Skip to content
Edge Computing Applications
We know that the concept of edge computing resonates with cloud computing centers. Especially after the widespread application of the concepts of 5G and the Internet of Things in the business scenarios of Industrial Internet, the number of connected smart terminals and the data that needs to be processed are increasing, leading to rising costs and growing customer demands for computing power to be pushed down to the edge of data sources.
In other words, edge computing is closely related to the Internet of Things and its connected data acquisition devices. The relatively mature application scenarios mainly include smart transportation, smart mining, smart factories, security monitoring, smart logistics, smart agriculture, and so on. Due to the large amount of data collected, if all this data is first sent back to the cloud computing center for computation and analysis before being returned to the data collection site to complete the operational loop, both network latency and network operating costs become bottlenecks in the data loop. Thus, edge computing has emerged. Clearly, edge computing is closely related to large-scale data collection, and the subsequent real-time data analysis and feedback loop often form the basis of AI applications. In a report, Dave McCarthy, Global Infrastructure Practice Research Director at IDC, even stated that AI has become the “most common workload” in the field of edge computing.
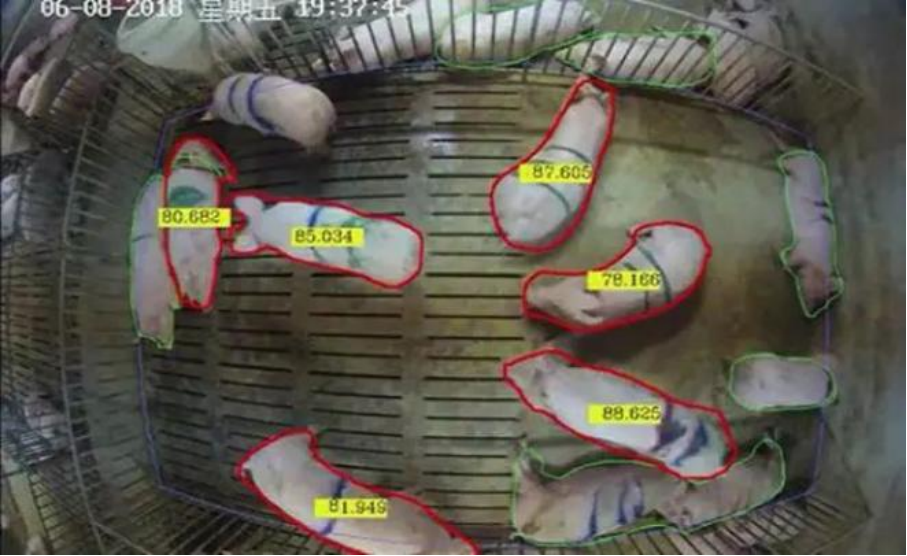
For example, in animal husbandry, systems upgraded with edge AI computing infrastructure can automatically complete tasks such as entry and exit recognition, transfer recognition, foreign biological recognition, trajectory monitoring, area anomaly monitoring, and personnel clothing recognition through cameras’ AI upgrades and the combination of edge and cloud, utilizing “pig face recognition” technology. This not only significantly saves labor costs but also enhances the professionalism and modernization level of enterprises.
Similarly, in the energy sector, oil and gas pipelines and their supporting pump stations are important routes for energy transportation. Once damage or failure occurs, whether on land or undersea, it can lead to serious environmental issues and incur high economic costs. Therefore, predictive maintenance for oil and gas delivery pipelines has gradually become widespread, and the “unsung hero” of predictive maintenance is also edge computing.
In the power industry, inspections of long-distance transmission lines are now more frequently completed through drones collecting video data on-site and backend AI computing analysis. At this time, ordinary drones face issues such as limited control distance, inability to coordinate multiple machines, and reliance on manual monitoring. Edge AI can effectively address these problems, for instance, by using regional edge computing nodes to enhance drone communication range and enable beyond-visual-range automated formation flying.
It should be noted that today’s AI is not only an important indicator of digital transformation and upgrading across various industries but more importantly, AI genuinely helps various industries save labor costs. Thus, edge computing, which expands the boundaries of AI applications, is witnessing explosive growth.
New Directions for AI Edge Computing
Undoubtedly, edge computing is an effective complement to cloud computing, expanding from cloud + edge + terminal collaboration. In the case of inspecting long-distance transmission lines, edge computing provides a computing node for the drone as the “terminal,” extending control distances to achieve beyond-visual-range automated flight and multi-machine collaboration.
In other words, edge computing is like a frontline command center, while the cloud serves more as the headquarters for centralized computing power optimization of AI models and backend data storage. Clearly, edge computing greatly expands the application range of cloud + terminal, and the computing power it provides can meet the localized processing needs of AI for data. Thus, it has become a consensus that edge computing will be the next top trend in the IT industry.
Currently, Quanmate is actively participating in the national-level large model computing power center construction from server rooms to AI servers and IB networks, providing quality services to various enterprises and research institutions. Quanmate also leverages its strengths in edge computing to integrate edge AI computing + cloud platform base + event processing circulation hub platform + portal terminal across multiple sectors such as smart communities, intelligent property management, smart security, and smart education, achieving in-depth practice of AI and continually exploring the application scenarios and potential of artificial intelligence technology in various fields, providing cutting-edge AI solutions for major industry clients to assist their transformation and digital construction in the new era of AI!
 As the application scenarios of edge computing become increasingly rich, the edge computing market will inevitably form more refined market classifications. Solutions will evolve from the traditional model of inserting as many GPU cards as possible into a single server to a more refined, clustered, and diversified development direction.
As the application scenarios of edge computing become increasingly rich, the edge computing market will inevitably form more refined market classifications. Solutions will evolve from the traditional model of inserting as many GPU cards as possible into a single server to a more refined, clustered, and diversified development direction.