 Click the blue text to follow immediately
Click the blue text to follow immediately
Introduction
MiniTest is a lightweight C++ unit testing framework that provides assertion testing, parameterized testing, grouped testing, performance testing, and Mock (mock objects), suitable for the unit testing needs of small projects.
Features of this framework:

-
Lightweight: No third-party dependencies, suitable for embedded systems, CLI tools, etc.
-
Easy to extend: Modular design, supports custom tests.
-
Supports parameterized testing: Use TEST_P to run multiple sets of input tests.
-
Supports performance testing:
Benchmarking with BENCHMARK_FUNC to measure function execution time.
-
Supports Mock: Easily mock dependencies with Mock::SetReturn.
Project Structure
MiniTest/│── include/ # Header files directory│ ├── TestAssert.hpp # Assertion macros│ ├── TestFramework.hpp # Basic testing framework│ ├── TestParams.hpp # Parameterized testing│ ├── TestSuite.hpp # Grouped testing│ ├── TestBenchmark.hpp # Performance testing│ ├── TestMock.hpp # Mock objects│── tests/ # Test cases│── CMakeLists.txt # CMake build script│── main.cpp # Main test entry│── README.md # Project documentationEnvironment Configuration
This project uses C++20 and is built with CMake.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.30)project(MiniTest)set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 20)include_directories(include)add_executable(MiniTest main.cpp)target_compile_options(MiniTest PRIVATE -finput-charset=UTF-8 -fexec-charset=UTF-8)Compile and Run
mkdir buildcd buildcmake ..make01
Assertion Testing
Example Code
TEST(TestBoolean) { ASSERT_TRUE(true);}TEST(TestFailure) { ASSERT_TRUE(false); // This test will fail}TEST(TestException) { ASSERT_THROW(throw std::runtime_error("error"), std::runtime_error);}TEST(TestSubtraction) { ASSERT_EQ(5 - 3, 2);}Complete Code
/*** ================================================== * @file TestAssert.hpp * @brief Assertion macro definitions, providing basic unit testing assertion functionality * @author mrDarker * @date 2025/03/18 * @version 1.0 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2025 mrDarker. All Rights Reserved. * ================================================== */#ifndef TEST_ASSERT_HPP#define TEST_ASSERT_HPP#include <iostream>#include <stdexcept>// Log when assertion fails#define ASSERT_FAIL(message) \\do { \\ /**std::ostringstream oss; \\ oss << "Assertion failed: " << message << " at " << __FILE__ << ":" << __LINE__; \\ std::cerr << "[ASSERT FAIL] " << oss.str() << std::endl; \\ TestLogger logger("AssertFailures"); \\ logger.LogMessage(oss.str()); \\ std::cout.flush(); \\ std::cerr.flush(); \\ throw std::runtime_error(oss.str()); \\ **/ \\} while (0)// Assertion: Check if true#define ASSERT_TRUE(condition) \\do { \\ if (!(condition)) { \\ ASSERT_FAIL(#condition " is false"); \\ } \\} while (0)// Assertion: Check if false#define ASSERT_FALSE(condition) \\do { \\ if ((condition)) { \\ ASSERT_FAIL(#condition " is true"); \\ } \\} while (0)// Assertion: Check if two values are equal#define ASSERT_EQ(expected, actual) \\do { \\ if ((expected) != (actual)) { \\ std::ostringstream oss; \\ oss << #expected " != " #actual " (" << expected << " != " << actual << ")"; \\ ASSERT_FAIL(oss.str()); \\ } \\} while (0)// Assertion: Check if two values are not equal#define ASSERT_NE(expected, actual) \\do { \\ if ((expected) == (actual)) { \\ std::ostringstream oss; \\ oss << #expected " == " #actual " (" << expected << " == " << actual << ")"; \\ ASSERT_FAIL(oss.str()); \\ } \\} while (0)// Assertion: Check if a statement throws a specified exception#define ASSERT_THROW(statement, exception_type) \\do { \\ bool caught = false; \\ try { \\ statement; \\ } catch (const exception_type&) { \\ caught = true; \\ } catch (...) { \\ ASSERT_FAIL("Unexpected exception type thrown"); \\ } \\ if (!caught) { \\ ASSERT_FAIL("Expected exception of type " #exception_type " not thrown"); \\ } \\} while (0)#endif // TEST_ASSERT_HPPSupported Assertion Macros
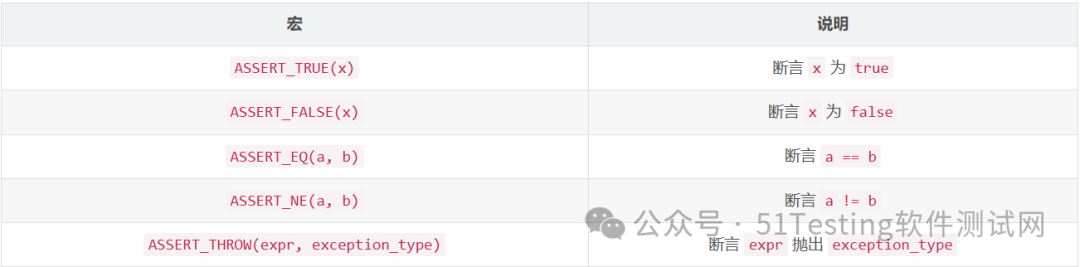
How It Works
1. ASSERT_* macros check the result of the expression.
2. If the assertion fails, it throws a std::runtime_error, causing the test to fail.
3. TestFramework::RunAllTests() is responsible for running all registered tests.
02
Parameterized Testing
Example Code
std::vector<std::tuple<int, int, int>> additionParams = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 9}, {3, 7, 10}, {6, -2, 4}, {8, 3, 12}};TEST_P(TestParamsAddition, additionParams, int a, int b, int expected) { ASSERT_EQ(a + b, expected);}Complete Code
/** * ================================================== * @file TestParams.hpp * @brief Parameterized testing framework, supports data-driven testing * @author mrDarker * @date 2025/03/18 * @version 1.1 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2025 mrDarker. All Rights Reserved. * ================================================== */#ifndef TEST_PARAMS_HPP#define TEST_PARAMS_HPP#include <vector>#include <string>#include <functional>#include <iostream>#include <sstream>#include <tuple>#include "TestLogger.hpp"// Storage structure for parameterized testsclass TestParams {public: // Register parameterized test template <typename Func, typename... Args> static void RegisterParamTest(const std::string& name, Func func, const std::vector<std::tuple<Args...>>& params) { for (const auto& paramSet : params) { std::ostringstream oss; oss << name << FormatParams(paramSet); GetParamTests().push_back({oss.str(), [func, paramSet]() { std::apply(func, paramSet); }}); } } // Run all parameterized tests static void RunAllParamTests() { TestLogger logger("ParamTests"); int passed = 0, failed = 0; for (const auto&[name, func] : GetParamTests()) { std::cout.flush(); std::cerr.flush(); std::cout << "[RUNNING] " << name << std::endl; try { func(); // No-parameter call std::cout << "[PASS] " << name << std::endl; logger.LogTestResult(name, true); ++passed; } catch (const std::exception& ex) { std::cerr << "[FAIL] " << name << " - " << ex.what() << std::endl; logger.LogTestResult(name, false); ++failed; } } // Print test statistics std::cout << "===========================================" << std::endl; std::cout << "Total: " << (passed + failed) << ", Passed: " << passed << ", Failed: " << failed << std::endl; std::cout << "===========================================" << std::endl; std::cout.flush(); std::cerr.flush(); }private: struct ParamTestCase { std::string name; std::function<void()> func; }; static std::vector<ParamTestCase>& GetParamTests() { static std::vector<ParamTestCase> paramTests; return paramTests; } // Format parameter list template <typename Tuple, size_t... Index> static std::string FormatTupleImpl(const Tuple& tuple, std::index_sequence<Index...>) { std::ostringstream oss; ((oss << (Index == 0 ? "" : ", ") << std::get<Index>(tuple)), ...); return "(" + oss.str() + ")"; } template <typename... Args> static std::string FormatParams(const std::tuple<Args...>& params) { return FormatTupleImpl(params, std::index_sequence_for<Args...>{}); }}; // Parameterized test macro#define TEST_P(test_name, param_data, ...) \\void test_name(__VA_ARGS__); \\namespace { \\ struct Register_##test_name { \\ Register_##test_name() { \\ static const auto _param_data = param_data; \\ TestParams::RegisterParamTest(#test_name, test_name, _param_data); \\ } \\ }; \\ static Register_##test_name g_register_##test_name; \\} \\void test_name(__VA_ARGS__)#endif // TEST_PARAMS_HPPHow It Works
1. TEST_P macro automatically generates test functions and registers them with TestParams::RegisterParamTest.
2. std::tuple<> stores different test data.
3. TestParams::RunAllParamTests() sequentially calls test cases and executes them with different parameters.
03
Grouped Testing
Example Code
TEST_SUITE(MathTests, TestSuiteAddition) { ASSERT_EQ(2 + 3, 5);}TEST_SUITE_F(MySuiteTestFixture, MathTests, TestAddition) { ASSERT_EQ(1 + 1, 2);}Complete Code
/** * ================================================== * @file TestSuite.hpp * @brief Test suite management, supports running specified test suites * @author mrDarker * @date 2025/03/18 * @version 1.1 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2025 mrDarker. All Rights Reserved. * ================================================== */#ifndef TEST_SUITE_HPP#define TEST_SUITE_HPP#include <vector>#include <functional>#include <unordered_map>#include <iostream>#include <ranges>#include <thread>#include "TestLogger.hpp"class TestSuite {public: // Structure: Test case struct TestCase { std::string name; // Test name std::function<void()> func; // Test execution function }; /** * @brief Register test to specified Suite * @param suite Test suite name * @param test Test name * @param func Test function */ static void RegisterTest(const std::string& suite, const std::string& test, const std::function<void()> &func) { GetSuites()[suite].push_back({test, func}); } /** * @brief Print all registered test suites */ static void ListSuites() { std::cout << "[AVAILABLE TEST SUITES]" << std::endl; for (const auto &suite: GetSuites() | std::views::keys) { std::cout << "- " << suite << std::endl; } } /** * @brief Execute Setup for specified test suite */ static void SetupSuite(const std::string& suite) { if (auto& setupFuncs = GetSetupFuncs(); setupFuncs.contains(suite)) setupFuncs[suite](); } /** * @brief Execute Teardown for specified test suite */ static void TeardownSuite(const std::string& suite) { if (auto& teardownFuncs = GetTeardownFuncs(); teardownFuncs.contains(suite)) teardownFuncs[suite](); } /** * @brief Get all test suite's Setup function mapping * @return std::unordered_map<std::string, std::function<void()>>& */ static std::unordered_map<std::string, std::function<void()>>& GetSetupFuncs() { static std::unordered_map<std::string, std::function<void()>> setupFuncs; return setupFuncs; } /** * @brief Get all test suite's Teardown function mapping * @return std::unordered_map<std::string, std::function<void()>>& */ static std::unordered_map<std::string, std::function<void()>>& GetTeardownFuncs() { static std::unordered_map<std::string, std::function<void()>> teardownFuncs; return teardownFuncs; } /** * @brief Run specified test suite, optional filter for single test * @param suite Test suite name * @param testFilter Specific test to execute (default is empty, execute entire suite) */ static void RunSuite(const std::string& suite, const std::string& testFilter = "") { auto& suites = GetSuites(); if (!suites.contains(suite)) { std::cerr << "[ERROR] Test suite '" << suite << "' not found.\n"; return; } auto& tests = suites[suite]; // If testFilter is empty, execute entire Suite if (testFilter.empty()) { std::cout << "[RUNNING SUITE] " << suite << std::endl; RunTests(tests, suite); return; } // Check if the Test exists auto it = std::ranges::find_if(tests, [&](const TestCase& test) { return test.name == testFilter; }); // If it exists, execute that Test if (it != tests.end()) { std::cout << "[RUNNING SINGLE TEST] " << suite << "::" << testFilter << std::endl; RunTests({*it}, suite); } else { std::cerr << "[ERROR] Test '" << testFilter << "' not found in suite '" << suite << "'.\n"; } } /** * @brief Run list of tests * @param tests List of tests to execute * @param suite Name of the test suite */ static void RunTests(const std::vector<TestCase>& tests, const std::string& suite) { TestLogger logger(suite); int passed = 0, failed = 0; // Execute Setup SetupSuite(suite); for (const auto& [name, func] : tests) { std::cout << "[RUNNING] " << name << std::endl; try { func(); std::cout << "[PASS] " << name << std::endl; logger.LogTestResult(name, true); ++passed; } catch (const std::exception& ex) { std::cerr << "[FAIL] " << name << " - " << ex.what() << std::endl; logger.LogTestResult(name, false); ++failed; } } // Execute Teardown TeardownSuite(suite); std::cout << "[SUITE] " << suite << " - Passed: " << passed << ", Failed: " << failed << std::endl; } /** * @brief Run all test suites */ static void RunAllSuites() { std::vector<std::thread> threads; for (const auto &key: GetSuites() | std::views::keys) { threads.emplace_back([key]() { RunSuite(key); }); } for (auto& t : threads) { if (t.joinable()) t.join(); } }private: /** * @brief Get all registered test suites */ static std::unordered_map<std::string, std::vector<TestCase>>& GetSuites() { static std::unordered_map<std::string, std::vector<TestCase>> suites; return suites; }}; // **Register Setup**#define TEST_SUITE_SETUP(suite_name, func) \\namespace { struct RegisterSetup_##suite_name { \\ RegisterSetup_##suite_name() { TestSuite::GetSetupFuncs()[#suite_name] = func; } \\}; static RegisterSetup_##suite_name g_registerSetup_##suite_name; } // **Register Teardown**#define TEST_SUITE_TEARDOWN(suite_name, func) \\namespace { struct RegisterTeardown_##suite_name { \\ RegisterTeardown_##suite_name() { TestSuite::GetTeardownFuncs()[#suite_name] = func; } \\}; static RegisterTeardown_##suite_name g_registerTeardown_##suite_name; } // **Register Normal Test**#define TEST_SUITE(suite_name, test_name) \\void test_name(); \\namespace { \\ struct Register_##test_name { \\ Register_##test_name() { TestSuite::RegisterTest(#suite_name, #test_name, test_name); } \\ }; \\ static Register_##test_name g_register_##test_name; } \\void test_name() // **Register Test with Fixture**#define TEST_SUITE_F(fixture_name, suite_name, test_name) \\class test_name : public fixture_name { \\public: \\ void Run(); \\}; \\namespace { \\ struct Register_##test_name { \\ Register_##test_name() { \\ TestSuite::RegisterTest(#suite_name, test_name, []() { \\ test_name instance; \\ instance.Run(); \\ }); \\ } \\ }; \\ static Register_##test_name g_register_##test_name; } \\void test_name::Run()#endif // TEST_SUITE_HPPHow It Works
1. TEST_SUITE(suite, test) registers tests with TestSuite::RegisterTest.
2. TEST_SUITE_F(fixture, suite, test) supports using SetUp() and TearDown().
3. TestSuite::RunSuite(“MathTests”) runs the entire test suite.
04
Performance Testing
Example Code
BENCHMARK_FUNC(MyTestFunction, 5);void MyTestFunction() { std::vector<int> data(100000); std::ranges::generate(data.begin(), data.end(), rand); std::ranges::sort(data.begin(), data.end());}Complete Code
/** * ================================================== * @file TestBenchmark.hpp * @brief Benchmark testing framework, supports multiple runs, average time statistics, and parameterized benchmarks * @author mrDarker * @date 2025/03/18 * @version 1.2 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2025 mrDarker. All Rights Reserved. * ================================================== */#ifndef TEST_BENCHMARK_HPP#define TEST_BENCHMARK_HPP#include <chrono>#include <functional>#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <unordered_map>#include "TestLogger.hpp"class TestBenchmark {public: // Normal benchmark test (no parameters) static void RegisterBenchmark(const std::string& name, const std::function<void()>& func, const int iterations) { GetBenchmarks()[name] = {func, iterations}; } // Parameterized benchmark test (with parameters) template <typename Func, typename... Args> static void RegisterBenchmark(const std::string& name, Func func, int iterations, Args... args) { auto wrapper = [func, args...]() { func(args...); }; GetBenchmarks()[name] = {wrapper, iterations}; } // Run all benchmark tests static void RunAllBenchmarks() { RunFilteredBenchmarks([](const std::string&) { return true; }, "AllBenchmarks"); } // Run specified benchmark test static void RunBenchmark(const std::string& name) { RunFilteredBenchmarks([name](const std::string& testName) { return testName == name; }, "Benchmark_" + name); } // Test the average execution time of a specific function template <typename ReturnType, typename... Args> static void BenchmarkFunction(const std::string& name, ReturnType (*func)(Args...), const int iterations, Args... args) { std::cout << "[BENCHMARK] Running " << name << " for " << iterations << " iterations..." << std::endl; std::vector<double> times; for (int i = 0; i < iterations; ++i) { std::cout.flush(); std::cerr.flush(); auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); if constexpr (sizeof...(Args) > 0) { func(args...); // Call function with parameters if there are any } else { func(); // Call function without parameters if there are none } auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli> duration = end - start; times.push_back(duration.count()); } double totalTime = 0; for (const double t : times) totalTime += t; const double avgTime = totalTime / iterations; std::cout << "[BENCHMARK] " << name << " Avg Time: " << avgTime << " ms" << std::endl; }private: struct BenchmarkCase { std::function<void()> func; int iterations{}; }; static std::unordered_map<std::string, BenchmarkCase>& GetBenchmarks() { static std::unordered_map<std::string, BenchmarkCase> benchmarks; return benchmarks; } // General performance test execution static void RunFilteredBenchmarks(const std::function<bool(const std::string&)>& filter, const std::string& logCategory) { TestLogger logger(logCategory); for (const auto& [fst, snd] : GetBenchmarks()) { if (!filter(fst)) continue; const auto& [func, iterations] = snd; std::cout << "[BENCHMARK] Running " << fst << " for " << iterations << " iterations..." << std::endl; std::vector<double> times; for (int i = 0; i < iterations; ++i) { std::cout.flush(); std::cerr.flush(); auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); func(); auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli> duration = end - start; times.push_back(duration.count()); } double totalTime = 0; for (const double t : times) totalTime += t; const double avgTime = totalTime / iterations; std::cout << "[BENCHMARK] " << fst << " Avg Time: " << avgTime << " ms" << std::endl; logger.LogMessage("[BENCHMARK] " + fst + " Avg Time: " + std::to_string(avgTime) + " ms"); } }}; // Normal benchmark test (no parameters)#define BENCHMARK(test_name, iterations) \\void test_name(); \\namespace { \\ struct Register_##test_name { \\ Register_##test_name() { \\ TestBenchmark::RegisterBenchmark(#test_name, test_name, iterations); \\ } \\ }; \\ static Register_##test_name g_register_##test_name; } \\void test_name() // Specify function benchmark test#define BENCHMARK_FUNC(func, iterations, ...) \\namespace { \\ struct Register_##func { \\ Register_##func() { \\ TestBenchmark::BenchmarkFunction(#func, func, iterations, ##__VA_ARGS__); \\ } \\ }; \\ static Register_##func g_register_##func; }#endif // TEST_BENCHMARK_HPPHow It Works
1. BENCHMARK_FUNC registers MyTestFunction and runs it 5 times.
2. TestBenchmark::BenchmarkFunction() calculates the average execution time.
05
Mock Objects
Example Code
MOCK_METHOD(int, GetRandomNumber, ());TEST(TestMockExample) { Mock::SetReturn(GetRandomNumber, 42); ASSERT_EQ(GetRandomNumber(), 42);}Complete Code
/** * ================================================== * @file TestMock.hpp * @brief Mock object framework, supports Mock method and return value setting * @author mrDarker * @date 2025/03/18 * @version 1.0 * @copyright Copyright (c) 2025 mrDarker. All Rights Reserved. * ================================================== */#ifndef TEST_MOCK_HPP#define TEST_MOCK_HPP#include <unordered_map>#include <functional>#include <typeindex>#include <map>class Mock {public: // Set return value for Mock method template <typename ReturnType> static void SetReturn(ReturnType (*func)(), ReturnType returnValue) { auto wrapper = [returnValue]() -> ReturnType { return returnValue; }; GetMockFunctions<ReturnType>()[reinterpret_cast<void*>(func)] = wrapper; } // Call Mock method template <typename ReturnType> static ReturnType Invoke(ReturnType (*func)()) { auto& mockMap = GetMockFunctions<ReturnType>(); auto it = mockMap.find(reinterpret_cast<void*>(func)); if (it != mockMap.end()) { return it->second(); } // std::cerr << "[MOCK ERROR] Function '" << typeid(func).name() << "' not mocked!\n"; return ReturnType(); // Default return 0 / empty value } // Clear Mock template <typename ReturnType> static void Reset() { GetMockFunctions<ReturnType>().clear(); } // Clear all Mock methods static void ResetAll() { mockStorage().clear(); }private: // Store different types of Mock methods template <typename ReturnType> static std::unordered_map<void*, std::function<ReturnType()>>& GetMockFunctions() { static std::unordered_map<void*, std::function<ReturnType()>> mockFunctions; return mockFunctions; } static std::map<std::type_index, void*>& mockStorage() { static std::map<std::type_index, void*> storage; return storage; }}; // MOCK_METHOD macro#define MOCK_METHOD(returnType, functionName, params) \\ returnType functionName params; \\ namespace { \\ struct RegisterMock_##functionName { \\ RegisterMock_##functionName() { \\ Mock::SetReturn(functionName, returnType()); \\ } \\ }; \\ static RegisterMock_##functionName g_register_mock_##functionName; \\ } \\ returnType functionName params { return Mock::Invoke(functionName); }#endif // TEST_MOCK_HPPHow It Works
1. MOCK_METHOD defines a Mock method.
2. Mock::SetReturn(func, value) sets the return value.
3. Mock::Reset() clears the Mock method.
06
Run Tests
int main() { TestFramework::RunAllTests(); TestParams::RunAllParamTests(); TestBenchmark::RunAllBenchmarks(); TestSuite::RunAllSuites(); return 0;}Conclusion
MiniTest provides assertions, parameterized, grouped, performance testing, and Mock, suitable for unit testing in small C++ projects.
✅ Lightweight, no third-party dependencies✅ Supports parameterized testing✅ Supports performance testing✅ Supports Mock✅ Easy to extend
END

Link:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_58648890/article/details/146364148
This article is reprinted with permission from 51Testing. The text contained in the reprinted article comes from the author. If there are any issues regarding content or copyright, please contact 51Testing for deletion.
 Like and Share
Like and Share Share
Share View
View