Real-time ray tracing will become standard. In addition to the iPhone equipped with Apple’s self-developed A-series chips, most Android manufacturers’ SoCs come from Qualcomm, MediaTek, and Samsung.
Real-time ray tracing will become standard. In addition to the iPhone equipped with Apple’s self-developed A-series chips, most Android manufacturers’ SoCs come from Qualcomm, MediaTek, and Samsung.
Image source: wccftech. Qualcomm, MediaTek, and Samsung are not deeply involved in the independent design of CPU and GPU architectures for their SoCs, leaning more towards Arm’s public architecture. This raises a problem: when the Arm public architecture is poorly designed, it can easily trigger a chain reaction, leading to poor performance of flagship chips and ultimately causing widespread overheating and power consumption issues in Android flagship products.
Image source: “Game of Thrones”. If the chip foundry’s yield rate is also low, it is simply adding insult to injury. In recent years, high-end Android SoCs have fallen into such a vicious cycle, dragging down various Android flagships. Originally considered a niche knowledge of SoCs, it has gradually become a selection awareness for ordinary consumers. However, compared to the more challenging process technology, once Arm’s public architecture is finalized, it can still be gradually improved through optimization.
Originally considered a niche knowledge of SoCs, it has gradually become a selection awareness for ordinary consumers. However, compared to the more challenging process technology, once Arm’s public architecture is finalized, it can still be gradually improved through optimization.

The first generation Armv9 CPU core. Image source: Arm. Last year, Arm introduced the Armv9 instruction set in its public architecture, bringing three new public CPU cores: Cortex-X2, Cortex-A710, and Cortex-A510. Ultimately, in Snapdragon 8 Gen1 and Dimensity 9000, this new architecture has seen some improvements over the previous generation, but there is still significant room for optimization. At the recent Total Compute Solutions 2022 conference, Arm announced the latest generation of its public architecture, including three new Cortex-A CPU cores and a new series of GPUs. The new generation of CPU architecture cores focuses on optimization and enhancement, while the GPU represents a significant innovation. The CPU emphasizes improving energy efficiency. Arm’s chip advantage lies in energy efficiency, but the emergence of the super-large core Cortex-X has also significantly improved the absolute performance of mobile Arm chips. The new generation Cortex-X3 is still aimed at peak performance, achieving a 25% performance improvement at the same clock frequency of 3.3GHz as Cortex-X2.
At the recent Total Compute Solutions 2022 conference, Arm announced the latest generation of its public architecture, including three new Cortex-A CPU cores and a new series of GPUs. The new generation of CPU architecture cores focuses on optimization and enhancement, while the GPU represents a significant innovation. The CPU emphasizes improving energy efficiency. Arm’s chip advantage lies in energy efficiency, but the emergence of the super-large core Cortex-X has also significantly improved the absolute performance of mobile Arm chips. The new generation Cortex-X3 is still aimed at peak performance, achieving a 25% performance improvement at the same clock frequency of 3.3GHz as Cortex-X2. If X3 runs at 3.6GHz, it shows a 34% improvement compared to some mainstream laptop processors. Clearly, the overclocking potential of the Cortex-X3 and its higher performance (and power consumption) are designed for Arm’s PC, not for the next generation of mobile flagship SoCs.
If X3 runs at 3.6GHz, it shows a 34% improvement compared to some mainstream laptop processors. Clearly, the overclocking potential of the Cortex-X3 and its higher performance (and power consumption) are designed for Arm’s PC, not for the next generation of mobile flagship SoCs. The large core Cortex-A715, from its naming, seems more like an improvement over the previous A710, focusing on efficiency. After optimizing the core structure, the Cortex-A715 brings a 5% performance improvement while reducing power consumption by 20%. From the curve, regardless of the state, A715 has a better energy efficiency ratio compared to A710. For this reason, Arm also stated that at the same frequency and cache, A715 has performance comparable to X1.
The large core Cortex-A715, from its naming, seems more like an improvement over the previous A710, focusing on efficiency. After optimizing the core structure, the Cortex-A715 brings a 5% performance improvement while reducing power consumption by 20%. From the curve, regardless of the state, A715 has a better energy efficiency ratio compared to A710. For this reason, Arm also stated that at the same frequency and cache, A715 has performance comparable to X1.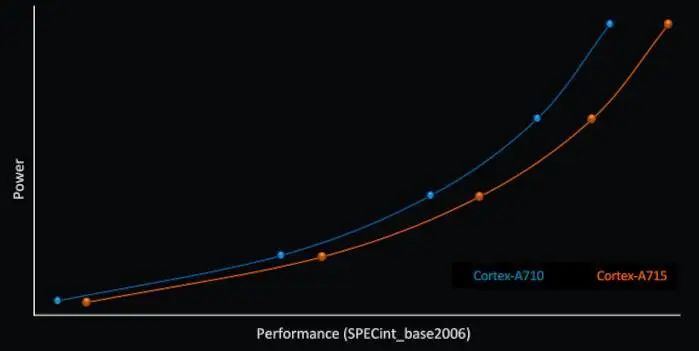 Additionally, on the large core, Arm has completely eliminated support for 32-bit apps. Therefore, the instruction decoder size of A715 has been reduced by four times compared to its predecessor, making the A715 core more efficient in area, power, and execution. The mid-core is still named Cortex-A510, but Arm has optimized it and refers to it as the refreshed A510 (it feels more like a complete redo of A510, as the previous version had many issues). The new A510 core has improved timing and optimized efficiency, thus reducing power consumption by 5%. Most importantly, the A510 has reintroduced support for 32-bit apps.
Additionally, on the large core, Arm has completely eliminated support for 32-bit apps. Therefore, the instruction decoder size of A715 has been reduced by four times compared to its predecessor, making the A715 core more efficient in area, power, and execution. The mid-core is still named Cortex-A510, but Arm has optimized it and refers to it as the refreshed A510 (it feels more like a complete redo of A510, as the previous version had many issues). The new A510 core has improved timing and optimized efficiency, thus reducing power consumption by 5%. Most importantly, the A510 has reintroduced support for 32-bit apps. Thus, this brand new A510 will also be applied in IoT and other fields, not just targeting smartphones. In addition to the optimization iterations of the three self-owned Cortex cores, Arm’s DSU (DynamIQ Shared Unit) has also been updated to support 12 cores and 16MB of L3 cache.
Thus, this brand new A510 will also be applied in IoT and other fields, not just targeting smartphones. In addition to the optimization iterations of the three self-owned Cortex cores, Arm’s DSU (DynamIQ Shared Unit) has also been updated to support 12 cores and 16MB of L3 cache.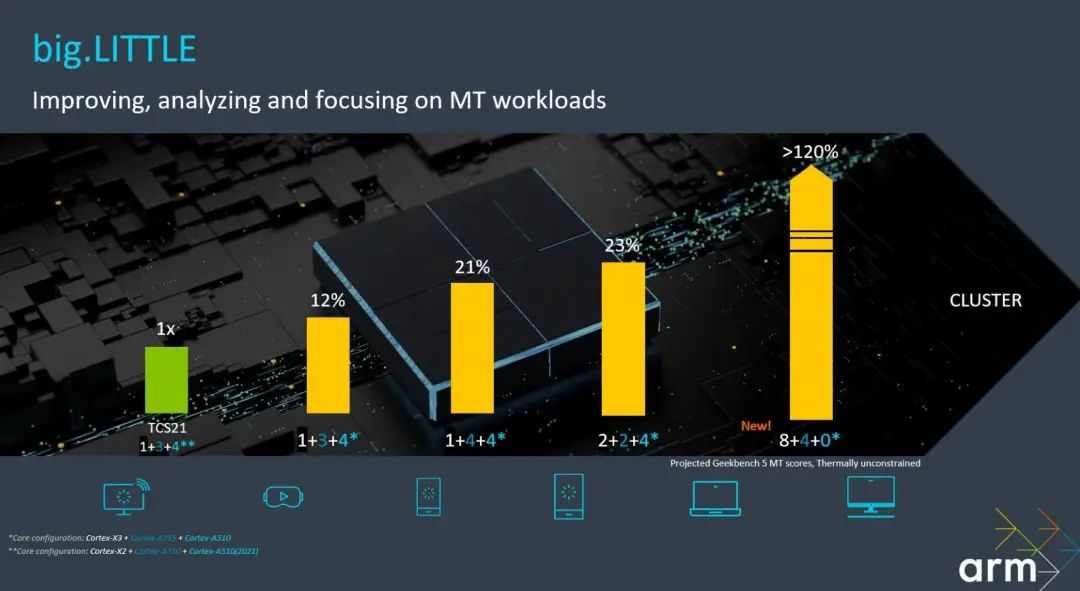 As a result, future Arm processors may have a richer core combination. In addition to the common 1+3+4 tri-cluster architecture, it could also be 1+4+4, 2+2+4, or even in some high-performance chips, an extreme combination like 8+4+0. Overall, Arm’s new generation of Cortex cores focuses on optimizing the previous generation’s structure, striving to provide better energy efficiency and correcting some unreasonable designs from the previous generation. Furthermore, Arm’s core design is not limited to smartphones but is beginning to expand its coverage across various cores, with the super-large core X3 focusing on the PC field, while the mid-core A510 has stronger compatibility for IoT and other areas. GPU ray tracing will become standard. Historically, Arm’s public GPUs have been somewhat weaker compared to CPU cores, resembling a basic configuration. The public Mali GPU has been continuously iterated, and in the previous generation of flagship chips, the public Mali’s performance has approached that of Qualcomm’s self-developed Adreno.
As a result, future Arm processors may have a richer core combination. In addition to the common 1+3+4 tri-cluster architecture, it could also be 1+4+4, 2+2+4, or even in some high-performance chips, an extreme combination like 8+4+0. Overall, Arm’s new generation of Cortex cores focuses on optimizing the previous generation’s structure, striving to provide better energy efficiency and correcting some unreasonable designs from the previous generation. Furthermore, Arm’s core design is not limited to smartphones but is beginning to expand its coverage across various cores, with the super-large core X3 focusing on the PC field, while the mid-core A510 has stronger compatibility for IoT and other areas. GPU ray tracing will become standard. Historically, Arm’s public GPUs have been somewhat weaker compared to CPU cores, resembling a basic configuration. The public Mali GPU has been continuously iterated, and in the previous generation of flagship chips, the public Mali’s performance has approached that of Qualcomm’s self-developed Adreno. With the release of the new generation of CPU cores, Arm has also updated its new generation of public GPUs. Unlike previous routine upgrades, this time Arm has introduced a brand new Immortalis flagship series.
With the release of the new generation of CPU cores, Arm has also updated its new generation of public GPUs. Unlike previous routine upgrades, this time Arm has introduced a brand new Immortalis flagship series.

Immortan Joe. Image source: “Mad Max 4”. The biggest difference in functionality between the Immortalis series and Mali is the support for ray tracing, and in terms of cores, the Immortalis-G715 has at least 10 cores, while the Mali-G715 can accommodate 7-9 cores. The difference in core count and hardware support for ray tracing gives the Immortalis-G715 a broader range of applications, similar to Cortex-X3, which seems to be paving the way for Arm’s desktop chips. Arm’s product management director Andy Craigen claimed that the Immortalis-G715 only used 4% of the shader core area, yet achieved a threefold performance improvement through hardware acceleration. In fact, the previous generation Mali-G710 GPU already provided software-based ray tracing. Additionally, Samsung’s Exynos 2200 also collaborated with AMD to introduce hardware support for ray tracing. Both Arm and chip manufacturers are laying the groundwork for mobile ray tracing, but currently, most demonstrations are just a few demos, and game developers have not taken clear action.
Arm’s product management director Andy Craigen claimed that the Immortalis-G715 only used 4% of the shader core area, yet achieved a threefold performance improvement through hardware acceleration. In fact, the previous generation Mali-G710 GPU already provided software-based ray tracing. Additionally, Samsung’s Exynos 2200 also collaborated with AMD to introduce hardware support for ray tracing. Both Arm and chip manufacturers are laying the groundwork for mobile ray tracing, but currently, most demonstrations are just a few demos, and game developers have not taken clear action.
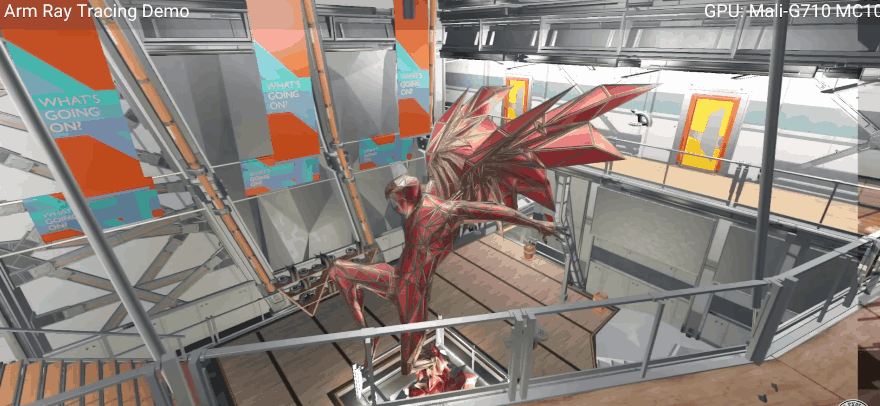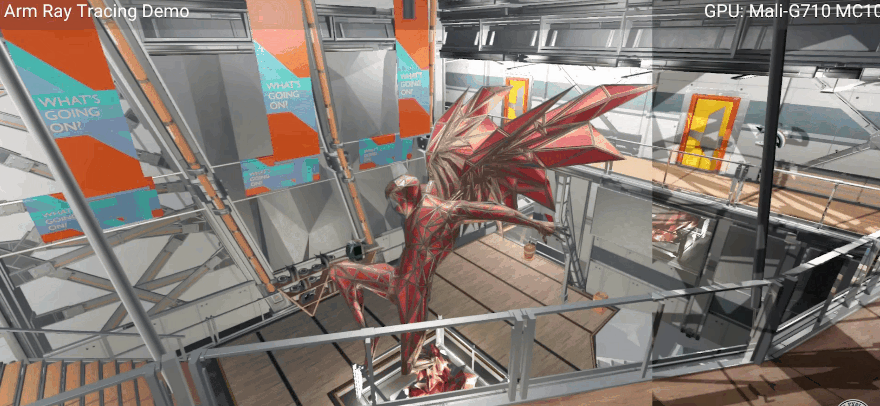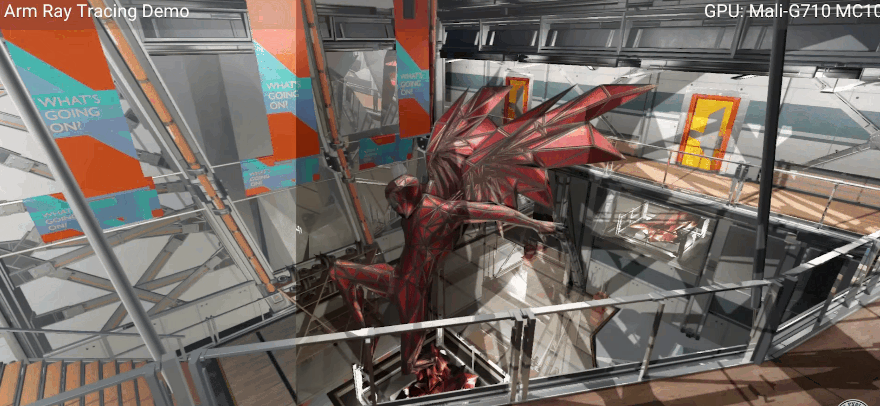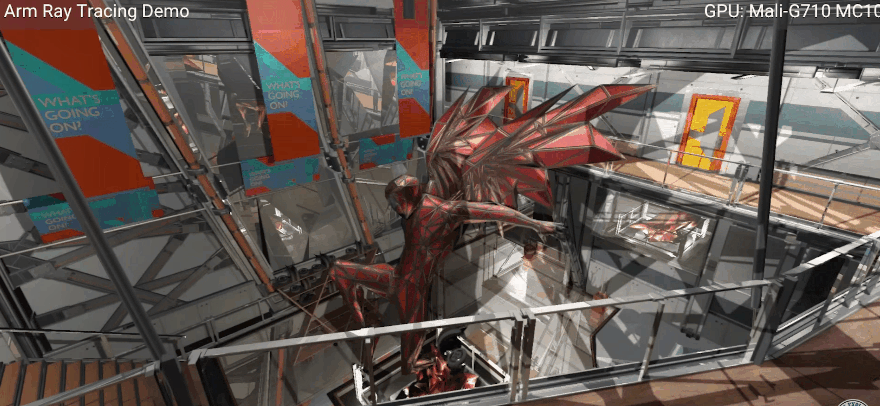
New GPU ray tracing demonstration demo (the animation is compressed), pay attention to the changes in light and shadow. Image source: Arm. For mobile 3D games, widespread hardware ray tracing support feels like the calm before the storm. However, Arm’s Paul Williamson hinted in an interview with TheVerge that once terminals equipped with the Immortalis-G715 GPU are launched next year, there will be corresponding products to provide interesting experiences.

Image source: Android Authority. The regular updated Mali-G715, like the Cortex-A715, focuses on improving energy efficiency, achieving a 15% energy efficiency optimization compared to G710. Additionally, Arm has updated a GPU positioned slightly below the Mali-G715, the Mali-G615, which differs by having fewer cores (less than 6), targeting mid-range Arm processors. If the Mali-G715 and G615 are regular iterations, then the hardware support for ray tracing in the Immortalis-G715 is indeed a significant upgrade, providing better computational performance for 3D graphics. The Immortalis series GPUs, similar to the Cortex-X super-large cores, seem to be prepared for desktop processors, indicating that Arm is beginning to make strides in the Arm PC space. Chip manufacturers are starting to target the Arm PC field. In addition to Qualcomm, Samsung Exynos and MediaTek will directly utilize Arm’s public CPU and GPU architecture, although core frequency and process technology may differ.
The Immortalis series GPUs, similar to the Cortex-X super-large cores, seem to be prepared for desktop processors, indicating that Arm is beginning to make strides in the Arm PC space. Chip manufacturers are starting to target the Arm PC field. In addition to Qualcomm, Samsung Exynos and MediaTek will directly utilize Arm’s public CPU and GPU architecture, although core frequency and process technology may differ.

AMD’s involvement has not saved the Exynos 2200. Following Samsung’s previous generation Exynos 2200’s collaboration with AMD to launch the Xclipse GPU, currently, the mainstream SoC market only has MediaTek developing the Dimensity series based on Arm’s public architecture. Similar to Samsung Exynos finding collaboration with AMD, Qualcomm has directly acquired NUVIA, a company with its own Arm chip architecture design, aiming to develop its own Arm architecture chips. Qualcomm is also preparing a chip codenamed “Hamoa,” with the initial goal of competing with Apple’s M chips. Its CPU will introduce self-designed IP architecture cores instead of Arm’s public architecture. Many analysts have indicated that Qualcomm plans to incorporate self-designed IP CPU cores into Snapdragon chips, provided their performance is sufficiently excellent.
Qualcomm is also preparing a chip codenamed “Hamoa,” with the initial goal of competing with Apple’s M chips. Its CPU will introduce self-designed IP architecture cores instead of Arm’s public architecture. Many analysts have indicated that Qualcomm plans to incorporate self-designed IP CPU cores into Snapdragon chips, provided their performance is sufficiently excellent. Apple chips have already outpaced Qualcomm, MediaTek, and Samsung. The reason for not switching directly like Apple’s A chips is that the market share of Snapdragon chips is too large, and the risk is too high. Nowadays, Arm’s public architecture resembles a foundation, increasingly approaching a reference for manufacturers.
Apple chips have already outpaced Qualcomm, MediaTek, and Samsung. The reason for not switching directly like Apple’s A chips is that the market share of Snapdragon chips is too large, and the risk is too high. Nowadays, Arm’s public architecture resembles a foundation, increasingly approaching a reference for manufacturers.

Apple chips are synonymous with “differentiation.” Capable chip manufacturers are gradually beginning to design their own core architectures to achieve stronger differentiation, similar to Apple’s A and M chips, thereby gaining more orders. Arm’s public architecture is also beginning to focus on building the Arm ecosystem, with the peak performance improvements of the super-large core Cortex-X and Immortalis series GPUs aimed at laying the groundwork for Arm PC processors. The redesign of Cortex-A510 has improved backward compatibility. The smartphone market has transformed into a saturated market, and for chip manufacturers like Qualcomm and core IP providers like Arm, the potentially lucrative Arm PC field may be their next growth point.
Jay Chou’s “The Greatest Work” Full Interpretation, He is Still the King of Music

Xiaomi 12S Ultra First Review: Thousands of Photos, In-Depth Comparison with Leica/Vivo/OPPO, Has Xiaomi Imaging Really Made It?