


Scientific Materials Station
Article Information
Selective Two-Electron and Four-Electron Oxygen Reduction Reactions Based on Cobalt-Based Electrocatalysts
First Author: Liang Zuozhong
Corresponding Authors: Liang Zuozhong, Cao Rui
Affiliation: Shaanxi Normal University

Scientific Materials Station
Main Points of the Article
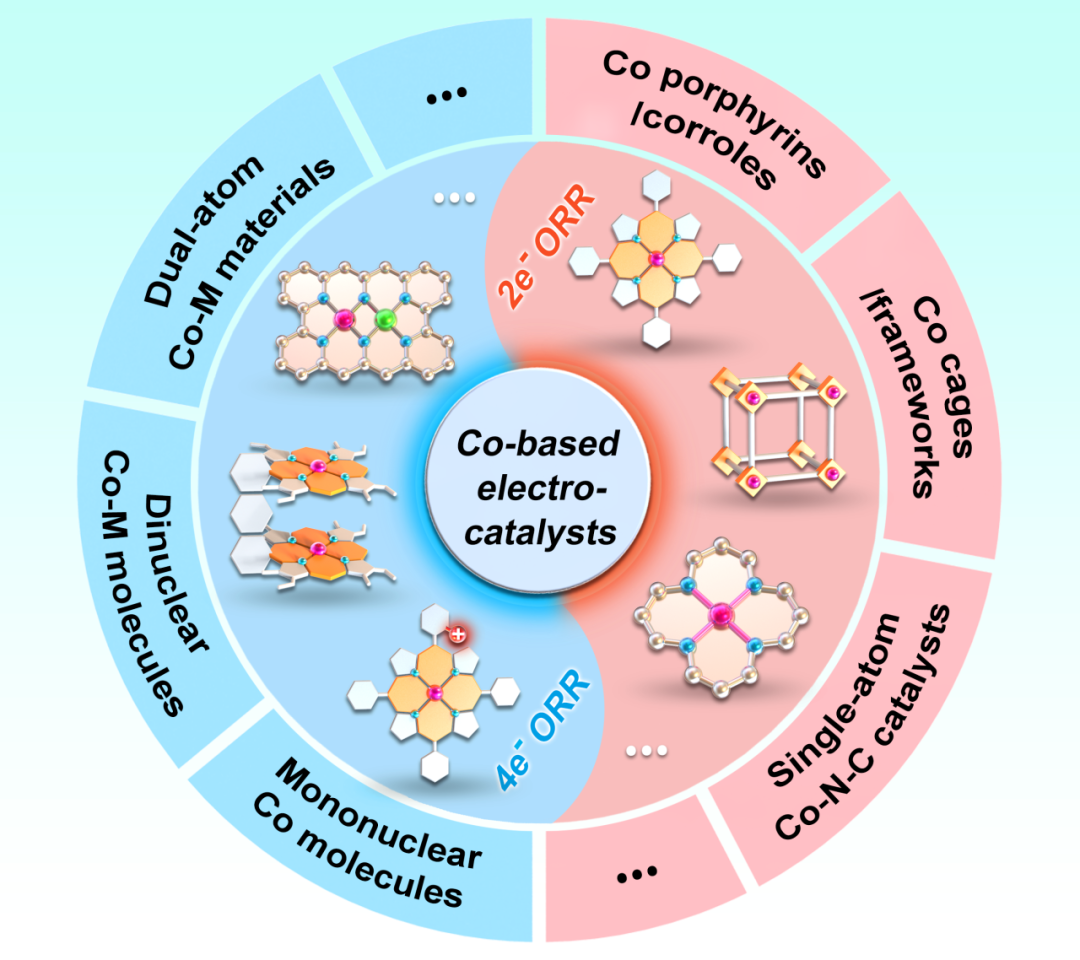
The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) can proceed via two pathways: four-electron (4e⁻) and two-electron (2e⁻). Among these, the 4e⁻ ORR, which produces water (H2O) as the sole product, is a core reaction for fuel cells and metal-air batteries; while the 2e⁻ ORR can be utilized for the electrocatalytic synthesis of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). In practical applications of ORR, precise control over the selectivity of the reaction pathway is crucial, and understanding the structural effects on ORR selectivity is the theoretical basis for this control. Cobalt-based electrocatalysts are widely studied in the field of ORR due to their high activity, low cost, and ease of synthesis. More importantly, by rationally designing their structure, cobalt-based electrocatalysts can achieve high selectivity for either the 2e⁻ or 4e⁻ ORR pathway, making them an ideal model system for studying the intrinsic structure-activity relationship of ORR.
This review first explains the reaction mechanisms of ORR and the methods for evaluating selectivity, systematically summarizes the research progress of cobalt-based electrocatalysts with 2e⁻ and 4e⁻ selectivity (especially cobalt porphyrin catalysts), and summarizes several key structural factors that regulate ORR selectivity. Based on this, targeted suggestions for future research directions of cobalt-based ORR electrocatalysts are proposed. This review provides a scientific basis for the rational design of highly selective 4e⁻/2e⁻ ORR molecular catalysts and material catalysts, while the structural regulation strategies of cobalt-based electrocatalysts also provide important insights for the design and development of other metal-based ORR electrocatalysts.
Scientific Materials Station
Article Link
Selective two-electron and four-electron oxygen reduction reactions using Co-based electrocatalysts
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2025/cs/d4cs01199f
Scientific Materials Station
Corresponding Author Introduction

Liang Zuozhong, Associate Researcher at Shaanxi Normal University. Graduated with a Ph.D. in Engineering from the School of Chemical Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology in June 2016, under the supervision of Academician Chen Jianfeng. From September 2014 to September 2015, he conducted joint training at the Department of Chemistry, New York University, with Professor Bart Kahr as his co-supervisor. He joined Professor Cao Rui’s team at the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shaanxi Normal University in July 2016, was promoted to Associate Researcher in 2019, selected for the “Youth Talent Support Program of Shaanxi Province” in 2020, and recognized as a “2023 Youth Science and Technology Star of Shaanxi Province” in 2022. In recent years, he has mainly engaged in the design, preparation, and application research of catalysts for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution, hydrogen evolution, and oxygen reduction reactions in the field of new energy, including projects funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (2 general projects, youth projects), key R&D programs of Shaanxi Province, and basic research plans of the Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation, among others. He has published over 30 papers as (co-)first author or corresponding author in well-known academic journals such as Chem. Soc. Rev. (2 papers), Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (4 papers), Adv. Mater. (1 paper), and J. Am. Chem. Soc. (1 paper), including 5 highly cited papers and 1 hot paper.

Cao Rui, Professor at Shaanxi Normal University, PhD supervisor, recipient of the National Outstanding Youth Science Fund, and Deputy Director of the Key Laboratory of Applied Surface and Colloid Chemistry of the Ministry of Education. Bachelor from Peking University (2003), Ph.D. from Emory University (2008), postdoctoral fellow at Emory University (2008-2009) and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2009-2011). He joined Renmin University of China in 2011 and transferred to Shaanxi Normal University in 2014. Professor Cao Rui’s research area is molecular electrocatalysis, focusing on the development of novel metal porphyrin/corrole molecular catalytic systems for fundamental research on energy molecular catalytic transformations such as water oxidation, hydrogen evolution, and oxygen reduction. His main research directions include: (1) study of molecular catalytic reaction mechanisms; (2) study of structure-activity relationships of molecular catalysts; (3) study of the phase transformation of molecular catalysts. He has published over 170 papers as corresponding author in journals such as Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (24 papers), J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2 papers), Chem. Sci. (5 papers), ACS Catal. (7 papers); invited to write review articles for Acc. Chem. Res., and authored reviews for Chem. Rev. (2 papers) and Chem. Soc. Rev. (3 papers); selected for the National High-Level Talent Introduction Program in 2011, received the Ho Ying-dong Young Teacher Fund in 2018, and the “Young Scientist Award” from the International Porphyrin and Phthalocyanine Association in 2020; serves on the award committee for the Chemistry Europe Award; serves as the chair of the editorial board of ChemSusChem, editorial board member and guest editor for Chem. Soc. Rev., and youth editorial board member and guest editor for Chinese J. Catal., Chinese Chem. Lett., J. Electrochem., and ChemPhysChem.
Research Group Website Link:
http://glx.sy.snnu.edu.cn/thecaogroup/index.htm



Add Official WeChat to Join Discussion Groups
SCI Carbon Dioxide Mutual Aid Group
SCI Catalytic Materials Exchange Group
SCI Sodium-Ion Battery Exchange Group
SCI Ion Exchange Membrane Experience Group
SCI Fuel Cell Exchange Group
SCI Supercapacitor Exchange Group
SCI Aqueous Zinc Battery Exchange Group
SCI Water Electrolysis Mutual Aid Group
SCI Gas Diffusion Layer Experience Group
Note: [Name – Institution – Research Direction]
Note
🔹If there are any copyright issues with this content, please contact us for timely resolution.
🔹We welcome readers to share and promote this article.
🔹”Scientific Materials Station” will continuously improve its level to share higher quality material consulting with readers, welcome to follow us.
For submissions, please contact [email protected]
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the authors of this article for their strong support of this report.
Share

Support with a Like

Click to View