In recent years, with the intensification of global environmental and climate crises, countries have actively participated in actions to address global climate change, achieving agreements such as the Paris Agreement and the Glasgow Climate Pact. As one of the signatories to the Paris Agreement, China has proactively assumed its responsibilities, solemnly proposing carbon peak and carbon neutrality targets. Against this backdrop, the ground transportation sector, notorious for high carbon emissions, has become a focal point for emissions reduction in China’s dual carbon goals. The new energy vehicle industry, as a green alternative to traditional fuel vehicles, is gradually entering a phase of rapid explosive growth. However, alongside the production and sales growth in this industry, the recycling of new energy power batteries has become a key issue for the industry’s clean, low-carbon, and sustainable development.
Currently, the earliest batch of power batteries in China has entered the phase of scrapping or is on the verge of being scrapped. Used batteries are closely related to the ecological environment and metallic chemical resources, making the establishment of a sustainable recycling system for new energy vehicle power batteries highly significant. This article will analyze the current status of new energy vehicle power battery recycling in China, identify existing problems, and propose preliminary optimization suggestions.
1. Analysis of the Current Status of the New Energy Power Battery Industry
As the process of global climate change governance accelerates, China continues to increase its investment in carbon neutrality-related fields, launching a series of policies such as fiscal subsidies and tax reductions to promote the development of environmentally friendly industries. Benefiting from policy support, China’s new energy vehicle industry has shown rapid development since 2015. According to data from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, in 2022, domestic new energy vehicle production and sales reached 7.058 million and 6.887 million units, respectively, representing year-on-year increases of 96.9% and 93.4%, with a market share as high as 25.6%. In terms of average growth rate, the new energy vehicle industry is expected to maintain rapid development and is likely to exceed 10 million units in production and sales around 2025.
With the development of the new energy vehicle industry, China’s power battery industry has also made significant progress. According to data from the China Automotive Power Battery Industry Innovation Alliance, in 2022, the cumulative installed capacity of power batteries in China reached 294.6 GWh, a year-on-year increase of 90.7%. However, due to the relatively short lifespan of power batteries, generally between 5 to 8 years, the earliest batch of power batteries is currently at or nearing the scrapping phase. Power batteries are composed of casing materials, positive and negative electrode materials, electrolytes, separators, and other materials. Although these materials do not contain highly toxic heavy metals like mercury and lead, they do contain valuable metals such as cobalt, nickel, and copper, as well as electrolytes and organic solvents. If discarded power batteries are not properly recycled and treated, they can pose significant environmental and safety risks to individuals and society, severely harming the social environment and individual health. Conversely, if the high-value metals contained in discarded power batteries, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, can be reasonably recycled, it can generate substantial economic benefits. Under the influence of factors such as the pandemic, the prices of metals like lithium, nickel, and cobalt have seen astonishing increases compared to pre-pandemic levels, with some metal prices rising by more than 200%. This underscores the significant economic benefits of recycling high-value metals from discarded power batteries. Therefore, establishing a sustainable power battery recycling industry is of great importance. As the new energy vehicle industry continues to expand, the total amount of scrapped power batteries will increase, and the power battery industry will gradually enter a period of large-scale scrapping. Thus, it is evident that the recycling of new energy power batteries in China will face a surge in demand in the coming years.
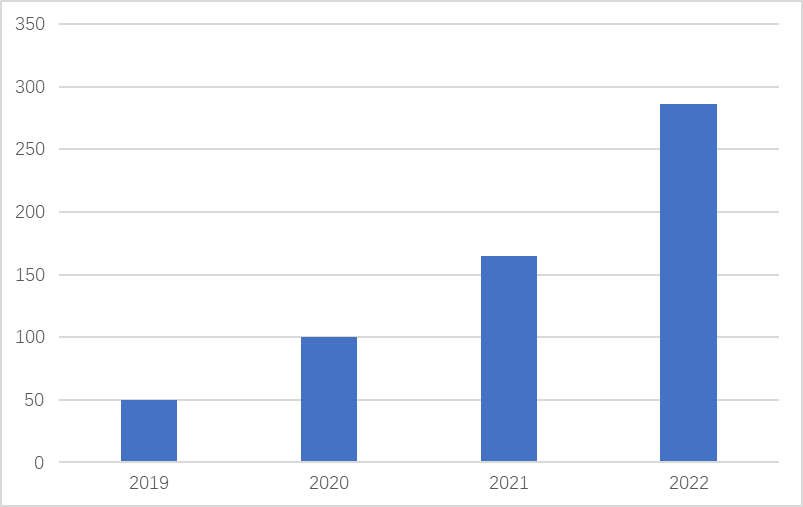
Specifically, based on the existing scale of the power battery recycling market, according to data from China Energy News, as shown in Figure 1, the power batteries produced in China began to enter the batch scrapping period in 2019, with a market scale of approximately 5 billion yuan that year. According to data from the China Automotive Technology Research Center, the cumulative market scale of retired power batteries in China reached 28.6 billion yuan in 2022. In terms of market demand, the theoretical recovery volume of discarded power batteries in China in 2021 was 294,000 tons, and it is expected to reach 540,000 tons, 600,000 tons, and 1.2 million tons from 2023 to 2025, with a projected total of 3.001 million tons by 2030, corresponding to a market space of nearly 150 billion yuan. According to the High Industry Research Institute (GGII), it is expected that by 2025, the cumulative retired power batteries in China will reach 137.4 GWh, with the market showing a significant explosive growth trend.
2. Analysis of the Current Status of the New Energy Power Battery Recycling System
(1) Policy Progress
As early as 2012, China established relevant policies regarding the scrapping and recycling of power batteries based on the development plan of the new energy vehicle industry, continuously improving and developing related policies in line with the development of the new energy vehicle industry. As shown in Table 1, the development of policies related to power battery recycling in China over the past decade has shown distinct phases, roughly divided into three stages: the budding stage, the exploratory stage, and the gradually improving stage. In the first stage (before 2015), the policies issued by the central government related to power battery recycling were relatively scattered and did not appear in independent documents, lacking clear policy direction. In the second stage (from 2015 to 2018), two major policies, the “Technical Policies for the Recycling and Utilization of Electric Vehicle Power Batteries (2015 Edition)” and the “Technical Policies for the Recycling and Utilization of Electric Vehicle Power Storage Batteries (2015 Edition),” marked a watershed as the government began to pay attention to the recycling planning of power batteries, gradually introducing special policies for long-term layout. In the third stage (from 2018 to the present), the government has gradually shifted policy content from normative and guiding to practical implementation based on previous policy planning, promoting the recycling process of related industry enterprises through the establishment of pilot projects and the construction of recycling systems. In 2022, the National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and the Ministry of Ecology and Environment strengthened their focus on the recycling of discarded power batteries, issuing multiple relevant policies, including the recycling system for waste materials, heavy metal pollution prevention, and hazardous waste environmental management, deeply focusing on the construction of the power battery recycling system, and clarifying the positive role of recycling and reutilization of power batteries in improving resource utilization efficiency, ensuring the sustainable and healthy development of the new energy vehicle industry, and reducing environmental pollution. Overall, the formulation and issuance of policies are well-matched with the development process of the domestic power battery recycling industry. Although there are still shortcomings in detailed requirements such as battery recycling technology, there have been policy advancements in related areas such as regional layout and infrastructure support, and the green development of the power battery recycling industry faces urgent high-quality requirements.
Table 1: Development History of Domestic Policies Related to Power Battery Recycling
|
Time |
Policy |
Issuing Agency |
Content |
|
2012.9 |
“Energy Saving and New Energy Vehicle Industry Development Plan” |
State Council |
Proposes to formulate management measures for the recycling and utilization of power batteries, establish a management system for the cascade utilization and recycling of power batteries, and put forward clear requirements for the construction of the recycling and utilization system of power batteries. |
|
2014.7 |
“Guiding Opinions on Accelerating the Promotion and Application of New Energy Vehicles” |
State Council |
Proposes to research and formulate policies for the recycling and utilization of power batteries, exploring methods such as funds, deposits, and mandatory recycling to promote the recycling of discarded power batteries, and establishing a sound recycling system for discarded power batteries. |
|
2016.1 |
“Technical Policies for the Recycling and Utilization of Electric Vehicle Power Batteries (2015 Edition)” and “Technical Policies for the Recycling and Utilization of Electric Vehicle Power Storage Batteries (2015 Edition)” |
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Ministry of Commerce, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine |
Guides enterprises to reasonably carry out the design, production, and recycling of electric vehicle power storage batteries, establishing a recycling system that links upstream and downstream enterprises. |
|
2016.12 |
“Interim Measures for the Management of Recycling and Utilization of New Energy Vehicle Power Storage Batteries” (Draft for Comments) |
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology |
Clearly stipulates the responsibilities for design, production, recycling, comprehensive utilization, and regulatory management. |
|
2017.1 |
“Implementation Plan for the Extension of Producer Responsibility” |
State Council |
Clarifies that automobile manufacturers bear the primary responsibility for the recycling and utilization of power storage batteries. |
|
2017.7 |
“Regulations on the Access Management of New Energy Vehicle Manufacturers and Products” |
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology |
Implements traceability information management for new energy vehicle power batteries, tracking and recording the recycling and utilization of power batteries. |
|
2018.1 |
“Interim Measures for the Management of Recycling and Utilization of New Energy Vehicle Power Storage Batteries” |
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Ministry of Environmental Protection, and other departments |
Provides important guarantees for the healthy development of the recycling and utilization industry of new energy vehicle power storage batteries. |
|
2018.7 |
“Notice on Doing a Good Job in the Pilot Work of Recycling and Utilization of New Energy Vehicle Power Storage Batteries” |
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, and seven other departments |
Determines to carry out pilot work for recycling and utilization of new energy vehicle power storage batteries in 17 regions, including Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Guangdong, and China Tower, and sets corresponding target tasks for each pilot region, which helps establish a relatively concentrated and cross-regional recycling system. |
|
2019.2 |
“Guiding Opinions on Strengthening the Construction of Green Data Centers” |
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, National Government Affairs Administration, National Energy Administration |
Proposes to pilot the use of cascading power batteries as energy storage batteries for data centers under the premise of meeting reliability requirements. Promotes resource utilization of waste electrical and electronic products, implementing source control and green production, maximizing resource utilization efficiency throughout the product lifecycle. |
|
2019.11 |
“Guidelines for the Construction and Operation of Recycling Service Outlets for New Energy Vehicle Power Storage Batteries” |
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology |
Requires new energy vehicle manufacturers and related enterprises to establish recycling service outlets in accordance with national management requirements through self-built, co-built, or authorized methods, allowing cooperation and shared use of recycling service outlets among new energy vehicle manufacturers, power battery manufacturers, scrapped vehicle recycling and dismantling, and comprehensive utilization enterprises. |
|
2020.3 |
“Key Points for Industrial Energy Conservation and Comprehensive Utilization Work in 2020” |
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology |
Promotes the construction of a recycling and utilization system for new energy vehicle power storage batteries, deepening pilot work, accelerating the exploration and promotion of market-oriented models with strong technical and economic feasibility, and cultivating a number of backbone enterprises for recycling and utilization of power batteries. |
|
2021.8 |
“Technical Specifications for the Pollution Control of Waste Lithium-ion Power Storage Batteries (Trial)” |
State Council |
Standardizes and guides the handling process of waste lithium-ion power storage batteries. |
|
2022.6 |
“Notice on Further Promoting the Informatization of Hazardous Waste Environmental Management” |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment |
Further enhances the level and capability of informatization in hazardous waste environmental management, deepening pilot projects for the collection and transportation of waste lead-acid batteries. |
|
2022.11 |
“Notice on Doing a Good Job in the Stable Development of the Lithium-ion Battery Industry Chain and Supply Chain” |
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, State Administration for Market Regulation |
Encourages cooperation among upstream resource enterprises, lithium battery recycling enterprises, terminal application enterprises, system integration, channel distribution, and logistics transportation enterprises to implement the requirements of the “14th Five-Year Plan for Industrial Green Development,” improving the recycling and utilization system of discarded new energy vehicle power batteries and enhancing comprehensive utilization levels. |
|
2022.12 |
“Outline of the Strategic Plan for Expanding Domestic Demand (2022-2035)” |
Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, State Council |
Accelerates the construction of a recycling system for waste materials, regulating the development of the recycling and utilization industries for automobiles, power batteries, etc. |
Data Source: Compiled from public information, organized by the International Research Institute of Green Finance at Central University of Finance and Economics
(2) Current Status of Industry Practices
The construction of the recycling system has begun to yield results.The recycling system for automobile power batteries in the new energy sector refers to the collection, transportation, and recycling of discarded power batteries generated by various stakeholders in the new energy vehicle sector. With the large-scale retirement of power batteries in China’s new energy vehicles, the recycling system for discarded power batteries has begun to take shape. Currently, under the policy requirements of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and other relevant departments, automobile manufacturers, as the primary responsible entities for recycling, have initially established recycling service outlets in accordance with relevant management requirements, building shareable recycling service outlets through self-construction, cooperative construction, and other methods across various links of new energy vehicle manufacturing, power battery manufacturing, scrapped vehicle recycling and dismantling, and comprehensive utilization. According to statistics from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, by the end of August 2022, more than 190 automobile manufacturers and comprehensive utilization enterprises for power batteries had established over 10,000 recycling service outlets in 326 administrative districts across 31 provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities. From 2013 to 2021, the number of registered recycling enterprises for power batteries surged from 214 to 25,000, with numerous participants almost covering the entire new energy vehicle industry chain.
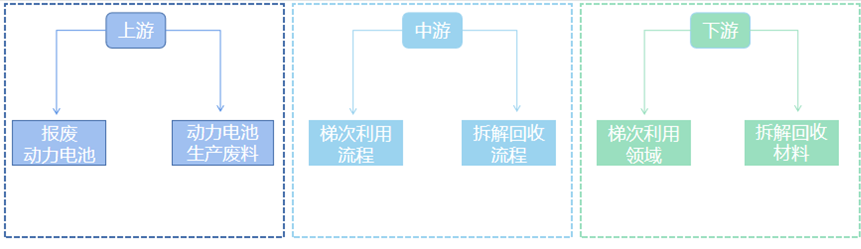
Figure 2: Power Battery Recycling Industry Chain
Data Source: Compiled by the International Research Institute of Green Finance at Central University of Finance and Economics
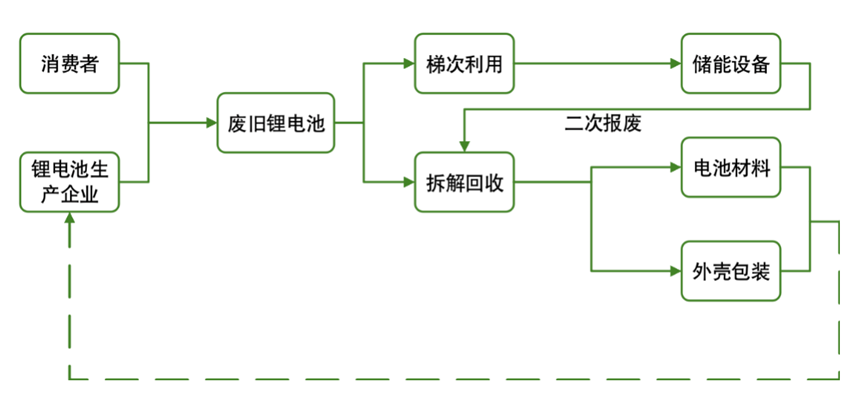
Figure 3 The Recycling Process of Discarded Lithium Batteries
Data Source: International Research Institute of Green Finance at Central University of Finance and Economics, organized based on public information
Cascade utilization concepts have entered the initial stage of industrialization.Cascade utilization refers to applying discarded power batteries in other fields to extend their lifecycle, thereby lowering costs and achieving social and environmental benefits. Currently, power battery manufacturers, new energy vehicle manufacturers, and related enterprises are actively advancing relevant technology research, demonstration projects, and business models in areas such as backup power for communication base stations, energy storage in power systems, low-speed electric vehicles, and other small-scale energy storage applications to expand the application range and life cycle of power batteries. Although this approach is limited by factors such as the scale of battery retirement, it remains one of the mainstream research directions in the field of battery recycling.
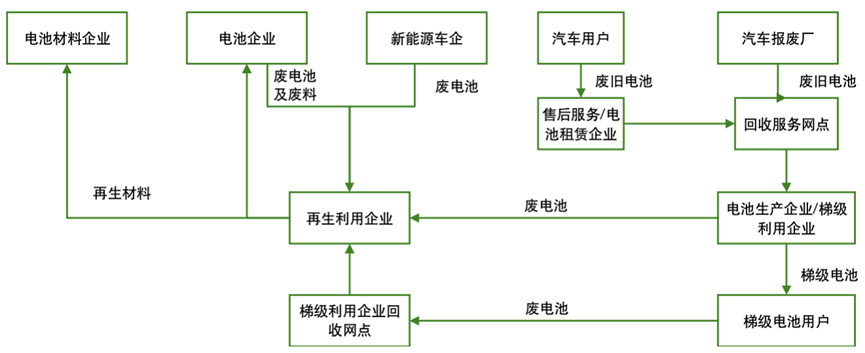
Figure 4 The Recycling Process of Power Lithium Batteries
Data Source: International Research Institute of Green Finance at Central University of Finance and Economics, organized based on public information
Recycling has established a certain industrial foundation.Recycling refers to dismantling, crushing, and smelting discarded power batteries to recover valuable metals such as lithium carbonate and cobalt, achieving effective resource circulation. Currently, China has established a certain industrial foundation in the recycling of power batteries, with enterprises predominantly adopting hydrometallurgical processes, which have mature technical processes and high recovery rates for target elements, while also meeting relevant safety and environmental protection requirements.
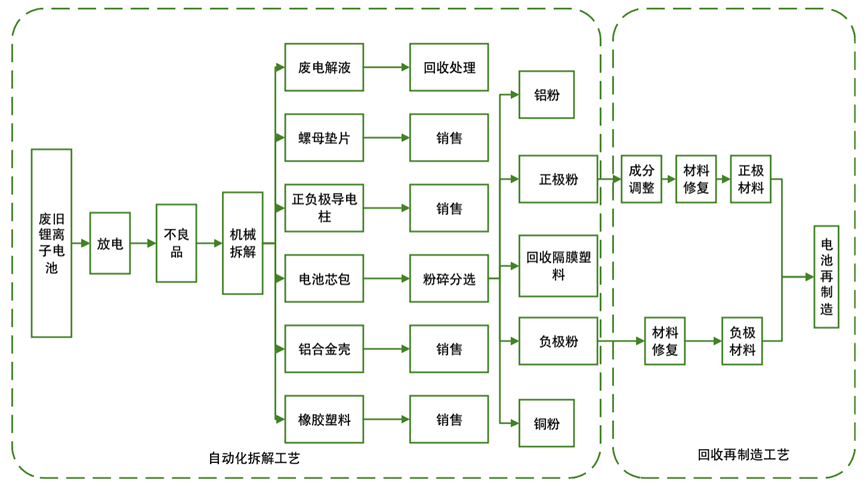
Figure 5 The Full Process of Physical Recovery and Reutilization of Power Lithium Batteries
Data Source: International Research Institute of Green Finance at Central University of Finance and Economics, organized based on public information
3. Issues and Recommendations in the Power Battery Recycling Industry
(1) Policy Level: Improve Relevant Laws and Regulations, Enhance Policy Precision and Direction
Currently, the management of the recycling and utilization of power storage batteries in the new energy vehicle sector in China is mainly based on policies, norms, and standards issued by relevant departments such as the State Council, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and the Ministry of Science and Technology. Although these policies, norms, and standards cover various aspects of the recycling of discarded power vehicles, they lack legal enforceability, leading to insufficient constraints on recycling enterprises, and the rights and obligations of various parties cannot be clearly defined legally, which may cause confusion in the recycling system. Moreover, due to the absence of a dominant legal framework, when conflicts arise between policies, norms, and standards among different departments and regions, coordination becomes difficult, significantly reducing the effectiveness of the final execution of relevant policies, norms, and standards.
To address the current lack of specific laws and regulations in the recycling and utilization of power batteries, relevant legislative bodies in China should formulate targeted, legally binding laws and regulations, clarifying the responsibilities and functions of various departments and institutions to prevent conflicts between departments. Additionally, it is necessary to clarify the responsibilities and obligations of the participants in each link of the entire recycling and utilization process of power batteries, accompanied by corresponding punitive mechanisms to ensure the enforceability of the laws and regulations. Furthermore, relevant policy-making departments should adopt a macro perspective, establishing a holistic view to consider the overall impact of policies, guiding local governments to implement differentiated support policies tailored to local conditions, emphasizing targeted policy guidance for the new energy vehicle industry, and providing more preferential support. Lastly, relevant departments should strengthen the connections between the new energy vehicle and waste power battery recycling industries, promoting mutual development. Finally, further policies and regulations regarding environmental information disclosure and carbon footprint accounting for enterprises can be introduced to encourage new energy vehicle and power battery enterprises to focus on sustainable development.
(2) Market Level: Accelerate the Construction of an Efficient Recycling System and Supporting Industrial Facilities
As mentioned earlier, based on relevant departmental policies, automobile manufacturers have been clearly identified as the main entities in the recycling system for new energy vehicle power batteries in China, needing to actively assume their responsibilities and fulfill corresponding obligations at all stages of recycling. However, due to the late start of the recycling system in China, its underdevelopment, and the lack of legally binding laws and regulations, the responsibilities of various stakeholders have not been effectively implemented. Additionally, reasons such as unreasonable pricing practices by traders and informal recycling enterprises have led to a significant number of discarded power batteries flowing into illegal channels, causing certain negative impacts on society, the environment, and individuals.
To address the inadequacies of the market recycling system, regulatory departments and industry self-regulatory organizations need to work together to build an efficient and comprehensive recycling system. Relevant departments should first actively communicate with industry self-regulatory organizations to understand the basic needs of the power battery recycling industry and clarify the responsibilities of various stakeholders in the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain. Based on the results of these communications, they should provide policy support and conduct pilot projects on a small scale, promoting broader implementation only after a significant improvement in recycling effectiveness. During the promotion process, attention should also be paid to the supporting industrial facilities, such as the construction of environmental protection projects for wastewater discharge from recycling projects for discarded power batteries. Additionally, relevant regulatory departments should further tighten the recycling process for discarded batteries, focusing on cracking down on various illegal activities, blocking the flow of discarded power batteries into illegal channels, and raising the safety and environmental access conditions for resource recycling and reutilization enterprises, ensuring the proper recycling and utilization of discarded power batteries to promote social and environmental development.
(3) Enterprise Level: Accelerate Technological Research and Development, Enhance Awareness of Sustainable Internal Control
Currently, China’s relevant technologies in the power battery recycling field are on par with international advanced levels, and in some areas of recycling technology, they have even reached international leading levels. However, in terms of key technologies for industrialization, China remains relatively backward. Taking the recycling technology of power batteries as an example, due to the slow progress of the industrialization of key technologies and high usage costs, some power battery recycling enterprises still adopt manual disassembly techniques and traditional recycling processes, which not only fail to effectively address the environmental issues posed by discarded batteries but also introduce certain safety hazards.
To tackle this issue, enterprises need to explore branch lines along their development path to assist in resolving the problem. First, taking emerging vehicle manufacturers in the new energy sector as an example, based on long-term development thinking, they should consider adding waste battery recycling links, transforming the input of power batteries from external purchases into a part of the internal product cycle. By actively participating in the research and development of waste power battery recycling technologies and processes, they can generate more economic benefits while also achieving comprehensive control over the product lifecycle, thus enhancing service quality. Secondly, for traditional battery enterprises, increasing investment in battery recycling lines and technological research and development can help them maintain their original advantages in specialized production, seizing significant industry opportunities in the context of sustainable development, achieving sustainable growth through in-depth research and industry collaboration in talent reserves, recycling technologies, and recycling models.
Related Articles:
References
[1]Li Yuke, Li Zhenbiao. Current Status, Issues, and Recommendations for Recycling and Utilization of Power Batteries in China’s New Energy Vehicles [J]. Resource Recycling, 2019, (8): 32-37
[2]Ding Xiao, Xu Shujie, Li Longhui. Research on the Construction and Development of the Management System for Recycling and Utilization of Power Batteries in China’s New Energy Vehicles [J]. Times Automobile, 2020, (24): 91-92, 108
[3]Zhao Shijia, Xu Nan, Qiao Yingjun, Yang Bo. Suggestions for Accelerating the Recycling and Utilization of Power Batteries in China’s New Energy Vehicles [J]. Chinese Engineering Science, 2018, Vol. 20, (1): 144-148
[4]Jiang Dong, Su Chunyang, Fang Shuaijun, Yuan Rui, Chang Gehui. Current Situation and Countermeasures of the Recycling and Utilization Industry for Discarded Power Batteries in China [J]. Times Automobile, 2020, (6): 16-17
.2022
Tao Zhendong Research Assistant at the Yangtze River Delta Green Value Investment Research Institute
Shi Yichen Chief Economist at Zhongcai Green Guidance (Beijing) Information Consulting Co., Ltd.
