
Serial Communication refers to a communication method for data transmission through serial ports. Data is transmitted bit by bit through data signal lines and ground lines. Common serial ports include RS-232, RS-485, and RS-422. It is important to note that serial ports are only interface standards, specifying the electrical standards of the interface, and not communication protocols. They do not define the interface plug cables or the protocols used.
Serial communication has advantages such as long transmission distances, low costs, and stable reliability. It is widely used in industrial control, automation equipment, instruments, and peripheral devices for low-speed data transmission. Many engineers have certainly encountered RS-232, RS-485, and RS-422 in their daily work. Do you know what the differences are?
01
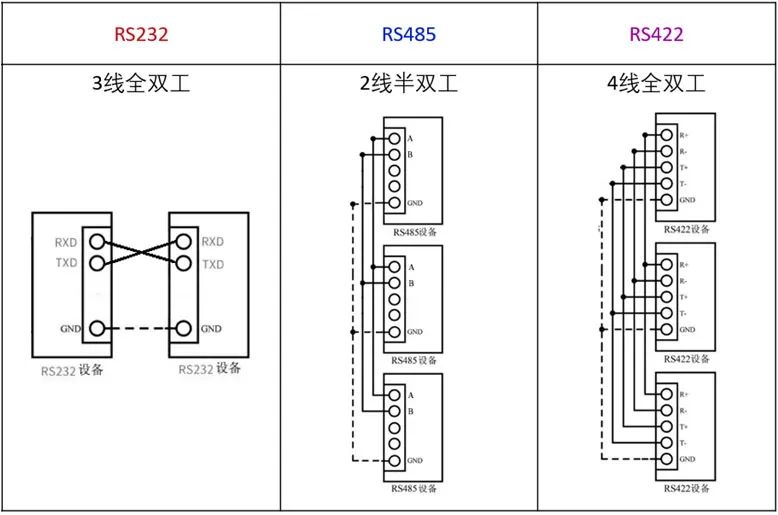
Different Hardware Pin Interface Definitions
RS-422

RS-485

RS-422

02
Different Operating Modes
Serial communication established a standard protocol early on, with DB9 (9 pins) being a typical standard interface. Because serial communication is asynchronous, data transmission can be achieved using only two wires.
Typical operating modes are: RS-232: 3-wire full duplex; RS-485: 2-wire half duplex; RS-422: 4-wire full duplex.
Half Duplex mode uses the same transmission line to send and receive data, but cannot transmit and receive simultaneously. Data transmission allows data to flow in both directions, but at any time, only one party can send data while the other party receives data. Each end in half-duplex communication requires a transceiver switch to determine the direction of data transmission. Due to the switching, there is a time delay, resulting in lower information transmission efficiency.
Full Duplex mode allows data to be transmitted simultaneously in both directions. Thus, full duplex communication combines two simplex communication methods, requiring both sending and receiving devices to have independent receiving and sending capabilities. In full duplex mode, each end has a transmitter and a receiver, resulting in relatively higher information transmission efficiency.
Simplex Communication has one party fixed as the sender and the other fixed as the receiver. Data transmission is unidirectional, using one transmission line.
*RS-485 also has two-wire and four-wire connection methods. When using the four-wire method, only point-to-multipoint communication can be achieved (i.e., only one master device with the rest as slave devices), while the two-wire method is more commonly used.
03
Different Communication Methods
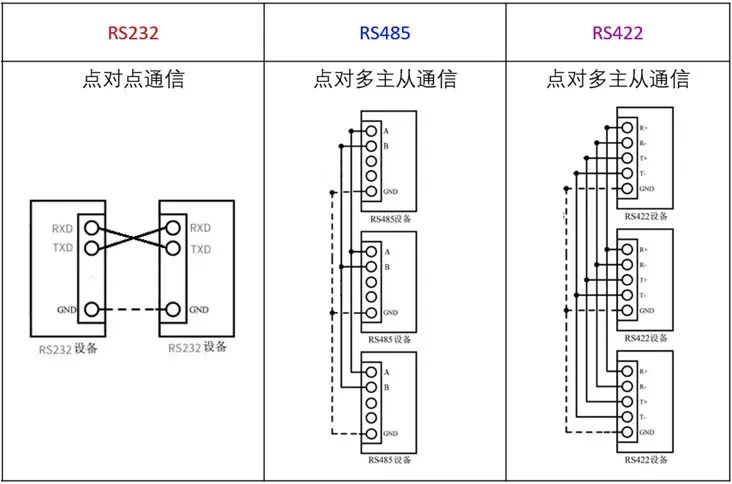
RS-232 is limited to point-to-point communication, which does not allow networking capabilities, leading to the development of RS-422 and RS-485, which can connect and control multiple devices through one serial port.
RS-232: only allows point-to-point communication; RS-485 and RS-422: can achieve point-to-multipoint communication.
04
Different Logical Characteristics
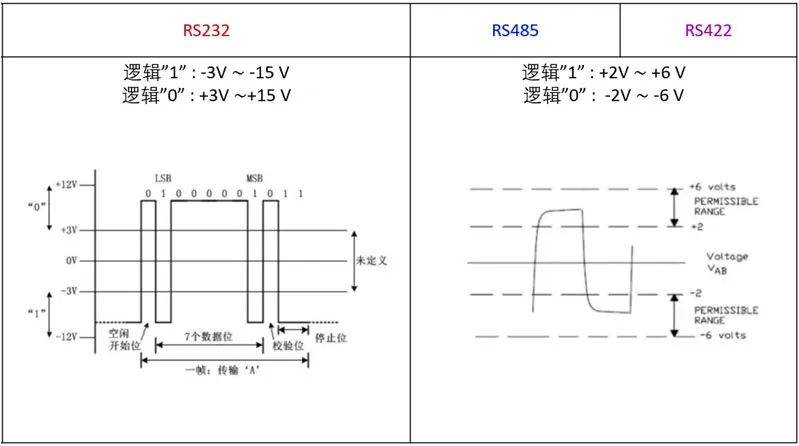
We know that data transmission in serial communication is represented by 0 and 1, determined by high and low voltage levels, as follows:
RS-232: Logic “1”: -3V ~ -15V; Logic “0”: +3V ~ +15V;
RS-485: Logic “1”: +2V ~ +6V; Logic “0”: -2V ~ -6V;
RS-422: Logic “1”: +2V ~ +6V; Logic “0”: -2V ~ -6V;
05
Differences in Anti-Interference, Transmission Distance, and Transmission Rate
Overview of Anti-Interference, Transmission Distance, and Transmission Rate
| Interface | RS-232 | RS-485 | RS-422 |
| Anti-Interference | Prone to common mode interference, weak anti-noise interference. | Uses differential transmission, strong anti-interference. | Uses differential transmission, strong anti-interference. |
| Transmission Distance | Within 50m | Up to 1200m | Up to 1200m |
| Transmission Rate | 20KB/s | 10MB/s | 10MB/s |
Comparison Between RS-232 and RS-485
Anti-interference: The RS-485 interface uses a balanced driver and differential receiver combination, offering good anti-noise interference. The RS-232 interface uses one signal line and one return line, forming a common ground transmission method, which is prone to common mode interference.
Transmission Distance: The maximum transmission distance for RS-485 is standard at 1200 meters (at 9600bps). The RS-232 transmission distance is limited, with a maximum standard value of 50 meters, practically usable at about 15 meters.
Communication Capability: The RS-485 interface allows connection of up to 128 transceivers on the bus, enabling users to easily establish a device network using a single RS-485 interface. RS-232 only allows one-to-one communication.
Transmission Rate: RS-232 has a lower transmission rate, with a baud rate of 20Kbps during asynchronous transmission. The maximum data transmission rate for RS-485 is 10Mbps.
Comparison Between RS-422 and RS-485
RS-422 has four signal lines: two for sending (T+, T-) and two for receiving (R+, R-). Because RS-422 has separate sending and receiving lines, it can send and receive simultaneously (full duplex).
RS-485 only has two data lines: sending and receiving are both A and B. Because RS-485 shares two lines for sending and receiving, it cannot send and receive simultaneously (half duplex).
Note! Instrument Point-to-Point Communication strives to ensure the accuracy of original content but does not take responsibility for any technical or writing errors.