
Recently, one of the top conferences in integrated circuit design, the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC 2025), was held in Boston, USA. At this year’s CICC, three high-level papers from the PMIC Laboratory of the National Demonstration Microelectronics Institute at the University of Science and Technology of China were selected. PhD students Liu Zeguang and Min Qingqing, along with master’s student Wang Baochuang, attended this grand event to showcase the latest research achievements of the University of Science and Technology of China.
High Efficiency and High Integration Dual-Path
Single-Inductor Dual-Output DC-DC Converter Chip
Master’s student Wang Baochuang reported on the topic “A 94.5%-Peak-Efficiency Dual-Path Single-Inductor Dual Output Converter with Reduced Inductor Current and Output Voltage Ripple” at the technical session on “Hybrid DC-DC Converters”. Inspired by the dual-path concept, this work innovatively proposes a dual-path single-inductor dual-output converter.

High Efficiency and High Integration Dual-Path
Single-Inductor Dual-Output DC-DC Converter Chip Presentation Site
This converter not only supports a voltage conversion ratio from 0 to 1 and any load difference but also provides three additional advantages due to its dual-path architecture. First, the direct current and current ripple in the inductor are significantly reduced, allowing for the use of smaller inductors and reducing conduction losses, thereby increasing power density and improving efficiency. Second, the reduced inductor current decreases the discontinuous current in the energy distribution switches, thus reducing voltage spikes and enhancing system reliability. Third, since the inductor and flying capacitor alternately provide current to the output, the output voltage ripple is reduced.
Additionally, this design proposes a novel control strategy compatible with the dual-path topology, achieving excellent dynamic performance. Experimental results show that this converter achieves a peak efficiency of 94.5% under similar voltage conversion ratio conditions and can provide a maximum total load current of 5A using a compact inductor sized 3.2×2.5×1.2mm³.
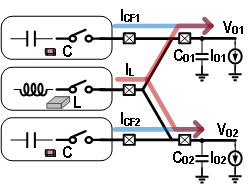
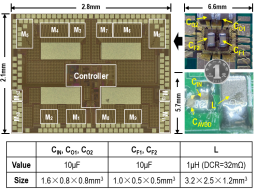
Chip Schematic Diagram
High Efficiency Fast Transient Response Soft Switching
Converter Chip
PhD student Min Qingqing reported on the topic “A Zero-Voltage-Switching Buck Converter with Conduction-Loss Minimized ZVS Operation and Auxiliary Inductor Transient Reuse Technique Achieving up to 8.3% Efficiency Improvement and 42% Voltage Droop Reduction” at the technical session on “Power Converter Techniques”.
High Efficiency Fast Transient Response Soft Switching Converter Chip Presentation Site
To address the efficiency limitations caused by overlapping losses in high-voltage DC-DC converters, this work proposes a high-efficiency soft switching topology to eliminate overlapping losses and enhance conversion efficiency; it also innovatively proposes an optimized soft switching control strategy that modulates the voltage drop across the energy storage capacitor in the soft switching topology to optimize the additional conduction losses introduced by the soft switching topology, achieving optimal efficiency improvement for high-voltage DC-DC converters; during the load transient response phase, the auxiliary inductor is reused to charge and discharge the output capacitor in parallel with the main inductor, enhancing the converter’s load transient response capability. Experimental validation shows a peak efficiency of 93.4% and a 42% reduction in load transient voltage droop.
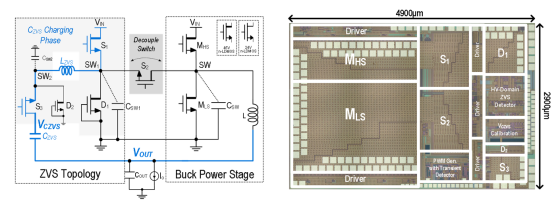
Chip Schematic Diagram
Fast Response Hybrid Topology
LLC Resonant Converter

Fast Response Hybrid Topology LLC Resonant Converter Presentation Site
PhD student Liu Zeguang reported on the research achievement titled “A 100A 48-60V to 1V Hybrid LLC Resonant Converter with 51mV Droop for a 70A/20ns Load Transient” at the technical session on “Hybrid DC-DC Converters”. This research addresses the power supply bottleneck for multi-core CPUs/GPUs in data centers by proposing a hybrid topology LLC resonant converter to solve the issues of insufficient voltage regulation and slow load transient response in traditional LLC converters. Experiments show that this converter can stably output 0.8-1V under 48-60V input and support a load of 100A; under a load current change of 70A in 20ns, the output droop is only 51mV, with a transient response speed improvement of over 3 times, reaching an industry-leading level.
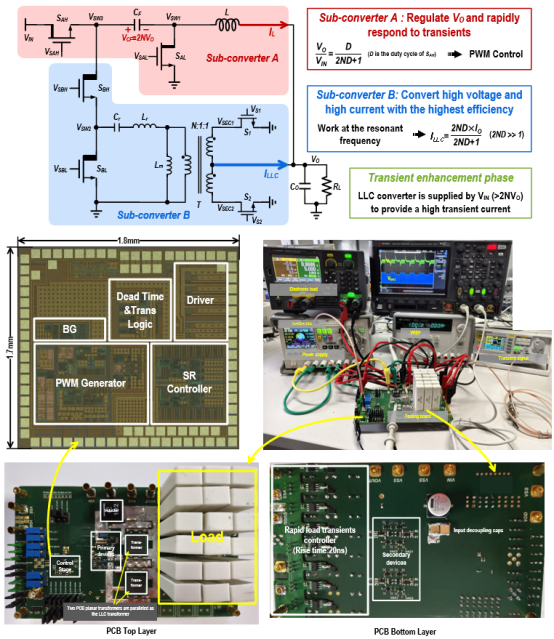
Circuit Structure and Testing Environment Photo
Thus, CICC 2025 concluded successfully, while PMIC’s exploration of chips continues. PMICers witnessed the collision of cutting-edge technologies, leaving their footprints on the map of science. In the future, we will also keep moving forward, continuously studying, and continue our journey in chip innovation!