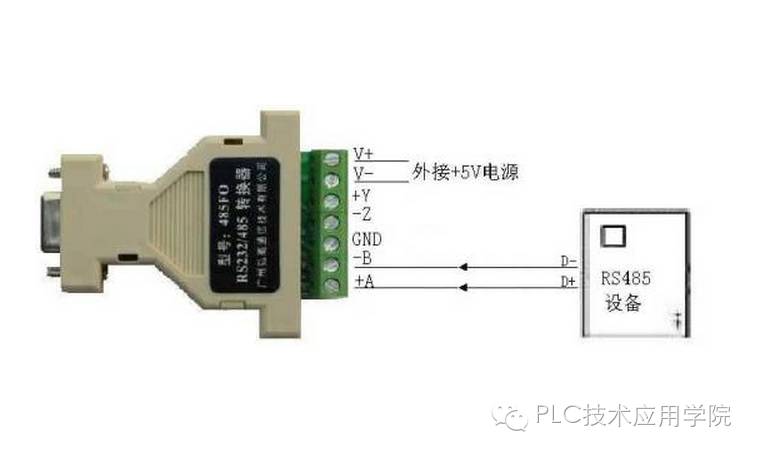
RS-485 belongs to wired transmission, so it requires a hardware transmission medium, which can actually be just two wires. The signal transmitted over these two wires is the same; the sender splits this signal into two, but the receiver restores it to the original signal. The advantage of this method can be compared with RS-232; RS-232 also requires two wires, and more often needs a ground wire, making it three wires. Ignoring the ground wire, the remaining two wires have one wire transmitting the data signal, while the other transmits the clock. The signal is sent out as it was by the sender, and the receiver does the same processing. Therefore, the receiver of RS-485 can cancel out the interference introduced during transmission, whereas the receiver of RS-232 cannot. This means that RS-485 has strong anti-interference capability, allowing it to transmit signals over thousands of meters, while RS-232 can only transmit over tens of meters.
MODBUS is just one type of communication protocol, like Chinese and English; it is a language for communication, a language for machines to communicate with each other. Before communication can occur, there must be a bridge for communication, which is the transmission medium, such as RS-485 or RS-232, or other electrical standards. The same protocol can use different transmission media like RS-485 or RS-232, but two different protocols cannot coexist on the same transmission line.
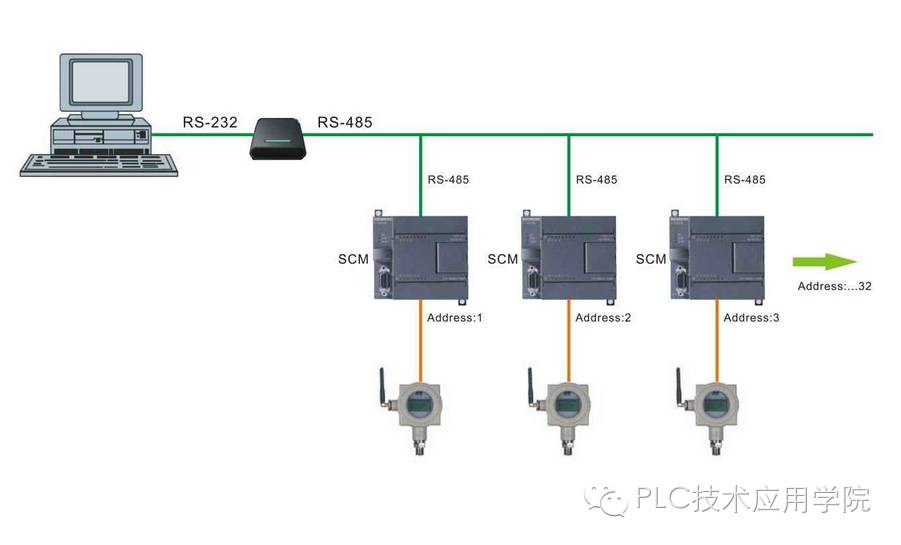
Generally, we use RS-485 interfaces for Modbus communication. RS-485 communication typically has a length of 1200 meters. When this length cannot meet usage requirements, fiber optics may be introduced as a transmission medium, though this requires a photoelectric converter. However, this connection method seems difficult to establish. The best way is to connect Modbus communication to an Ethernet and then transmit data via fiber optics.
RS-485 has the following characteristics:
1. The RS-485 interface uses a combination of balanced drivers and differential receivers, enhancing common-mode rejection and providing good noise resistance.
2. The maximum standard transmission distance for RS-485 is 4000 feet, but it can actually reach 3000 meters. In addition, the RS-232-C interface allows only one transceiver on the bus, meaning it has single-station capability. In contrast, the RS-485 interface allows up to 128 transceivers on the bus, meaning it has multi-station capability, allowing users to easily establish a device network using a single RS-485 interface. The advantages of RS-485, such as good noise resistance, long transmission distances, and multi-station capabilities, make it the preferred serial interface. Since the RS-485 interface forms a half-duplex network, it typically only requires two wires, and therefore uses shielded twisted pair wiring. The RS-485 connector uses a DB-9 9-pin plug, connecting to the intelligent terminal RS-485 interface using DB-9 (socket), and the keyboard interface connecting to the keyboard using DB-9 (pin).
3. The electrical characteristics of RS-485: Logic “1” is represented by a voltage difference of + (2-6)V between the two wires; Logic “0” is represented by a voltage difference of – (2-6)V. The signal levels are lower than those of RS-232-C, making it less likely to damage the interface circuit chips, and this level is compatible with TTL levels, facilitating connections with TTL circuits.
4. The maximum data transmission rate for RS-485 is 10Mbps.