Scan to FollowLearn Embedded Systems Together, learn and grow together

One of the main differences between RT-Thread and many other RTOS like FreeRTOS is that it is not just a real-time kernel, but also has a rich set of middleware components, as shown in the figure below.
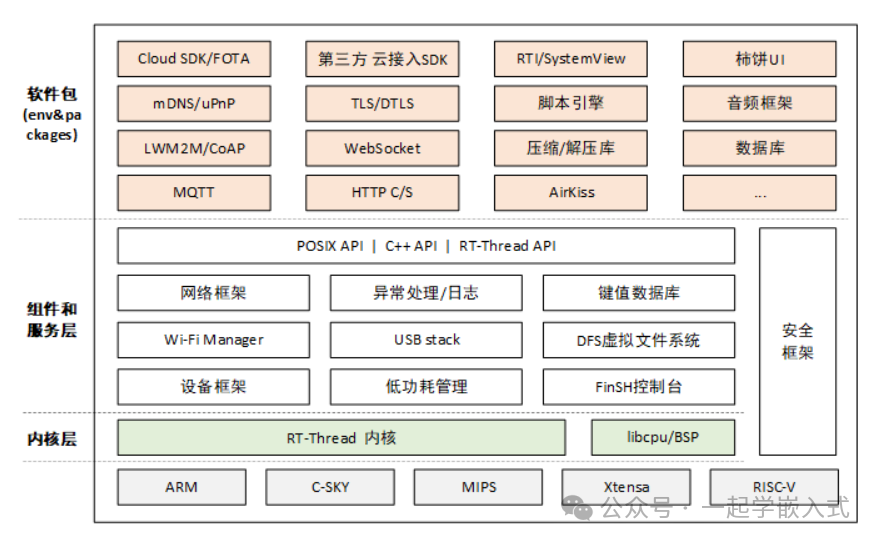
FreeRTOS and RT-Thread are two common embedded real-time operating systems (RTOS), and they have some differences in design philosophy, kernel architecture, ecosystem, and application domains:
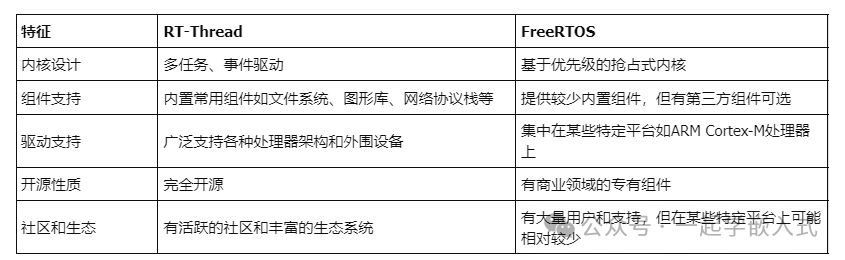
Kernel Design:
The FreeRTOS kernel is a priority-based preemptive kernel, where the execution order of tasks is determined by their priority and can be preempted by higher-priority tasks.
The RT-Thread kernel is multitasking and event-driven, allowing tasks to communicate and synchronize through events, messages, etc., enabling more flexible handling of multitasking scenarios.
Component and Driver Support:
RT-Thread has a rich set of built-in components and driver support, such as file systems, network protocol stacks, graphics libraries, etc., and has broader support for different processor architectures and peripheral devices.
FreeRTOS offers fewer components but can be extended through third-party components. Its driver support mainly focuses on specific platforms like ARM Cortex-M processors.
Open Source Nature:
RT-Thread is fully open source, allowing users to freely view, modify, and distribute the source code.
FreeRTOS is also open source, but there are some proprietary components in the commercial domain that require purchasing a commercial license to use.
Community and Ecosystem:
RT-Thread has an active community and a rich ecosystem, where users can obtain technical support, share experiences, and access a large number of open-source projects for reference and use.
FreeRTOS also has a large user base and support, but may be relatively less on certain specific platforms.
In summary, FreeRTOS is more suitable for simple real-time system applications with lower resource requirements, while RT-Thread is better suited for complex multitasking scenarios, with more component and driver support, as well as a more flexible event-driven mechanism.
The choice depends on project requirements, hardware platforms, and developer preferences.
Source: RT-Thread IoT Operating System
This article is sourced from the internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author. If there is any infringement, please contact for removal.

Follow 【Learn Embedded Systems Together】 to become better together..
If you find the article good, click “Share”, “Like”, or “Recommend”!