
| Technology | Discussion |
China’s leading media outlet in the telecommunications industry

Author: Zhao Xiaofei
Source: IoT Think Tank (iot101)
Submission email for discussions: [email protected]
The connection forms of the Internet of Things (IoT) are becoming increasingly diverse, with LPWAN being one of the most notable forms, catering to a large number of low-power IoT scenario demands.
Recently, the well-known market research firm IoT Analytics released the latest global Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) tracking and forecasting report. The report indicates that the number of global LPWAN connections continues to grow, reaching nearly 1.3 billion by the end of 2023, with an expected compound annual growth rate of 26% over the next few years, projected to reach 3 billion connections by 2027. The connection forms of the Internet of Things are becoming increasingly diverse, with LPWAN being one of the most notable forms, catering to a large number of low-power IoT scenario demands.
LPWAN Maintains Stability in IoT Connection Forms
In May 2023, IoT Analytics released a forecast for global IoT connections, predicting that the number of IoT connections will reach 16.7 billion in 2023, with LPWAN accounting for 8% of the total with 1.3 billion connections; by 2027, the proportion of LPWAN connections is expected to reach 10% of the total connections.
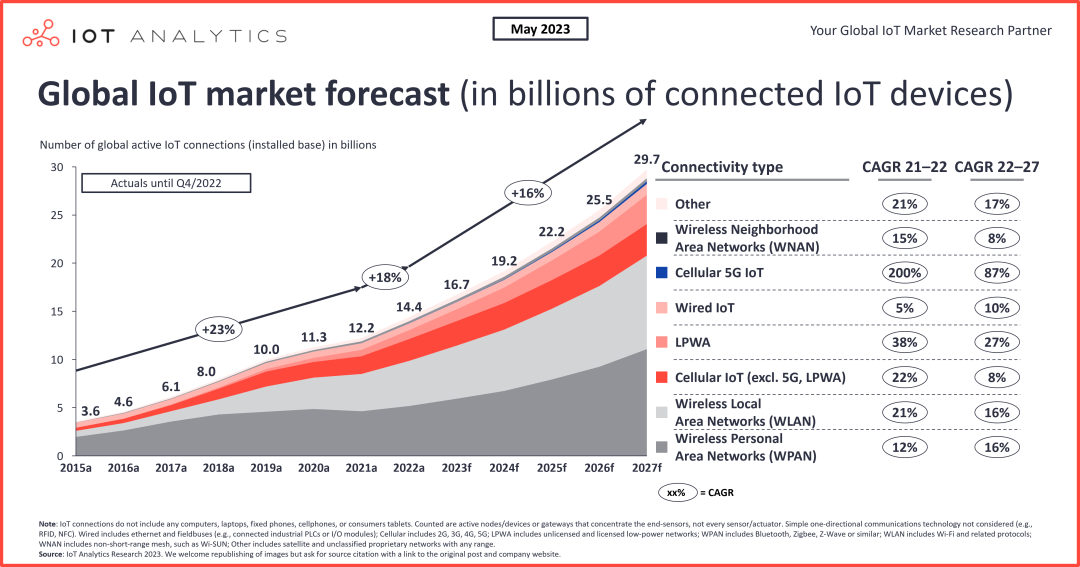
According to IoT Analytics’ tracking forecast data, the proportion of IoT connections using short-range communication methods, including wireless personal area networks and wireless local area networks, exceeds 70%, while the proportion of IoT connections using long-range communication methods, including 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, and LPWAN, is less than 30%.
LPWAN began to be used in the IoT around 2015, and in less than ten years, its share has grown from 0 to 8%, reflecting strong market demand. With the rapid growth of demand for connection methods such as 5G and Cat.1 bis, LPWAN has ended its rapid growth phase, but by 2027, its share is still expected to reach 10%, indicating that demand remains stable, supporting the stability of LPWAN’s share.
Since the proportion of long-range IoT connections is less than 30% of the total IoT connections, the 10% of LPWAN connections account for more than one-third of the long-range IoT connections, highlighting its importance in long-range IoT.
Dominance of NB-IoT, LoRa, and LTE-M
Industry practitioners are quite familiar with LPWAN. Since 2015, more than a dozen LPWAN technologies have emerged globally, and after market validation, a dominant pattern has formed with NB-IoT and LTE-M representing licensed spectrum LPWAN technologies, and LoRa and Sigfox representing unlicensed spectrum LPWAN technologies. Sigfox has maintained a very low market share, having little impact on overall market changes, thus the LPWAN field is primarily dominated by NB-IoT, LoRa, and LTE-M. Overall, this field exhibits the following characteristics:
1. Driven by the Chinese market, NB-IoT currently and in the future occupies more than half of the market
According to IoT Analytics’ tracking, the proportion of global connections using various LPWAN technologies in 2023 is as follows: NB-IoT accounts for 54%; followed by LoRa, which occupies 29%; LTE-M ranks third with a share of 14%; while Sigfox accounts for only 1%.
It is expected that by 2027, the market shares of various LPWAN technologies globally will be: NB-IoT’s share will further expand to 58%; LoRa will remain in second place with a share of 24%; LTE-M’s share will be 15%; and Sigfox will still be at 1%.
Table: Proportions of Different LPWAN Connection Types (Source: IoT Analytics)
| Connection Type | 2023 | 2027 |
| NB-IoT | 54% | 58% |
| LoRa | 29% | 24% |
| LTE-M | 14% | 15% |
| Sigfox | 1% | 1% |
As is well known, starting in 2016, China began to vigorously promote the application of NB-IoT, expanding various scenarios. In 2017, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued a notice on “Comprehensively Promoting the Construction and Development of Mobile IoT (NB-IoT)”, proposing development goals for NB-IoT from multiple perspectives, further promoting the development of the NB-IoT industrial ecosystem. It can be said that NB-IoT was the undisputed main theme of the Chinese IoT market during those years.
In recent years, due to the commercialization of 5G and the large-scale application of LTE Cat.1, the industry’s attention to NB-IoT has not been as high, but the number of NB-IoT connections continues to grow. Compared to other LPWAN connections, NB-IoT connections hold an absolute advantage. IoT Analytics tracking data shows that by the end of 2023, the proportion of NB-IoT connections in all LPWAN connections in China reached 81%; at the same time, China’s NB-IoT connections accounted for an astonishing 84% of the global total.
It is precisely due to the contribution of China’s NB-IoT connections that NB-IoT can continue to grow in the global LPWAN market, occupying more than half of the market.
2. Excluding the Chinese market, LoRa still leads in LPWAN connections
China has the largest IoT market in the world, far exceeding other countries. To reflect the market situation in other global regions, market research institutions generally exclude the influence of China and examine the market conditions outside of China. If we do not consider the Chinese market, the LPWAN market structure in other countries and regions presents a different picture, with LoRa’s connection numbers leading the global market.
IoT Analytics tracking data shows that in the global market excluding China, in 2023, LoRa’s connection numbers accounted for 41% of the total LPWAN connections, LTE-M accounted for 31%, while NB-IoT only accounted for 20%.
In 2016, LoRa’s connection numbers reached their peak, exceeding 70%, but since then, LoRa’s connection numbers have continued to decline. This is mainly because before 2016, the cellular technology standards for NB-IoT and LTE-M had not yet been finalized, and there was no substantial commercialization. Additionally, after the establishment of the LoRa Alliance, the technology was vigorously promoted for global penetration, effectively educating the market before the commercialization of cellular IoT technologies, gaining global market recognition and promoting a niche technology to a de facto global standard. In contrast, Sigfox, during the same period, did not seize this window of opportunity due to its relatively conservative business model. After the standards for NB-IoT and LTE-M were finalized, the influence of the cellular network ecosystem globally allowed these technologies to rapidly take off, becoming strong competitors to LoRa.
However, leveraging the foundation laid in recent years, along with the very flexible business and commercial cooperation models of the LoRa ecosystem, LoRa is expected to maintain a stable market share and influence in the IoT market in the coming years. Various vertical industry enterprises, internet companies, and OEM manufacturers are increasing their applications of LoRa. For example, Amazon AWS has released multiple products based on LoRaWAN, and its self-developed communication technology Sidewalk also incorporates LoRa modulation technology, becoming an important player in the LoRa ecosystem; similarly, the world’s largest module manufacturer, Quectel, has recently released LoRa module products.
IoT Analytics predicts that by 2027, excluding the Chinese market, LoRa will still hold a 36% share of the global LPWAN market, remaining the leader in LPWAN technologies.
3. The influence of overseas licensed spectrum LPWAN technologies will further increase
IoT Analytics predicts that by 2027, excluding the Chinese market, the share of LTE-M connections in LPWAN will reach 35%, while the share of NB-IoT connections will be 23%, both higher than the shares in 2023.
Unlike the Chinese market, many mainstream telecom operators overseas prefer to deploy LTE-M for LPWAN technologies. Although operators like Vodafone and Deutsche Telekom in Europe were the first to build NB-IoT networks, American operators have prioritized LTE-M as their mainstream LPWAN technology. This difference in network construction strategies has led to a higher share of LTE-M in the overseas market for licensed spectrum LPWAN technologies.
Overseas, the development of NB-IoT has been slower compared to the Chinese market, but in recent years, it has shown signs of acceleration and has begun to adopt various innovative practices and new use cases. For example, based on the IoT-NTN in the 3GPP R17 standard series, overseas institutions are promoting the development of NB-IoT satellite communications. In July 2023, the low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite operator Sateliot, based in Spain, successfully tested end-to-end roaming 5G cellular networks in space using NB-IoT in collaboration with Telefónica. Such applications are continuously emerging overseas.
New Trends in LPWAN
According to IoT Analytics analysts, future LPWAN technologies and markets will form some new trends, including
1. Integration and Collaboration
Over the past decade, LPWAN technologies have become more popular. As the market matures and establishes a foothold in IoT connections, various LPWAN technologies seem to be shifting from early intense competition to a greater focus on integration and collaboration.
In July 2023, American company Semtech announced a partnership with UnaBiz. These two companies are the owners of LoRa and Sigfox technologies, respectively, and they focus on LPWAN connections, integrating UnaBiz’s Sigfox 0G technology into Semtech’s LoRa Edge and LoRa Connect platforms.
Additionally, Semtech’s acquisition of Sierra Wireless aims to promote a combination of unlicensed and licensed spectrum IoT product offerings.
2. Addressing Some Limitations of LPWAN
LPWAN has some limitations that still need to be addressed. According to IoT Analytics, some LPWAN technologies are designed around point-to-point connections and cannot support large-scale data loads, while some scenarios require large data transmissions. To address this issue, improvements to transmission protocols are needed to ensure complete data packet delivery. In this context, the Mioty Alliance has emerged, introducing a method called TSMA based on the European Telecommunications Standards Institute standard ETSI TS 103 357, which can split sensor data packets into smaller sub-packets and transmit them at different frequencies and time stamps. The receiving end’s algorithm will monitor a large number of sub-packets and reassemble them into complete messages, ensuring that even if one or several frequencies are interfered with, the complete message can still be received.
Of course, in the Chinese market, LPWAN is not limited to NB-IoT and LoRa; there are multiple technology camps that improve upon the shortcomings of NB-IoT and LoRa, effectively meeting the diverse demands of various vertical sectors. Although their scale is not as large as that of NB-IoT and LoRa, they have also formed mature solutions and achieved a certain level of deployment. Thanks to China’s vast market and the diversity of digital transformation needs across industries, various IoT technologies can find their positioning and establish their own paths to survival.