Source: ICT New Horizons – Smart City Special Edition, original title: “Shenzhou Agriculture: How NB-IoT Applications Empower Agricultural Digitalization,” by Zhang Dandan, President of Shenzhou Agriculture DC Agriculture.
Trends and Potential of Agricultural Digitalization
Compared to other industries, the current agricultural sector in China remains quite traditional, with relatively backward application of information technology. As the older generation gradually retires, the labor force engaged in agriculture is continuously decreasing, and the demographic dividend is gradually fading; at the same time, the completion of land rights confirmation and land circulation is leading agricultural production towards centralization, moderate scale, and industrialization. This industrialization requires a shift from extensive, experience-based production methods to digital and scientific approaches.
Agricultural production is highly dependent on climate, weather, and other natural environments. Ancient people invented the 24 solar terms based on their perception of climate and experience. In today’s highly developed information technology era, it is evidently necessary to utilize collected data and scientific analysis to guide agricultural production, transforming from “relying on the heavens” to “knowing the heavens”.

There is a vast amount of data closely related to agricultural production, such as meteorological data, environmental data, soil moisture and fertility data, water quality data, plant and animal data, plot data, circulation data, and price data. The collection and analysis of these data will significantly improve the quality of agricultural products, reduce production costs, minimize agricultural pollution, and enhance agricultural efficiency. Therefore, the digitalization of agriculture has immense potential and application space.
How NB-IoT Empowers Agricultural Digitalization
Agricultural data collection has some characteristics:
-
First, it is relatively dispersed. For a single farm, there are many types of data to collect, but the collection points for the same type of data may not be numerous, and farms are often scattered in suburban or remote areas;
-
Second, the cost requirements for data collection are relatively high. Given the low agricultural output value, the construction and subsequent operation/maintenance costs of collection points must be kept low for widespread promotion;
-
Additionally, wiring and power supply in outdoor areas are inconvenient, so data collection should ideally be transmitted wirelessly and powered by solar energy or batteries.

Using NB-IoT technology for transmission offers: low power consumption, with normal operating power consumption less than 20mA, allowing a single battery to last for several years; low cost, with both module and operational costs significantly lower than cellular networks, while battery power also greatly reduces deployment and hardware costs on farms; compared to small wireless transmission, there is no need to deploy gateways, making installation simple; wide coverage and a high number of connections effectively address the issue of dispersed agricultural data collection points. NB-IoT technology makes the collection of agricultural production and circulation data a convenient task, providing a solid foundation for the digital development of agriculture through comprehensive and extensive data collection.
Application Scenarios of NB-IoT in Agricultural Digitalization
For crops growing in soil, if the soil temperature, moisture, EC value, and pH value do not meet the crop’s requirements and are not within the appropriate range, it will affect the absorption of nutrients, crop growth, and photosynthesis. By dynamically and real-time sensing these data at low cost and making timely adjustments, crops can have suitable growing conditions, ensuring yield and quality.
If the temperature and humidity for the growth of plants and animals are not suitable, it will lead to frequent occurrences of pests and diseases; the occurrence of pests and diseases will result in excessive use of pesticides and antibiotics, thus affecting the quality and safety of agricultural products. If real-time and accurate collection of temperature and humidity can predict pest and disease occurrences in advance, environmental control can reduce or avoid such occurrences.
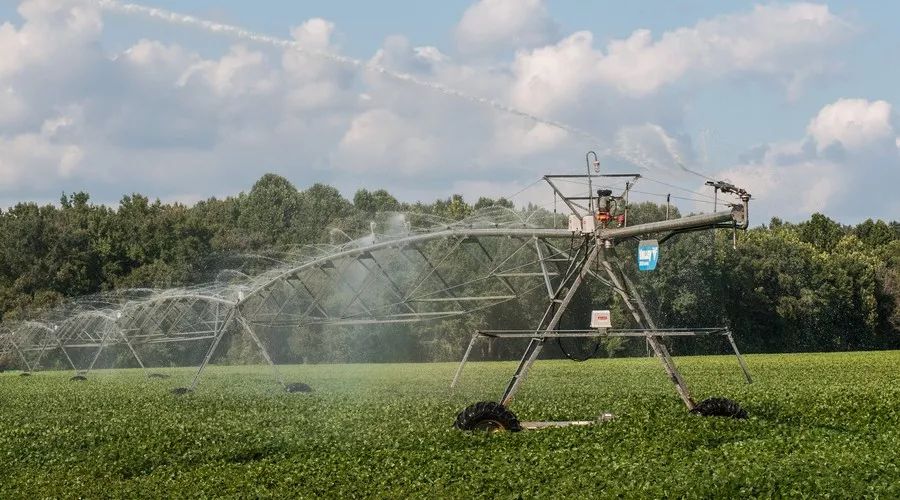

North China is very water-scarce, and agricultural irrigation accounts for over 65% of total water usage, making it the largest water consumer. To promote scientific water use in agricultural irrigation and conserve water, China is currently implementing comprehensive agricultural water pricing reforms, with accurate water measurement as the foundation. Water meters and sensors for measuring water need to be installed in outdoor ditches and wells, which brings challenges in power supply and signal transmission, requiring significant manpower for on-site manual readings, leading to untimely data acquisition and an inability to provide scientific guidance for irrigation water use.
With the application of NB-IoT, the acquisition of agricultural water data becomes more timely, comprehensive, and convenient, helping the entire irrigation area achieve precise water scheduling while also guiding scientific water use on farms. The digitalization and scientific management of water use improve the efficiency of agricultural irrigation, achieving water-saving agriculture.
In the livestock industry, it is challenging to monitor the health status of grazing cattle and sheep in a timely manner. If measures are not taken promptly when they fall ill, not only is treatment difficult, but it may also spread to other livestock, causing significant losses. By developing smart collars based on NB-IoT, real-time collection of location information, behavior data, and vital signs of cattle and sheep can be achieved. Through the collection and application of this data, monitoring of livestock can be implemented to prevent loss, provide early warnings for diseases, and enable timely treatment, as well as monitor the estrus of dairy cows to increase milk production, thus promoting refined management of livestock and reducing farming risks.
The data collected by smart collars can also be provided to insurance companies and banks, promoting the development of agricultural insurance and rural loans; at the same time, this data can be shared on e-commerce platforms, enabling pre-ordering and pre-selling of livestock, thereby increasing the added value of livestock products.
In modern agricultural industries, there is a vast amount of data to be collected and transmitted, and NB-IoT is just one method of data transmission, which may not be suitable for all scenarios. Data collection should be application-oriented, selecting different data collection and transmission methods based on different site conditions. The core value of NB-IoT is to make the construction of the Internet of Things more convenient and the acquisition of data more efficient.
Some Application Practices by Shenzhou Agriculture
The R&D team of Shenzhou Agriculture has upgraded soil information collection instruments and environmental information collection instruments based on Huawei’s NB-IoT modules and has achieved data collection and transmission in the agricultural park in Weifang, Shandong, while also building an agricultural cloud service platform on Huawei Cloud, using data analysis to guide irrigation and fertilization, as well as to provide warnings and analyze pests and diseases, all achieving good results.
In addition, the R&D team of Shenzhou Agriculture has upgraded irrigation water meters to NB-IoT transmission technology and has developed smart collars for animals based on NB-IoT, which are currently undergoing testing. With the large-scale deployment of NB-IoT base stations and comprehensive network coverage, these smart devices will have broad application prospects in the future.
The application of NB-IoT will continuously promote the Internet of Everything in agriculture and rural areas, and the vast amount of data generated by the Internet of Everything will continuously drive the digital development of agriculture, ultimately achieving agricultural intelligence with the advancement of algorithms and computing power. Shenzhou Agriculture, leveraging years of experience and accumulation in the agricultural field, is continuously exploring and developing IoT products and cloud service applications for modern agriculture, empowering agricultural digitalization with the support of Huawei’s Internet of Everything and cloud ecosystem.