structure Crosses Fire Compartments
Note:
1. In Figure 3, the bus only crosses the fire compartment, and if no devices are connected within the fire compartment, a short-circuit isolator is not required in that compartment. The short-circuit isolator in the ring structure can be set on either side of fire compartment 1 or fire compartment 2.
2. Some device manufacturers’ short-circuit isolator products occupy address numbers, and the address count is based on the manufacturer’s specified address count.
3. Short-circuit isolators can be placed in module boxes or mounted on walls near the route, with a bottom edge height of 2.2m. When installed in a ceiling, the bottom edge should be 0.2m from the ceiling, and there should be a maintenance ceiling nearby, clearly marked. Short-circuit isolators in tree structure can also be concentrated in weak current vertical shafts.
4. Short-circuit isolators for ring and tree structures generally cannot be interchangeable.
5. If the fire detector itself has isolation functionality, a separate short-circuit isolator does not need to be installed.
6. Whether to adopt a tree structure or ring structure for the bus circuit is determined by the designer, who will select the appropriate products.

